Calculation of pipe parameters
Any highways as components of the system are laid according to strictly defined rules, technical requirements and standards. Sewage system pipelines are no exception. The main conditions for long-term and trouble-free operation of the wastewater disposal system are the correct calculation of parameters and compliance with tightness. And one of the main parameters is the slope depending on the diameter of its section.
Rules for laying sewer pipes
Cast iron pipes are gradually becoming a thing of the past. Their use has decreased so much that even buying such a pipe has become a problem. Therefore, we will consider only non-metallic pipes for drains. Basically, these are PVC products.
To ensure normal operation of the sewer system, when installing mains, it is necessary to follow some mandatory rules:
- In any dynamic system, turns, braking, and unevenness lead to malfunctions. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid turns and bends in sewer pipes whenever possible, and also to reduce the number of joints. The ideal sewer system is a straight and smooth inclined pipe. Any bend or joint increases resistance to flow, which can lead to leakage or clogging.
- The ratio of the height of the lower end of a 1 meter long pipe to the upper end is designated as “i” and is measured in centimeters. For example, for a pipe from a washbasin i = 0.03. This means that when installing a pipe, its edge closest to the source of waste should be 3 cm higher than the farthest one relative to the horizontal surface.
- The slope angle of horizontal sections cannot be made unlimitedly large. Significantly exceeding certain values leads to undesirable consequences in the form of clogging of channel branches. The pipe should be 1/3 full when draining. Therefore, it is not recommended to make a slope more than 0.15
- All pipe connections must be made with a socket facing the flow of wastewater. This significantly reduces the likelihood of leaks during operation
- Various cuttings and shortening of factory products are undesirable. If necessary, only straight sections of plastic pipes of small diameter can be cut and then checked for leaks. It is strictly forbidden to use products with chips, cracks, or without O-rings and gaskets.
- Displacement of pipes from the calculated position is unacceptable. They are fastened on straight sections with open laying every 50 cm. Curvilinear sections are fixed before and after bending, and in the presence of branches, each direction is fixed individually.
- When marking, the angle of inclination sewer pipe measured from the instrument horizon and not from the construction plane of the floor, walls or ceiling. The horizon can be determined using a water level or a laser level.
Selection of pipes and other elements of the sewerage system
When installing sewerage systems in a private house, pipes with a diameter of 50 mm, 110 mm, 160 mm, and less often - 200 mm are used.
Small diameter pipes - 50 and 110 mm - are used in drainage lines from sources: 50 mm - from sinks, showers, household appliances, 110 mm - from toilets.
Pipes of large diameters are used as risers and external sewer lines.
The minimum slopes for all of them are as follows:
- 50 mm - 0.03
- 110 mm - 0.02
- 110 mm - 0.02
- 160 mm - 0.008
- 160 mm - 0.008
- 200 mm - 0.007

Plastic pipes for internal and external communications
Plastic pipes for internal and external communications differ from each other in the composition of the material and some properties. They have and different colour: red or orange - pipes for external use, dark gray - for internal use. External pipes can be installed indoors. But internal ones are not allowed to be used for external communication.
The selection of sewerage elements such as corners, crosses, tees and elbows is carried out according to the project or diagram. The goal of all changes in flow direction is to make the turns smooth. This will eliminate possible deposits of sediment and clogging, and will also ensure silent passage of water through the mains.
To prevent the formation of air cavities in wastewater channels and unpleasant odors, a fan ventilation line must be provided in the system. It is usually performed by extending the risers above the upper level of water supply, that is, to the roof surface. The slope of the pipe for such ventilation is not provided, so it is installed vertically. The end of such a pipe is a separator designed to quickly mix the exhaust gases with atmospheric air.
Installation of sewer lines

Installation of sewer networks
Channels for draining water from sources are marked based on their location points and the placement of sewer risers. The slope is calculated from the drain point to the channel entry point into the riser. The slope of the sewer pipe must be no less than 0.02 - 0.03 and no more than 0.15.
The risers are located vertically and serve to collect sewage from all levels. They have a diameter of 100 or 160 mm, and the water drainage channels are connected to them using crosses or tees. Somewhat above the water inlet from the level, it is necessary to place an inspection - a technological opening for maintenance.
External lines are made with large diameter pipes for outdoor use. They receive all the wastewater from the risers and move it to treatment devices or storage tanks.
It is not allowed to transition from a vertical riser to a horizontal external main at one right angle. It is necessary to use 2 turns of 45 degrees or 3 of 30.
Along the length of external highways, revisions are arranged at a rate of 1 per 25 meters of channel length.
When laying external channels, the load on the soil above the sewerage channels from roads, temporary buildings, and others should be taken into account. When laying pipes, the bottom of the trench must be thoroughly compacted. This is done in order to avoid soil subsidence and the formation of stagnant areas with zero or negative slopes.
Checking the functionality of the highway
Mechanical main sewer valve DN160
After completing the laying of all highways and before finishing finishing work in the premises or before digging trenches on the street, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive check of the system.
The following are subject to mandatory inspection:
- Horizontal drain channels.
- Risers.
- Ventilation channels and fan line.
- External highways.
The purpose of the inspection is to control the tightness of joints, connections, adapters and revisions. It is carried out visually as water passes through all channels. In this case, water flow along the entire length of the pipelines is not allowed.
After checking, particularly important and subsequently inaccessible connections can be wrapped with sealing tape, and also treated with a special compound or paint.

The pipe connection may become a leak point during operation.
When servicing systems that include plastic pipes, it is necessary to avoid the use of chemically active cleaning agents. Mechanical cleaning can be done using special devices and strict adherence to technology. In combination with high-quality installation, this will be the key to long-term operation of the sewer system.
Brief conclusion
How important are details in any construction process! Only millimeters separate a normal working sewer from a problematic one that requires constant repair. In order not to encounter such problems, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic technological requirements before installing the system. And also decide in advance which pipes to use, what slope the pipelines should have, and most importantly, whether you will do the installation yourself or entrust this task to specialists.
Related Posts
When designing a sewer system, an important factor is the correct calculation of the slope of the pipes.
Most of the sewerage operating schemes used have a gravity operating principle. The degree of pipe cleaning and uniform movement of flushed masses in the sewerage pipeline will depend on the correctly calculated inclination angle parameter.
The pipe inclination angle parameter determines the degree of change in the location of its working plane relative to the horizon line.
Unlike the standard measurement system, where the magnitude of the change in the angle of rotation is measured in degrees, the angle of inclination of sewer pipes is characterized by the difference in the heights of the lowest point of the pipe surface at its initial and final sections.
Photo: example of inclination angle for pipes of different diameters
For example, for a pipe with a diameter 50 mm recommended tilt angle per 1 m.p. is 0.03 m. That is for pipeline, length 3 m.p. the height difference will be – 0.03*3=0.09 m.p., or 9 cm
The most important thing in design is the correct calculation of the angle of inclination of the pipe.
Using the correct calculation methodology will help get rid of possible errors, which can ultimately lead to problems in the functioning of the sewer system.
Video: where to start laying a sewer system in a private house
Slope calculation
For sewer systems, there is currently a calculated and non-calculated method for determining the angle of inclination.
Non-settlement methodology gives recommended values for the height difference on a pipe section, depending on its diameter. The average change in value is 3% and may vary slightly due to operating conditions.
Calculation method used for systems with a relatively constant liquid pressure in the sewer system.
There are 2 calculation methods:
- compliance of the speed of movement of the liquid composition in the pipeline with the standard coefficient;
- calculation using the Callbrook-White formula.
Pipeline parameter matching formula:
V*√(H/d)>K,
- K– design coefficient for pipes made of plastic and glass ( 0,5 ). For other materials it is equal 0,6 ;
- H
- V– speed of movement of liquid masses;
- d– internal diameter of the pipe.
Callbrook-White formula:
v=-2√2gDI*log_10 ((K/3.71D+2.5LV/(D√2gDI)),
- v– average value of flow velocity;
- g- acceleration of gravity;
- D– internal diameter of the pipe;
- I– hydraulic slope;
- K– roughness of the inner walls of the pipes;
- V– kinematic viscosity of the liquid.
For private construction, the use of such calculation formulas is difficult - the fill rate of pipes and the movement of fluid depending on the angle of inclination are almost impossible to calculate.
Therefore, when designing sewer systems for a private house or separate apartment, a non-calculation method is used.
Pipe diameter calculation
The choice of pipe diameter for laying a sewer system is determined by the following parameters:
- for connecting plumbing points. The diameter of the pipe should not be less than the diameter of the outlet pipe of the device;
- the permeability of the pipe directly depends on its diameter and increases exponentially, i.e. useful pipe volume 200 mm. will be 3 times larger than the 110 mm section;
- During operation, complete filling of the pipe should be avoided. It is necessary that a small air gap remains for the unimpeded movement of the drainage masses.
In practice, to calculate the pipe diameter, the recommended data from SNiP - 2.04.01-85.
How to calculate the degree of filling of a pipe
An important indicator when calculating a sewer system is the degree of filling of pipes - the maximum possible volume of drained liquid located in the pipeline during operation of the devices.
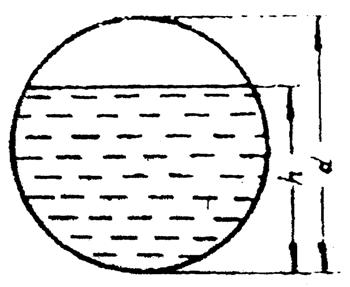 Photo: occupancy level
Photo: occupancy level This value is necessary to determine the maximum load on the riser during operation of all plumbing fixtures.
The pipe filling coefficient is the ratio of the maximum height of water (H) to the internal diameter of the pipe:
According to the norms SNiP - 2.04.03-85 There are the following standard values for the filling factor.
Standards for filling pipes of different diameters
| D, pipe diameter, mm. | 150-200 | 300-400 | 450-900 | >1000 |
| H/d | 0,6 | 0,7 | 0,75 | 0,8 |
The maximum water consumption value for one apartment is 4.8 l/s. This is the summing component for the simultaneous operation of two bathrooms, a bathtub and two sinks. In practice, for a private two-story house the value does not exceed 4 l/s.
To calculate the diameter of the pipes, you must follow SP 40-107-2003.
| Diameter of supply sewer pipe, mm | Angle of connection to the riser, degrees | Throughput of risers with diameter, mm | |
| 50 | 110 | ||
| 40 | 40 | 1,23 | 8,95 |
| 60 | 1,14 | 8,25 | |
| 87,5 | 0,76 | 5,5 | |
| 50 | 40 | 1,07 | 8,4 |
| 60 | 1 | 7,8 | |
| 87,5 | 0,66 | 5,2 | |
| 110 | 40 | — | 5,9 |
| 60 | — | 5,4 | |
| 87,5 | — | 3,6 |
As can be seen from the table, as the diameter of the supply pipe decreases, the throughput of the collector increases.
Ulon according to SNiP
Calculation using the formulas in the “slope calculation” section can only be applied to large sewerage systems - industrial complexes, central sewerage for multi-storey buildings, etc.
For carrying out external and internal sewerage there are limited values - minimum and maximum sewer slope.
Minimum slope
When laying the outer pipe, you should adhere to a slope of at least 0.015 m per 1 m.p.
Important! If this parameter is reduced, solid particles may remain in the inner plane of the pipe due to friction, which will lead to clogging.
Internal pipe routing should also be done according to this rule. The only exceptions may be short sections of the route (up to 1 m.p.). In this case, you can limit yourself to 0.01 per 1 lm, but then the likelihood of blockage will increase.
Maximum
The degree of maximum pipe slope directly depends on the flow speed. For plastic pipes maximum speed should not exceed 1.4 m/s.
As this parameter increases, the liquid is divided into fractions - solid particles settle, since their speed is significantly lower than the speed of water.
The maximum degree of slope should not exceed 3%.
Internal sewerage
Internal sewerage is designed to discharge wastewater into the central sewer system or into a treatment well (septic tank).
When designing an internal sewerage system, it should be taken into account that The composition of the liquid passing through it is divided into the following types:
- gray– dirty water coming from washbasins, sinks and bathtubs. It does not contain a large amount of solid elements, as a result of which its speed of movement is constant throughout the entire length of the pipeline;
- black– waste entering the system from the toilet.
In addition to human waste products, other objects can fall into sewer pipes - napkins, small debris, etc. This leads to inhomogeneity of the flow in density, which affects the speed of the liquid - the solid part moves slower, and the liquid faster.
That is why it is necessary to adhere to the standards for the inclination of pipes so that the speed of movement for such masses is the same.
- maintain the required slope;
- minimum number of rotating elements in the system. In this case, the riser should not contain rotating parts;
- all internal wiring can be made from pipes with a diameter of 50 mm, with the exception of the toilet. For it, the supply pipe must be at least 100 mm in cross-section;
- Calculating the laying scheme is a job for a specialist who will take into account all the features of the building and the use of the sewerage system. If you don’t have confidence in your own abilities, contact specialized companies.
 Photo: internal sewerage
Photo: internal sewerage In the apartment
Calculating the installation of sewer pipes in an apartment is no different from similar projects for a private house. The exception is the short length of the main line and the supply to the common house riser.
Important! When replacing cast iron pipes with plastic ones in an apartment, it should be taken into account that the wall thickness of cast iron ones is much greater. That's why, plastic pipes are often selected with a smaller diameter.
In a private house
Correct calculation of the slope of internal sewer pipes in a private house should be based on the following principles:
- taking into account floor unevenness. When calculating the slope, it is necessary to take the entry point into the riser as a basis. Using a level, he draws the installation line (along the wall) to the point of connection with the plumbing fixture. The height difference must comply with the standards;
- when connecting several points into one line, the total volume of drain liquid is taken into account.
The slope angle does not depend on the total volume of liquid, and is only important for uniform speed passing the drainage mass of different fractions.
For external sewer pipe
 Photo: external sewerage
Photo: external sewerage The laying of the external sewer pipeline is carried out according to the following method:
- the point of exit of the sewage system from the house is taken as a basis;
- when installing a pipe with a diameter 110 mm The slope of the sewer pipe should be 0.02 m; i.e. for a highway length 20 m the slope will be equal to 0.4 m;
- The terrain should also be taken into account. Traditionally, a drainage well is made in the lowest part of the site;
- the slope value is added to the depth of the pipe exit from the house and the required depth of the 2nd point of the main line at the drain well is obtained.
Important! Remember that the depth of the pipe must be below the freezing level of the soil in the very high point highways.
Hydraulic calculation
For correct hydraulic calculation of the system, it is necessary to take into account the limitations on the following parameters:
0,7
0,3
1/d_mm
- H– Amount of pipeline filling;
- V– speed of fluid movement;
- d– internal diameter of the pipe;
- d_mm– internal diameter of the pipe in mm;
- i— pipe slope.
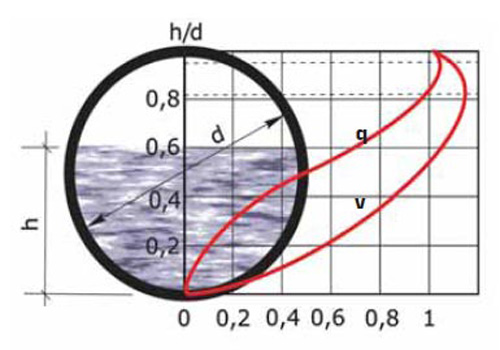 Photo: hydraulic calculation and slope of a sewer pipe
Photo: hydraulic calculation and slope of a sewer pipe The application of these design restrictions is mandatory. But when calculating the slope of a pipe of a certain diameter, you should use a combined method - fulfilling the conditions and recommended data from SNiP.
Calculations for pipes of different diameters
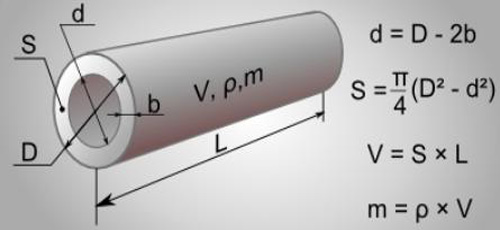 Photo: influence of diameter on other parameters
Photo: influence of diameter on other parameters Calculation of slope for sewer pipes of different diameters
| Pipe diameter. mm | Slope calculation | Resulting value | Slope according to SNiP |
| 50 | 1/50≤i≤0.15 | 0.02≤i≤0.15 | 0.03 m |
| 100 | 1/100≤i≤0.15 | 0.01≤i≤0.15 | 0.02 m |
| 110 | 1/110≤i≤0.15 | 0.009≤i≤0.15 | 0.02 m |
| 150 | 1/110≤i≤0.15 | 0.009≤i≤0.15 | 0.02 m |
| 160 | 1/160≤i≤0.15 | 0.006≤i≤0.15 | 0.008 m |
| 200 | 1/200≤i≤0.15 | 0.005≤i≤0.15 | 0.007 m |
| 300 | 1/300≤i≤0.15 | 0.003≤i≤0.15 | 0.004 m |
As additional tips for designing and laying internal and external sewerage systems, the following can be said:
- When laying pipes indoors, take into account possible natural shrinkage. Over time, the level of inclination may change and then additional adjustment will be required;
 Photo: slope taking into account natural settlement
Photo: slope taking into account natural settlement - The pipe connection angles must be at least 120°. If this cannot be done in some areas, install additional inspection hatches for cleaning;
 Photo: pipe connection angles are at least 120 degrees
Photo: pipe connection angles are at least 120 degrees - when laying hidden pipes indoors, make sure that the joints are completely sealed and make inspection hatches at intervals of 300-400 mm;
 Photo: hermetic joints
Photo: hermetic joints - External pipes are laid from the drain well to the house.
 Photo: laying from the drain well to the house
Photo: laying from the drain well to the house When independently designing and laying a sewer system, it is necessary to collect as much information as possible about the room where the work will be carried out and make calculations of the pipeline so that its length is minimal.
The simpler the system, the less likely it is to break down.
And always seek advice from specialists - the knowledge of other people will help you create a high-quality and reliable sewage system.
Video: display methods
For uninterrupted operation of external sewerage, it is necessary to organize the correct installation of pipes. The main parameter that should be taken into account is the correct slope of the pipeline. It directly depends on the dimensions of the pipe, namely the diameter. To determine the exact values, you need to refer to document SNiP 2.04.03-85.
SNiP 2.04.03-85 specifies the following standards: for d=110 mm we select a slope of 2 cm, for d=50 mm – 3 cm (per meter).
The quality of work subsequently depends on the correct angle of inclination.
Effect of slope
To create the system we use HDPE polyethylene pipes.
Let's look at some extreme cases:
1. Small angle of inclination. If the slope is less than the standard values, then the movement of the fluid will be very slow. The consequence of this will be the accumulation of solid elements on the inner walls. Also, to improve performance, it will be necessary to carry out regular inspections, otherwise blockages will inevitably occur.
2. Large angle of inclination. This option is also unfavorable, since water is removed too quickly, and solid particles are retained on the walls. This leads to frequent blockages. Therefore, the maximum angle of inclination should not exceed 15 cm per meter.
To organize the most correct work, it is necessary to strictly adhere to official building codes.
Checking the correct installation using a special device - a building level.

Installed system. The next stage is fixing the elements using concrete mortar.

If the branches are less than 1.5 m, then the angle of inclination may differ from the accepted values.
Determine the maximum deviation
The size of the diameter is influenced by the specific location in the system. The following factor must also be taken into account: the pipe should not be filled to the maximum during operation. During the calculations we use the recommendations of the regulatory document (SNiP 2.04.03-85).
The air gap in the sewer is an important parameter that determines the unhindered movement of waste.
The degree of fullness is expressed by the dependence of the parameter of the internal diameter of the system on the maximum height of the liquid inside.
Knowing the filling coefficient, it will be possible to fix the maximum pressure on the riser during operation. This parameter characterizes what volume of liquid can fill the sewer as much as possible during the operation of plumbing fixtures.
Quite often, when laying a sewer system, it is designed so that the drains move due to gravity, that is, by gravity. Therefore, when starting to design and then install a sewer system, it is necessary to accurately calculate and maintain the slope of the sewer pipes. In order to avoid mistakes when determining the optimal slope of sewer pipes, in this article we will consider the requirements and standards according to SNiP.
The installation of pressure sewers in private homes is more the exception than the rule. This technology is used only in cases where the installation of a gravity system is impossible.
A non-pressure sewer system, despite its simplicity, requires strict adherence to design rules. Otherwise, if there is no angle of inclination, or it does not correspond to the correct design parameters, then the entire wastewater system will malfunction or become completely unusable.
Construction of a gravity sewer system
The entire sewerage system is a branched pipeline that drains wastewater from plumbing fixtures and goes to the treatment plant.
Pipe angle
Any angle is measured in degrees, but this system is inconvenient to use in the construction of various pipelines. Therefore, in regulatory documents we are offered clearly verified sewer slope values, measured in centimeters per meter of pipe, as well as cross-sectional diameters of pipes for the bathroom, washbasin, kitchen sink, etc.
The influence of pipe inclination on the operation of the sewerage system
Confirming natural physical laws, any liquid flows towards the earth under the force of gravity. And it seems that any angle of inclination of the pipe is suitable for sewage drainage, but this is not at all the case.
Due to the fact that wastewater is far from the consistency of pure water, it is much thicker and contains various inclusions coming from the bathroom, kitchen and toilet: food waste, grease, etc., it is extremely important to prevent these inclusions from settling in sewer pipe. If this is not taken into account, then over time during the operation of the wastewater system, organic deposits will block the passage, and the entire system will become unusable.
To prevent this situation, on the one hand, during pipeline assembly, the smoothness of the internal surfaces of the parts is maintained as much as possible, and on the other hand, the optimal speed of fluid movement is achieved, due to a correctly calculated slope.
For your information! According to SNiP standards, the optimal speed of movement through pipes is 0.7-1 m/s.
The table shows the diameters of pipes for the bathroom, kitchen, toilet, etc.
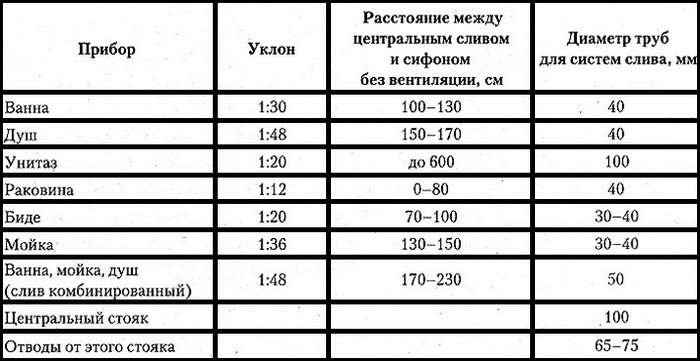
By observing the parameters indicated in the table, the speed of movement of the waste liquid will be optimal, carrying all solid inclusions into the treatment plant without delaying them.
Advice! You can avoid constant clogging of sewer pipes if the system initially works on the principle of self-cleaning.
Insufficient or too large angle of inclination of sewer pipes
If the inclination angle is insufficient, the flow velocity will be too low, and there is a high probability that all inclusions will precipitate. Gradually layering, the sediment will close the lumen of the pipe, which will lead to a gradual stop of the system.
An approach can also be called unprofessional when craftsmen try to make the greatest possible slope so that the drainage is fast and the sediment does not linger. This is a serious mistake that will entail a rework of the system. Main reasons:
- The high speed of water does not have time to “capture” solid particles;
- Sloping the pipes too strongly increases the risk that the liquid may completely block the sewer riser, and as a result, the water seals will be torn off. There is a sewer smell in the room.
Correct calculation of sewer slope
Calculation for internal sewerage system
In manuals and reference books there is a measurement of slope both in centimeters and in the form of a fraction, where the decrease in level to the length of the pipe itself is expressed.
For example, the indicated value of 0.04 means that the slope should be 4 cm per linear meter. This means that with a pipeline length of 10 meters, the top point must be made 40 cm higher than the bottom point (4 cm × 10 m).
We calculate the degree of filling of the pipe
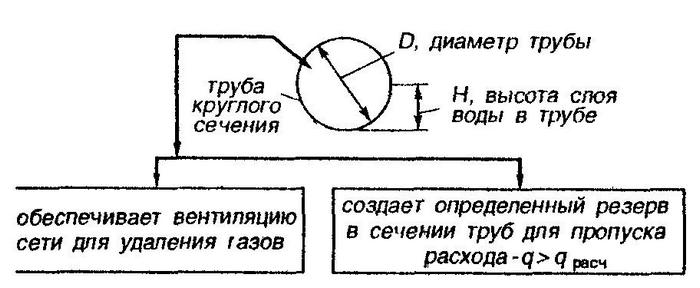
The optimal angle of inclination of the sewer is calculated taking into account the degree of filling of the pipe. This is done according to the formula:
K = H/D,
where K is the pipe fill level,
H – height of the liquid level in the pipe,
D is the diameter of the cross section of the pipe.
The pipe is completely empty at a value of K=0, and at a value of K=1 the liquid fills the lumen completely. For example, the height of the liquid level of a plastic pipe with a cross section of 110 mm in the bathroom is 55 mm, then the K value is 0.5 (55/110 = 0.5).
The normal operation of the drainage system is determined by the K value (pipe fullness value):
- For pipes with a rough inner surface K=0.6;
- With a smooth surface (for example, plastic) K=0.5.
A pipe fill value (K) equal to these indicators guarantees the movement of fluid in the system at optimal speed.
How to measure the angle of a pipe?
This figure schematically shows the minimum slopes of sewer pipes.
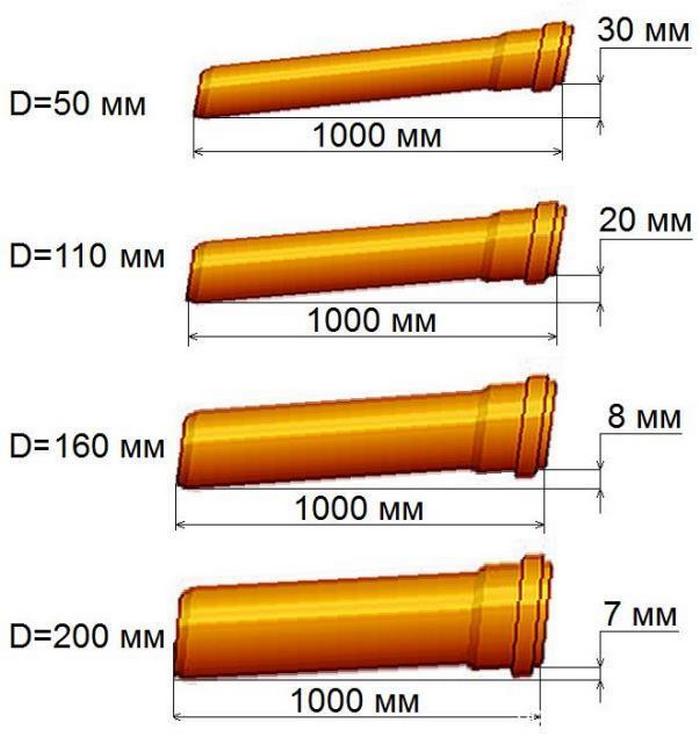
The diameter of the sewer pipe itself directly affects the minimum angle of inclination of the sewer. When constructing the system indoors (for example, in a bathroom), the following SNiP standards must be observed:
- The slope for pipes with a cross-section of 50 mm is 0.03;
- For sections from 85 to 100 mm, the slope is 0.02;
Also, each bathroom plumbing fixture requires its own standards for drainage:
- The outlet from the toilet is constructed using a pipe having a diameter of 100 or 110 mm. Then the minimum slope for a 100 mm section is 0.012, and the recommended slope is 0.02.
- The drain from the washbasin in the bathroom is organized using a pipe with a diameter of 40-50 mm. Then the minimum slope will be 0.025, and the recommended one will be 0.035.
Calculation for an external sewage system

When installing sewer networks outdoors, pipes with larger diameters (150 mm, 200 mm or more) are used than those laid indoors. Therefore, the calculated values will be different here:
- For a tube with a cross section of 150 mm, it is recommended to make a slope of 0.008. If it is not possible to maintain this indicator, then its value may be reduced to 0.007.
- With a diameter of 200 mm, the recommended value is 0.007, and the minimum slope is 0.005.
It is also necessary to take into account the limitation on the maximum permissible sewer slope of 0.15 (for the external system network). In other words, the system cannot operate effectively if the slope of the external pipeline is more than 15 cm per meter of length.
The proper operation of the entire sewer system depends on many components, and determining the correct slope is one of the most important aspects of its design. Any deviations from the standards threaten malfunctions during operation and a complete stop of the drainage system. And, it’s better to do everything correctly right away than to then suffer from constant cleaning or complete reworking of the pipeline in the bathroom, kitchen or area.