If your task is to save High resolution JPEG in Adobe Illustrator, and he treacherously gives you this: Unable to export at this resolution. Please lower the resolution and try again. Then you have come to the right place :) Because now we will solve exactly this problem. High resolution JPEG 300 dpi (300 ppi) may be needed for printing. Also, such files are great for microstocks if the JPEG size is about 25 megapixels. Almost everywhere they take these, even picky Fotolia. If you don’t yet know how to prepare and save vector illustrations for microstocks, then this is the place for you.
It’s clear that screen resolution will work for stock as well 72 dpi With large sizes in pixels in width and height. In this case, you can simply save the JPEG via Save for Web (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+S). This option has fields for entering the width and height of the output image. But for those who still want a high-resolution JPEG of 300 dpi, this method is not suitable. Remains File > Export. This is where you can choose the resolution. But it often fails if Adobe Illustrator decides that there is not enough RAM to complete the operation. That's when you might see this warning.
This is me trying to export a fairly simple picture to high-resolution 300 dpi JPEG in Ai CC. By the way, the CS6 illustrator swears in exactly the same way. For example, if an artboard in Illustrator is 1200x1200 px in size, then when exported at 300 dpi, the result will be a high-resolution JPEG with dimensions of 5000x5000 px.

I can offer two ways to get around this point and still save a beautiful, high-quality JPEG at 300 dpi.
1. Try previous version of Ai
Everything is simple here. If your version of Illustrator refuses to export to JPEG, then take any other one and try it through it.
In my case, Adobe Illustrator CS5 turned out to be more accommodating.
2. Rasterize the Ai file using Adobe Photoshop
We throw ai into Photoshop. Don't forget to put 300 dpi, smoothing Anti-aliased and all other settings you need.
Photoshop will render the vector file. Most likely you will have to wait a while while it works.

I don’t rule out that there are other clever ways :)
If you know any, then share them in the comments. We will exchange experiences.
Roman aka dacascas especially for the blog
Illustrator gives us a lot of possibilities for drawing, but the more complex the tools used, the greater the risk for printing. To prevent this from happening, you need to follow simple rules when creating and saving vector files for later use in creating printed products.
In this Adobe Illustrator tutorial, we won't go into anatomical details like color profiles and five-color printing. Our task is simply to learn how to decide how to save the image, depending on the drawing technique.
So, even the simplest vector image requires taking into account some nuances immediately at the stage of creating the file. If you prefer not to convert strokes into objects, so as not to increase the number of nodes and, accordingly, the processing time of the file, do not forget to check the box in the transformation palette, which will allow you to scale the strokes along with the image. The same goes for brushes.
If the illustration contains black outlines, they must be 100% black, without admixtures of other colors. The thickness of the contours should not be less than 0.1 mm, but it is better to set it from 0.15 mm and above. A large area of the image filled with black, on the contrary, must be “mixed”, that is, contain other colors besides black, otherwise the background will be dull. The total density of composite black depends on the profile of a particular printing house, and when the artist is unknown, it is customary to stay within the amount of 300%.
If the work is being created for replication and contains a background that fits to the very edges of the editing table, then it is advisable to slightly extend the background beyond the boundaries of the plan: as a rule, 3 mm around the perimeter. Otherwise, the illustration may simply be cut off; fields for graphic images in modular grids are not always present. There is no need to fence a garden with rulers and guides; Illustrator makes it possible to easily make overhangs beyond the cutting lines and save the pre-cut format by recording a PDF with the appropriate settings.


How to work with blue and green colors in preparation for printing
As a rule, illustrators with little experience in printing have problems with green and blue fills. These colors and their shades lose their attractiveness the most when printed in CMYK mode. Below you can see an example of what happens with blue and green.

What should I do? You just need to be able to deceive the human eye. The fact that the same color looks different on dark, white and low-contrast backgrounds has been known to every artist since his school years. Think carefully about your color scheme. In addition, their skillful use will force a person to “think out” the graphic information and see your illustration as brighter and more attractive than a four-color print shows. When the graphic style you choose allows you to apply gradients, use it.
If a technically simple image can be recorded in EPS or PDF formats and easily sent to print, then the use of transparency in combination with gradients, art brushes, patterns, transparency masks, raster effects requires more careful preparation. When the printing house is known in advance, all the nuances can be learned from the technologist. Ideally, they will simply accept your finished illustration, recorded in EPS version 9 and higher or PDF 1.4. Saving files in these formats allows you to open them through Illustrator in their “original” form and easily edit them. And modern equipment and software are loyal to transparency.
But when it is impossible to trace the further fate of the file, many prefer to play it safe. The good old, barbaric way to record such an illustration is to save it in EPS version 8. In this case, even radial gradients will be saved as masks in which the raster is placed. If this phenomenon does not bother you, feel free to use it. It will be difficult to do anything with this, not only on RIP, but anywhere else in general. However, be sure to keep the original vector image.
Another, more vector-friendly method is to reduce transparencies. When flattening, overlapping areas will be isolated as independent objects. Schematically: instead of two intersecting objects with transparency, you will get three opaque ones; the object resulting from the intersection area will be painted in the corresponding color. When preparing a file, it is advisable to enable the Overprint Preview function (Veiw menu).

Flattening affects both the objects with transparency and those on which they are superimposed. What is located in the layer above is not subject to reduction. When using art brushes, textures, text, patterns below transparent areas, you must first run the Expand command to avoid possible distortion. Please note that this operation increases the number of nodes, which does not affect the weight of the file for the better. Next we execute the Flatten Transparency command. Carefully look at the settings, Raster\Vector Balance should be in the extreme right position.
But when the file contains gradients one on top of the other with blending modes, do not be fooled by the Raster\Vector Balance engine turned towards 100% vector: complex areas that cannot be described by PostScript will be rasterized. What else will be rasterized? Using Gaussian Blur and Radial Blur, applying Drop Shadow, etc. will entail rasterization of some objects.


Don’t forbid yourself to use transparency, you just need to know all the tools of Adobe Illustrator well and don’t be afraid to experiment: sometimes to create the same shadows it’s enough to use the Blend Tool.
In general, it should be noted that a vector is not an end in itself; ultimately, the image is still rasterized for printing, but the machine will do it incomparably clearer and better than a “handmade” one. Therefore, you should try to preserve the vector as much as possible. However, there are cases when the size of the printed product is already completely known and scaling is not required, but the image is an prohibitive number of nodes and textures or a blurry abstract background. Obviously, in such cases there is no point in clinging to the vector; it is safer to preserve a high-quality raster.
A special case: luminous abstract backgrounds, which are more convenient to create in RGB, when simply translated into CMYK, lose half of the information about colors, transparency and are no good, and rasterization allows you to save the image, although with losses, but not so serious.


You can export your work from Illustrator to TIFF format by specifying the desired model and resolution. Or you can rasterize it by opening the file in Photoshop, and the modern editor does an excellent job with both PDF and EPS, and directly with the .ai file. One caveat: when requesting rasterization, in order to avoid loss of color information, the color model and color profile in which the vector file is written must remain (Photoshop itself offers them when opening by default). And only then the file is converted to the desired color space.
This method is useful for large-format printing when TIFF format is required and Illustrator does not allow you to create and export an image at the desired size. When creating illustrations for exhibition stands or outdoor advertising, interior decoration, we can easily work in vector at the scale at which we are comfortable. When opening a file in Photoshop, simply indicate the desired resolution and size in metric units (we act in that order).
If offset requires a resolution of at least 300 ppi (the same default value is usually set for laser printing with reservations), then the wide format in great importance ppi is not needed. Modern plotters will print a high-quality file for outdoor advertising saved at 24 ppi. Interior printing does not need to be set to a value higher than 150 (typically 96-120) - higher value It won’t add quality, but it will increase the file processing time.
It's not a big article, but it's in general outline the minimum that it is desirable to know when performing work for the printing industry. Good luck to all readers!
Stay up to date with the latest news about vector graphics, new lessons on working in Adobe Illustrator, articles and interviews on graphic design. The team works for you!
In this lesson we will learn how to crop our works, export them to JPG format for the website or print. We will also talk about EPS files, this is a universal format for saving vector graphics.
Saving files using Crop Area
When you need to export your file to JPG format, you will sometimes notice white areas around the image. This happens due to the images hidden behind the masks (see example below). Illustrator also exports the white outline of all objects, regardless of whether they are hidden or not. To solve this problem, you'll need to define a crop zone to tell Illustrator that this is the zone to export, instead of exporting the entire drawing.
Defining the Trimming Zone
Draw a rectangle to define the area you want to export. Select it and click Object>Crop Area>Make.

Crop marks will appear.

Click File>Export. Select the JPEG file type and click save. The JPEG Options window will appear. Depending on whether you're saving for the website or for print, you may need to change the settings.
For Website/Screen: Quality: 6-8 Resolution Depth: Screen
For print: Quality: 12 Resolution Depth: High

Save as EPS file
In the first tutorial I showed you an Illustrator .AI file. However, this type of file can only be opened in Illustrator. There is another universal format that designers usually save for printing and exporting their work in Indesign and QuarkXPress. This is EPS format. Click File>Save As and select the EPS file type. When you save, the EPS options window will appear. The default save should usually be fine. However, sometimes you may need to save for an older version if someone can't open your file.
Version: Choose Illustrator 8.0 if you want all programs to be compatible. However, transparent objects will appear matte.
Preview: Includes a quick view to view your work when importing into other programs.
Transparency Preset: Set it to High Resolution if you are going to print and if the work contains transparency.
Embed Fonts: Check the box if you want to include the fonts in the EPS so that they are available if someone opens them.

Saving to EPS is easy!
1.Why do you need to correctly save files with vector illustrations in EPS?
It is very important to save the file correctly. The first step is to save in EPS. Saving a file incorrectly can lead to either a huge file size or the fact that your file will simply not be accepted.
In order to save the file in EPS, you need to go to the Adobe Illustrator menu, select - file - save as... (File - Save As...)
2.How to name a file
Present different requirements to the vector file format/ Let's consider - common to all.
Specify the file name in Latin letters, for example, Galaktica, select the EPS file type below (Illustrator EPS), click Save.

The file names can be anything, you can use numbers, but not Russian letters.
For convenience, and so that your files in your work archive are in their place - and as you write works, I always call the files NUMBERS. This will make your life easier. I have folders with topics of work, and I name the files in ascending order from 1 - to.... infinity. In this case, you will avoid confusion on your computer and there will be no difficulties with downloading (since one name is required for the vector and a preview for it)
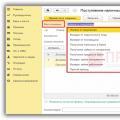
3.EPS parameters when saving
INSelect Illustrator 10 EPS version

In the column - Preview format - the default is TIFF (color 8-bit)

Select - NO.

In the Transparency column there should be no. If the button becomes active - Custom

Then you click on this button and move the slider for Balance of raster and vector graphics - to 100% vectors. Put - OK.

The rest remains as default. Click - OK.

4.How to save a file to view a vector illustration
A vector preview is a regular JPEG file created from EPS by rasterizing it, with exactly the same name.
That is, if we have a vector file called Galactica, then the rasterized copy should be called Galactica.jpg.
Let's consider our option with a digital name. Our preview should be named "49 jpg"

And set the image size to at least 15 megapixels. Those. so that the result of multiplying the height by the width is at least 15 million.
For example - at least 3000x5000.
Different microstocks require different image sizes, but the largest one is needed for Fotolia. Therefore, in order not to save in different sizes for different sites, we will save our JPG file in the maximum size.

And we immediately place our two files - vector and Jpg - into one compressed folder, which is required on some microstocks, such as Fotolia And Depositphotos.
We select both files with the name 49, hover the mouse cursor over them and right-click to bring up the menu, in which we select -send - another submenu will appear - select - compressed zip folder.

Any illustrator working through microstock or photobank understands the importance of vectors that allow you to achieve the best financial results due to its popularity among designers. They allow you to scale to any desired size, and also contain fully editable elements, which allows you to use the most original and daring ideas of the designer. However, to achieve optimal results, you need to understand how best to preserve finished products to make it more attractive to the buyer. For this we have collected some useful tips By proper preparation your vector files to save.
Avoid font conflicts
Remember to always convert the font to curved lines. Otherwise the file will open correctly only if operating system The computer will recognize the font used in the image. Creating your type outlines simply transforms each letter using editable shapes. Once you convert text to curved lines, you will no longer be able to edit it, so make sure the text meets your requirements before proceeding. Press Ctrl + A to select all text objects. Then select Type > Create Outlines.
Love cleanliness
Keep your files in order! A dirty file is as unattractive as a dirty desk, who wants to work with it? Keep customers coming back for more by taking a few extra minutes to get your illustrations in order.
To check for reference contours, hidden lines, or open paths, use the zoom lens around the illustration. To eliminate the listed defects, use the following commands: , and Adobe Illustrator will clean up the illustration itself.
Other questions
Try to keep your illustrations neatly within the confines of the desktop and always check within the drawing area for lone dots and open paths. All components of the illustration should be neatly organized and labeled in folders. Use layer palettes to more effectively present your illustrations to your microstock buyer.
file size
Reduce the size of the illustration. To do this, select File > Document Setup and set the frame size. Select your images by pressing Ctrl+A and then Alt+Shift drag on one corner of the bounding box to resize your artwork on the artboard.
Disable previews created by Adobe Illustrator. Rasterized previews result in unnecessary file size increases. When saving the file, in the EPS dialog box, select the “None” option for preview.
Remove unused symbols, graphic styles, brushes, and swatches. If your work palette is not active, select Window> Actions. Scroll down until the Remove Unused Palette Items option appears, select that action, and click the Play button at the bottom of the window panel.
Make sure your work is not rejected by photo stock at high resolution. To do this, use the Object > Flatten Transparency option. Make sure you do NOT rasterize your work as this will not make it truly vector.
Final Savings Protocol
Congratulations! You have created a piece of vector graphics. Before downloading, there is one more important step - saving!
Please note that microstock requires all vector images to be saved for Adobe Illustrator version 10 or higher. The reason for this is as follows. Let's assume that one of the users, using Illustrator 10, is trying to open an EPS Illustrator CS2 file that has been uploaded to a photo bank. The user will receive an error message warning that the file can only be opened in an updated version of Illustrator. File incompatibility is unfortunately a problem for many users, so microstock's policy is to standardize all vector images like Illustrator 10 or earlier (called a Legacy file).