Today we have to find out why we need to install an air vent in the water supply system. In addition, we will find out in which part of the water supply circuit it can be installed, what kind of air vents can be used there, and how to solve the problem of air in the water supply without an air vent. Let's get started.
About hot water supply
First, let's find out why airing of the water supply system occurs and how it interferes. Let's start from afar.
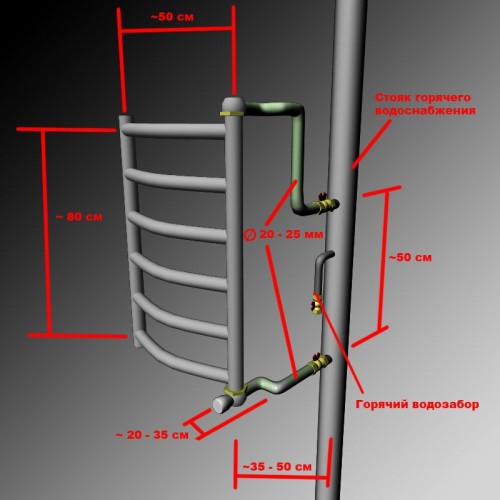
It always has a dead-end wiring: the bottling goes into risers, they branch into connections, and the connections end with taps of plumbing fixtures. Water moves in a dead-end circuit only due to water intake.
Dead-end DHW circuit
Until about the 70s of the last century, hot water supply systems (DHW) in all houses under construction were organized in the same way.
However, this wiring has two serious drawbacks:
- Having opened the hot water tap, the homeowner is forced to wait for several minutes for it to heat up. The wait is especially long at night and in the mornings, when in the absence of water supply the risers and hot water outlets cool down. This is not only inconvenient, but also contributes to unreasonably high water consumption;
Please note: when recording hot water consumption using a mechanical water meter, you are forced to pay for the entire volume passing through it. In fact, a significant part of this volume does not meet the requirements of current operational standards: the DHW temperature must be within the range of +50 - +75°C.

- Heating of bathrooms and combined toilets in apartment buildings, is provided by a heated towel rail powered by a hot water supply system. It is clear that in the absence of water intake in the dead-end system it will cool down. For the apartment owner, this means dampness and cold in the bathroom, and in the long term, a greater likelihood of fungal damage to the walls.

Circulation scheme
Since the late 70s - early 80s, hot water supply in new buildings gradually began to become circulating.
How it's implemented:
- Two hot water supply outlets are laid in the basement or subfloor of the house;
- Each bottling has an independent insertion into the elevator unit;
- The hot water supply risers are connected alternately to both dispensers and are connected by jumpers on the top floor or in the attic. From 2 to 7 risers can be combined into groups connected by circulation jumpers.

Please note: installing lintels in the attic is extremely unwise in cold climates. The author encountered it in the Far East: at a temperature in a cold attic of -20 - -30 degrees, stopping circulation in the hot water system (for example, during an emergency shutdown of hot water) causes the water in the jumper to freeze within an hour.
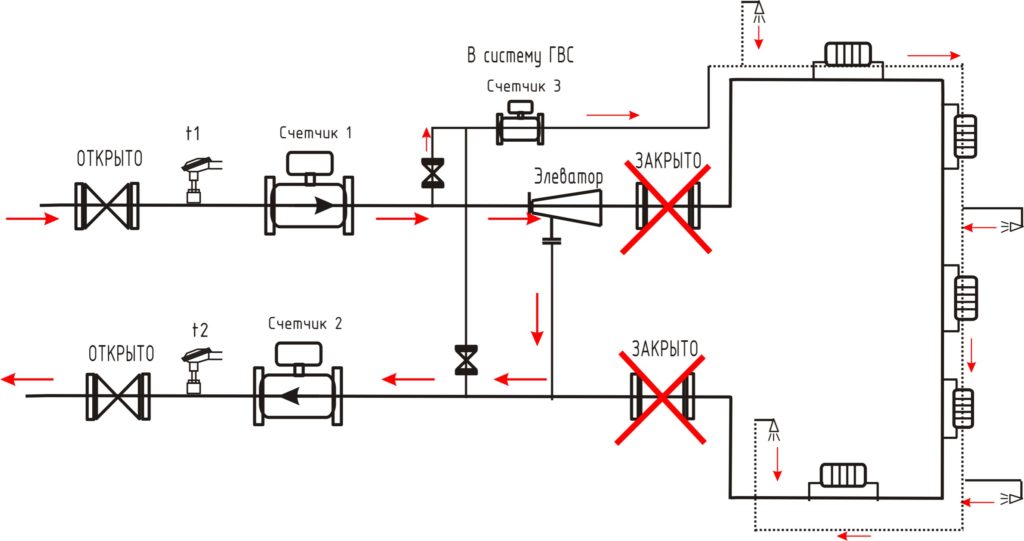
In order for water to continuously circulate through risers and bottlings, a pressure difference must be created between them. In the elevator unit and further, in the heating circuit powered from it, circulation is ensured by the pressure difference between the supply and return pipelines heating mains. The obvious way to supply hot water is between the supply and return connections.
However, in this case we are waiting an unpleasant surprise: a bypass between the pipeline threads will catastrophically reduce the drop at the water-jet elevator, preventing the heating from operating.
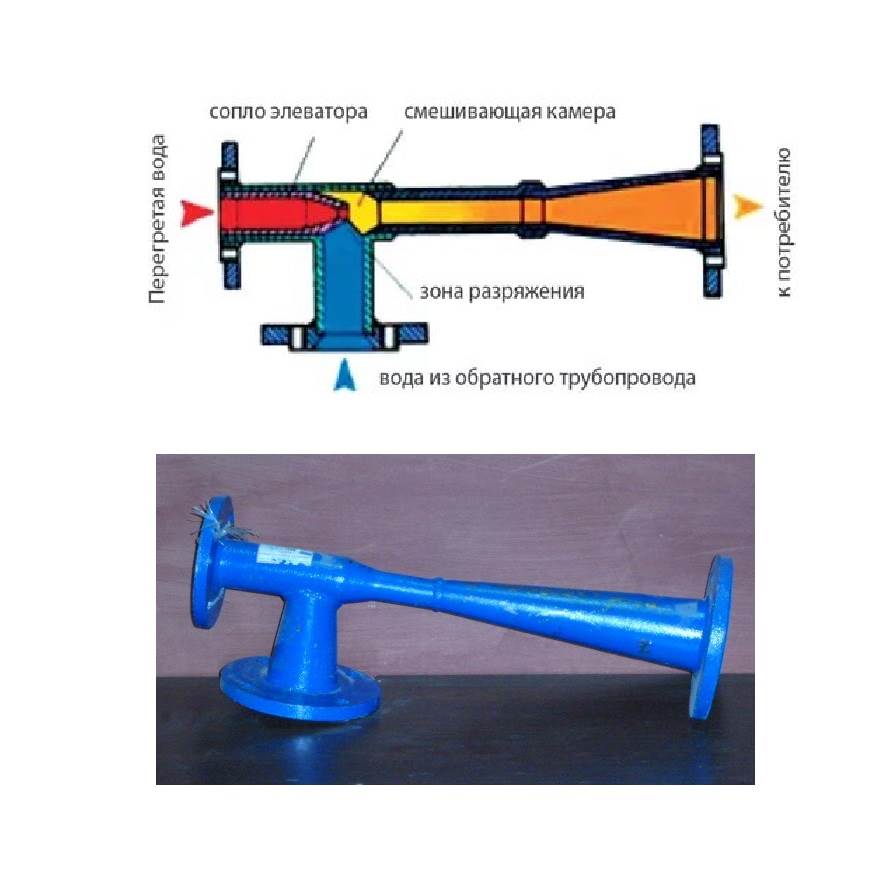
The problem can be solved simply and elegantly:
- The hot water supply cuts into the supply to the elevator at two points. Each of the inserts is equipped with shut-off valves;
- The flange between the inserts is equipped with a retaining washer. This is the name of a steel pancake in which a hole is drilled in the center with a diameter 1 mm larger than the diameter of the nozzle. During normal operation of the elevator and the associated movement of water along the supply line, such a washer creates a difference between the tie-ins of approximately 1 meter of water column (0.1 atmosphere);
- Exactly the same two tie-ins with the same retaining washer are mounted on the return pipeline.
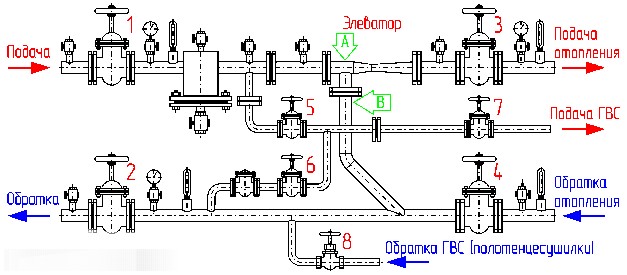
An elevator with hot water circulation taps has three operating modes:
- Hot water circulates from supply to supply. This scheme is used in spring and autumn, at a relatively low (up to 80 degrees) coolant temperature in a straight line of the heating main;
- From return to return. DHW switches to this mode in winter, when the supply temperature exceeds 80°C;
- From supply to return. So the hot water supply system with circulation is powered in the summer, when the heating is turned off, and the difference between the threads of the heating main is minimal or absent.
Air! Air!
Risers, or even the entire hot water supply circuit, have to be reset from time to time.
There are several reasons for this:
- Seasonal repair work(revision shut-off valves, scheduled testing of heating mains, etc.);

- Emergency work(elimination of gusts, leaks of risers and spills);
- Work in apartments with faulty valves(in particular, replacing these valves).
Now let's imagine what will happen when a pair of risers connected by a jumper is reset and then launched:
- Once you turn off the valves on the risers, unscrew the plugs and open any tap on any plumbing fixture, the water will completely drain from the paired risers and they will fill with air;

- When starting paired risers, air will be forced out by water pressure into the upper part of the closed circuit - into the jumper;
- Since the pressure difference driving the water is minimal, the air in the water supply system will completely stop the circulation in this section. The obvious consequences are the same long heating of water during tapping and cold heated towel rails.
The video in this article will help you learn more about how to remove air from a water supply system.
Manual and automatic air vents
How to remove air from a water supply system after it has been reset? The most logical solution is to bleed the air through an air vent installed directly on the jumper between the risers.
There you can find an air vent belonging to one of two types:
| Image | Description |
|
|
Manual (Maevsky faucet) - a plug with a screw-in valve using a key or a screwdriver. To eliminate air from the hot water supply system, just unscrew the valve a couple of turns, wait until the air coming out of the hole on the tap is replaced by water, and screw the valve back on. Sometimes you have to bleed the air two or three times as the water displaces new air bubbles into the upper part of the circuit. |
|
|
An automatic air vent for water supply does the same without the intervention of the owner. When its chamber is filled with air, the float connected to the spool lowers - after which the water pressure displaces the air plug. The floating float hermetically closes the spool. |
Useful: when installing a DHW jumper yourself, the Mayevsky tap can be replaced with a screw valve or a water tap. They are not so compact, but more convenient to use, since they open without the use of any tools.

The obvious advantage of the Mayevsky crane is its low cost. That is why, in Soviet-built houses, exclusively manual air vents were used.
However, from the point of view of ease of use, they are much inferior to automatic air vents:
- Some residents of the upper floors are simply afraid to use shut-off valves that are unfamiliar to them;
- Keys to Mayevsky taps with valves of complex shapes are constantly lost;

- Manifestations of excessive enthusiasm by residents, coupled with technical illiteracy, often lead to flooding of apartments. The fact is that a completely unscrewed valve (and even more so the tap itself) is almost impossible to screw in under pressure. Especially in the case when scalding hot water is gushing out of the hole. hot water.

Without air vent
How to remove air from a water supply system with your own hands if you do not have access to an air vent or if it is faulty?
The instructions are ridiculously simple:
- Close one of the DHW risers connected by a jumper;
- Fully open one or two hot water taps in any apartment along this riser. After a very short time, the air plug will fly out at the front of the water flow, and the water being discharged will heat up;
- After all the air has escaped, close the taps and open the valve on the riser.

A private house
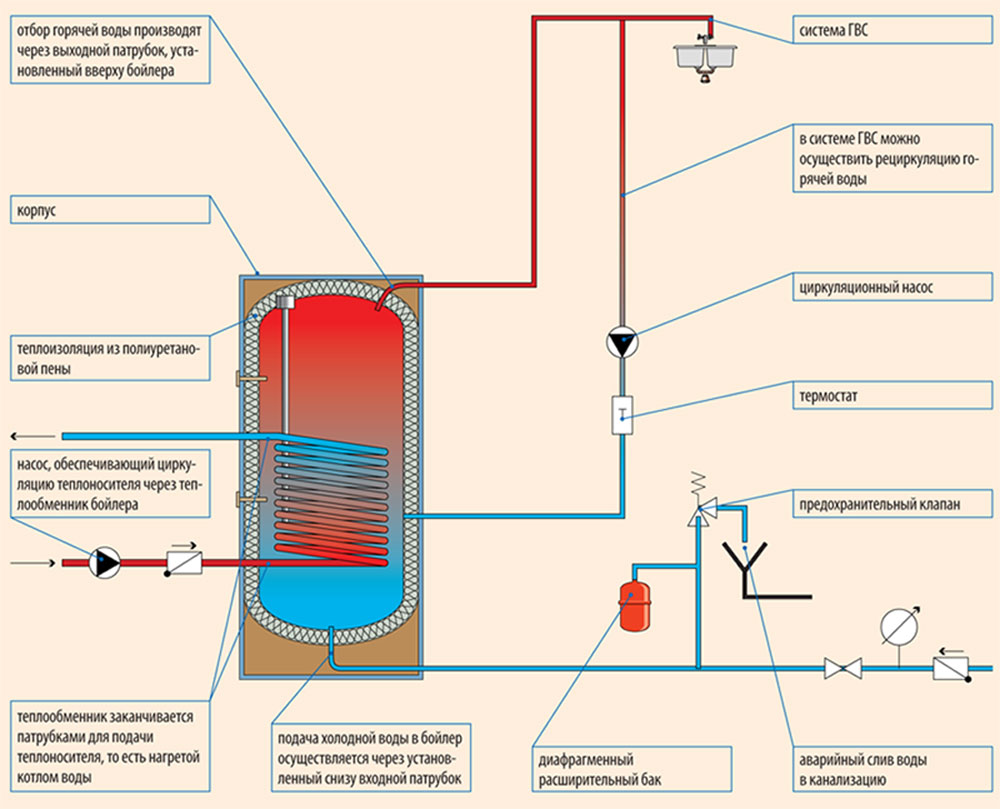
Is an air vent needed in the domestic hot water system of a private home?
The answer is pretty obvious. An air vent is necessary if yours uses recirculation and there are no plumbing fixtures at its highest point through which air can escape.
Note: the presence of a high-pressure circulation pump, coupled with the low contour height means that you don't have to worry about stopping the circulation. However, air in the DHW system often causes annoying hydraulic noise.
Conclusion
As you can see, problems in the operation of the hot water system often have very simple solutions. The video in this article will help you learn more about how to remove air from a water supply system. Good luck!
The air in the heated towel rail is main reason ineffective operation of the device. The towel drying device simply stops heating and therefore drying the towels.
The heated towel rail is an unusual pipe in the bathroom. First of all, it is an alternative replacement for radiators, which are often not installed in bathrooms. Secondly, a drying device paired with high-quality ventilation provides clean and dry air in the room, preventing the occurrence of fungus and mold.
As you know, the heated towel rail is warm even in the summer, when the heating is turned off, all because the device is connected to the hot water supply system. If the house is not connected to a centralized hot water supply, you can purchase an electric analogue.
Even a very beautiful heated towel rail may not heat well if there is air in it
Anyone who has used a heated towel rail for some time knows that you can’t live without it. The device is very useful in everyday life. Dry and warm towels are always waiting for you in the bathroom. You can dry small items (handkerchiefs, socks, etc.) or wet shoes on the heated towel rail.
The benefits of a heated towel rail in the home are well understood by parents who have to dry their children's gloves or boots every day in winter.
The main problem of the drying device
After a certain period of using the heated towel rail, you will find that it has stopped heating and at that moment it is absolutely.
This problem is often faced by residents of multi-storey buildings when the weather turns on in the autumn. centralized system heating. At this time (when the pipes are filled with water), air may appear in the pipes. Such plugs usually occur in the final parts of the heating system, which is the heated towel rail.
As soon as air appears in the pipes, the high-quality circulation of hot water is disrupted, and accordingly the drying device stops heating.
Leaving the heated towel rail unused for a long time can significantly affect your habits and the quality of bathroom ventilation, because high level Even a week's worth of humidity can affect the finish of the walls of the room.
If you are planning to install a towel dryer or have already installed it, you must be aware of all its possible problems and how to solve them.
Letting the air out of the heated towel rail yourself
Since the only problem that causes the device to malfunction is air, it needs to be eliminated.
As soon as you bleed the heated towel rail, it will work again at the same level. Removing air locks is quite easy; you can handle this problem yourself, without the help of specialists.
To make the mechanism warm again, air can be released in two ways:
- Classic or traditional way.
- Modern way.

On some models, the plugs are removed from the top of the heated towel rail; there is a valve for bleeding the plugs.
The traditional method of removing air involves draining water. Since the heated towel rail is connected to the water supply system, you just need to drain all the water along with any air pockets. In multi-storey buildings, water is drained on the top floor via a riser. If the drain is located in your apartment, it’s even easier - you can drain the water yourself.
Sometimes, draining all the water is not enough, so you will have to resort to the second option: unscrew the nut that secures the drying device to the pipes. The nut must be unscrewed very carefully and slowly. As soon as air comes out you should stop.
Be sure to remove everything from the bathroom in advance to avoid flooding, and place a water container under the mounting location.
A modern way to bleed air involves a device called the “Mayevsky tap”. Many heated towel rails are sold complete with a faucet, or it can be purchased separately.
The tap is attached to the drying device and is intended only for releasing air; it cannot shut off the water. The tap consists of an adjusting screw and a needle valve.
Using a special key or screwdriver, turn the screw, the valve will open, and the air will completely escape from the mechanism. The air must be released until water comes out without bubbles. Experts recommend flushing the water until a trickle of not warm, but even hot water flows.
Before carrying out all the work, also be sure to take precautions: remove everything from the bathroom that is afraid of moisture and place a water container under the heated towel rail.
When all the air has been released, tighten the screw back, after which the device should heat up again.
If you do not have a Mayevsky faucet and the possibility of purchasing one, you can bleed the air from the heated towel rail using improvised means.
To remove air from the pipes yourself you will need:
- pliers;
- screwdriver;
- key.
Connection diagram
Using available tools, you should perform work similar to the Mayevsky crane. It is absolutely not necessary to have plumbing skills. Arm yourself necessary tools, open the air vent, bleed the air and close it tightly.
You will first hear a noise - it is air coming out, then water will flow. Release the air until the water pressure increases and the water becomes warm.
As you noticed, draining the water is not at all difficult. You do not need to hire a master and spend money from the family budget.
Installation of Mayevsky crane
Do not be afraid that the Mayevsky crane is a complex design, difficult to install and expensive. Not at all, the faucet is just two parts: a conical screw and a body.

Mayevsky crane with key
The purpose of the faucet is to exhaust air to the outside, guarantee quality work heated towel rail.
The principle of operation of the device: when the tap is open, air from the system enters the housing, where it is removed through a side hole; When the screw is closed, neither air nor liquid can escape from the pipeline.
When choosing a Mayevsky tap, pay attention to the diameter external thread, it must match the size of your pipes that are used in the heating system.
Depending on the design, the Mayevsky tap can be opened and closed either by hand or with a special key or screwdriver.
When installing the faucet, make sure that the hole is at the bottom of the faucet. In this case, when collecting water, it will go directly into the container, and not onto the walls of the bathroom. And the tap itself needs to be mounted in the upper part of the heated towel rail to make it easier to release air.
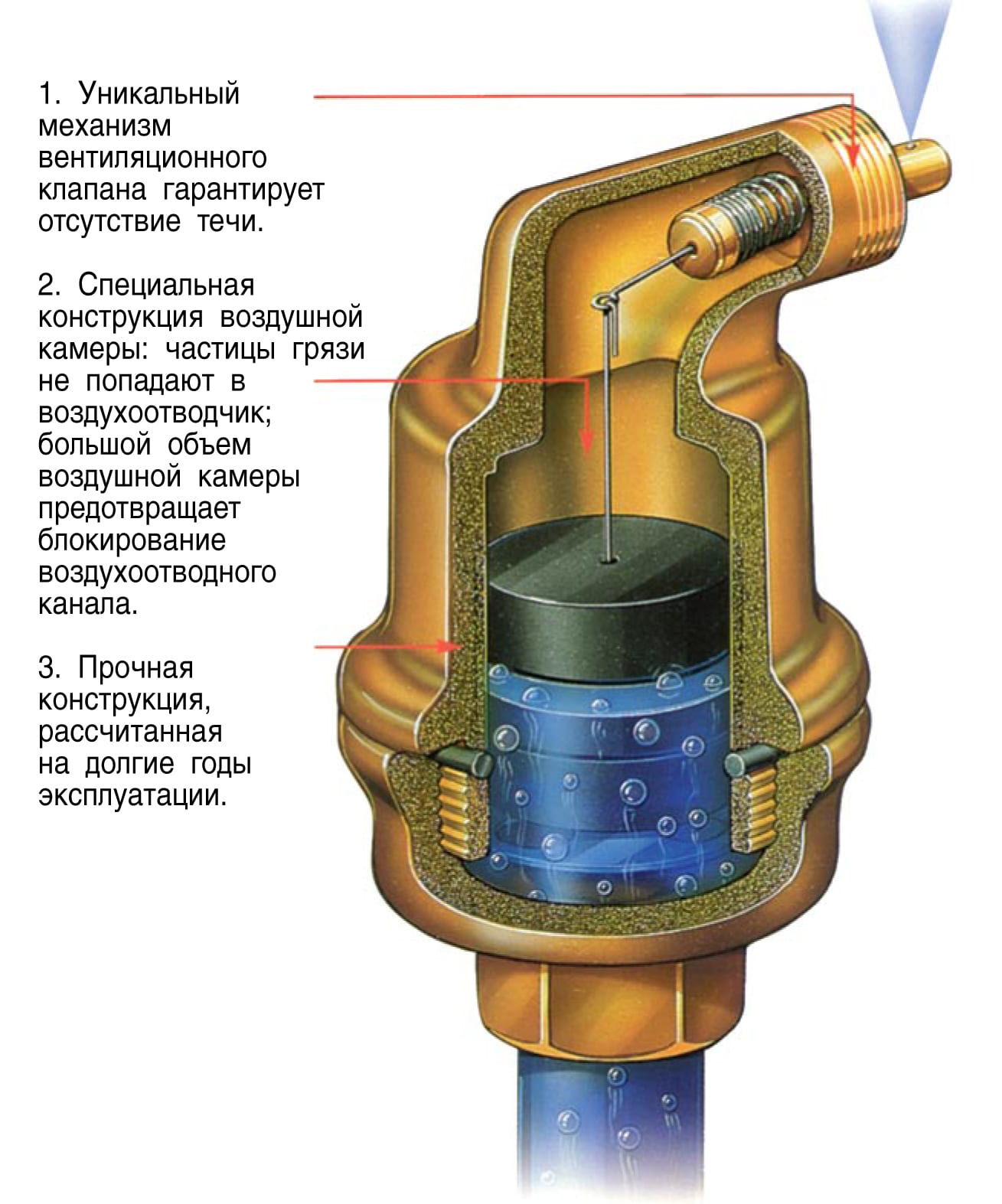
This is a device for removing air (gas) accumulations in water heating and water supply systems.
Why is it necessary to install this air vent?
During operation of closed-cycle heating devices, gases consisting of air, hydrogen, and oxygen are released, which must be released from the system so as not to disrupt its normal functioning. The most unpleasant consequences are noise effects and difficulties in water circulation, which leads to uneven heating of the space, corrosion and premature aging of pipes and parts.
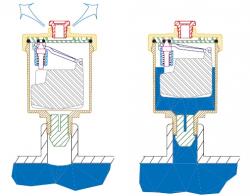
Operating principle of the air release valve
The operation of the automatic air release valve is very simple and is based on the Archimedes principle. When there is no accumulated air inside the valve, the float is in a raised position and, through a special mechanism, holds the pin shutter closed. The lowering of the float, caused by the accumulation of air inside the valve, leads to the opening of the valve and the subsequent release of air until the initial position is restored. When the system is filled and there is no water in the valve, the float is located in the lowest position and the air quickly comes out. You can prevent the release of air by screwing in the top plug. For normal use, the plug must be removed.
Example:
Removing gas accumulations is a task that must be resolved already at the design stage of the heating system. Air can enter heating systems in various ways: it partially remains in a free state when filled with water; as a result of air leaks during operation of an incorrectly designed heating system; introduced with make-up water in absorbed (adsorbed) form. Even in a system with deaerated water, hydrogen may appear mixed with other gases. The amount of free air remaining in pipes and devices when they are filled cannot be accurately measured, but in the case of a properly designed system, it is eliminated during the first days of operation. It is best if the heating system is filled before starting the heating season cold water from water supply network to a predetermined height of the building. Filling the system with water is carried out from the bottom up and is possible only by displacing the air in pipelines and heating devices into the atmosphere through appropriate devices: manual air valves and automatic air vents.
The amount of dissolved air (gas) introduced into the system with periodic additions of water during operation is determined depending on the air content in the makeup water. Cold tap water contains more than 30 g of air in 1 ton of water, make-up deaerated from the heating network - less than 1 g. An increase in water temperature leads to a significant decrease in the content of dissolved gases in it, and in those places where hot water is under pressure close to atmospheric, in the largest amount of gas adsorbed in it passes into the free state. Increasing pressure, on the contrary, delays this process. According to Henry's law, the amount of adsorbed gas at a given temperature is directly proportional to pressure. It should also be noted that air dissolved in water is more corrosive for steel pipes than atmospheric, since the oxygen content in it is 10-12% greater by volume. In addition, another reason for the “gas contamination” of heating systems is corrosion. Thus, during the oxidation of 1 cm3 of iron, up to 1 liter of hydrogen can be released. Considering all of the above, the main reasons for the appearance of gas (air) accumulations in closed heating systems include the introduction of air with make-up water and metal corrosion.
First of all, it is necessary to install air vents on aluminum radiators due to the fact that aluminum, acting as a catalyst on water, accelerates the process of its decomposition into hydrogen and oxygen. To a somewhat lesser extent, this applies to bimetallic radiators with aluminum heads. You should always remember: when servicing air vents in heating systems with aluminum radiators, it is prohibited to use open fire or smoke in the immediate vicinity of them, as this can lead to ignition of flammable gases released during operation of the system. And one more recommendation: according to theory, air vents with safety valves should be installed on all devices, including thin-walled steel panel radiators. By the way, Western European companies usually supply them this way, despite the fact that their operating conditions for heating systems are much better. And finally, concluding our consideration of the issue of application, we note: automatic air vent is the same integral element of the boiler safety group as the pressure gauge and safety valve.
It is allowed to tighten automatic air vents in place of Mayevsky valves, which are manual valves for releasing air. This is what the Mayevsky crane looks like: 
I do not recommend buying such air vents.