GOST for seamless hot-rolled pipes
- GOST 8732-78 Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes.
- GOST 550-75 Seamless steel pipes for the oil refining and petrochemical industries.
- GOST 9940-81 Seamless hot-deformed pipes made of corrosion-resistant steel.
- GOST 23270-89 Blank pipes for machining.
- GOST 30564-98 Hot-deformed seamless pipes made of carbon and alloy steels with special properties.
GOST for seamless cold-rolled pipes
- GOST 8734-75 Cold-deformed seamless steel pipes
- GOST 9941-81 Cold- and heat-deformed seamless pipes made of corrosion-resistant steel
- GOST 10498-82 Seamless extra-thin-walled pipes made of corrosion-resistant steel
- GOST 14162-79 Small-sized steel tubes (capillary)
- GOST 19277-73 Seamless steel pipes for fuel and oil pipelines
- GOST 9567-75 Precision steel pipes
- GOST 24030-80 Seamless pipes made of corrosion-resistant steel for power engineering
- GOST 1060-83 Cold-deformed seamless steel pipes for shipbuilding
- GOST 11017-80 Seamless steel pipes high pressure
- GOST 21729-76 Cold- and heat-deformed structural pipes made of carbon and alloy steels
National standards for steel pipes
List of GOST on steel pipes
- GOST R ISO 3183-3-2007 Steel pipes for pipelines. Specifications. Part 3. Requirements for class C pipes
- GOST R ISO 3183-2-2007 Steel pipes for pipelines. Technical conditions. Part 2. Requirements for class B pipes
- GOST R ISO 3183-2009 Steel pipes for pipelines in the oil and gas industry. General technical conditions
- GOST R ISO 3183-1-2007 Steel pipes for pipelines. Technical conditions. Part 1. Requirements for class A pipes
- GOST R ISO 10543-99 Seamless and welded hot-drawn steel pressure pipes. Ultrasonic thickness measurement method
- GOST R ISO 10332-99 Seamless and welded steel pressure pipes (except for pipes manufactured by submerged arc welding). Ultrasonic method continuity control
- GOST R ISO 10124-99 Seamless and welded steel pressure pipes (except for pipes manufactured by submerged arc welding). Ultrasonic method for monitoring delaminations
- GOST 28548-90 Steel pipes. Terms and Definitions
- GOST 20295-85 Welded steel pipes for main gas and oil pipelines. Specifications
- GOST 8734-75 Cold-deformed seamless steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 8645-68 Rectangular steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 11017-80 High pressure seamless steel pipes. Specifications
- GOST 10706-76 Electric-welded straight-seam steel pipes. Technical requirements
- GOST 10704-91 Electric-welded straight-seam steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 9567-75 Steel pipes precision. Assortment
- GOST 8731-74 Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Technical requirements
- GOST 8646-68 Steel pipes with hollow ribs. Assortment
- GOST 8644-68 Flat-oval steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 8642-68 Oval steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 8638-57 Drop-shaped steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 6856-54 Steel pipes of special profiles
- GOST 5654-76 Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes for shipbuilding. Specifications
- GOST 8639-82 Square steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 8467-83 Steel drill pipes with nipple connections for geological exploration drilling. Specifications
- GOST 13663-86 Steel profile pipes. Technical requirements
- GOST 30456-97 Metal products. Rolled sheet metal and steel pipes. Impact test methods
- GOST 12132-66 Electric-welded and seamless steel pipes for the motorcycle and bicycle industry. Specifications
- GOST 11249-80 Two-layer brazed rolled steel pipes. Specifications
- GOST 10707-80 Cold-deformed electric-welded steel pipes. Specifications
- GOST 10692-80 Steel, cast iron pipes and connecting parts for them. Reception, labeling, packaging, transportation and storage
- GOST 8733-74 Cold-deformed and heat-deformed seamless steel pipes. Technical requirements
- GOST 8732-78 Hot-deformed seamless steel pipes. Assortment
- GOST 8696-74 Electric-welded steel pipes with a spiral seam for general purposes. Specifications
- GOST 5005-82 Cold-deformed electric-welded steel pipes for cardan shafts. Specifications
- GOST 3262-75 Steel water and gas pipes. Specifications
- GOST 1060-83 Cold-deformed seamless steel pipes for shipbuilding. Specifications
- GOST 550-75 Seamless steel pipes for the oil refining and petrochemical industries. Specifications
- GOST 19277-73 Seamless steel pipes for oil and fuel lines. Specifications
- GOST 10705-80 Electric-welded steel pipes. Specifications
- GOST 10692-2014 Steel, cast iron pipes and connecting parts for them. Reception, labeling, packaging, transportation and storage
List of GOST on copper and brass trubles
- GOST 617-2006 Copper and brass pipes of round section for general purposes. Specifications
- GOST 21646-2003 Copper and brass pipes for heat exchangers. Specifications
- GOST R 52318-2005 Round copper pipes for water and gas. Specifications
- GOST 16774-78 Copper pipes of rectangular and square sections. Specifications
- GOST 494-90 Brass pipes. Specifications
Pipe - GOST for each type of pipe
Specialists of Lador Komplekt LLC are always happy to illuminate technical features proposed pipe rolling. Note that these products have a wide range of applications - including being used as fence posts, for laying pipelines, etc. According to the production method, steel pipes are divided into several types. The first type is seamless GOST pipe 8732-78, GOST 8734-75, GOST 10796-76, GOST 20295-85 (outer diameter of pipes 1-820 mm, special purpose - 1420 mm). The second type is a pipe made from ingots and pipe blanks by pressing or rolling.
The third type is welded GOST pipe 3262-75, GOST 10705, GOST 10707, GOST 3262, GOST 8639, GOST 8645, GOST 8642 (outer diameter of pipes 8-1620 mm, special purpose - up to 2500 mm or more) from sheet and strip steel with pre-forming. This type of pipe is in particular demand.
Our company has been a participant in the domestic metal pipe rolling market for several years now, and the practical experience acquired during this time provides a significant advantage over many similar enterprises and organizations. Dynamic development and flexible corporate policy make it possible to optimally satisfy the wishes of customers, no matter what difficulty the task has to be solved, and sometimes the deadlines are very limited.
We will quickly and correctly help you do right choice, helping you with advice. We remind you that we also produce electric-welded rectangular and square pipes GOST 13663-86 and round electric-welded pipes, its GOST 10705-91 (diameter from 10 to 530 mm) or round GOST pipe 10706-76 (diameter from 478 to 1420 mm). The fourth type is cast pipes (outer pipe diameter 50-1000 mm), produced on pipe casting machines.
Any construction product is produced subject to certain conditions and standards. And although many materials are subject to the requirements of one single GOST, round steel pipe, depending on the technology of its manufacture, belongs to different standards.
Application of round pipes
Main application steel pipes is their use as pipelines intended for transporting gas and various liquids, which most often are water and oil products. Depending on the transported environment, pipes may have:- galvanizing;
- anti-corrosion painting;
- polymer coating;
- processing with insulating materials.
In addition, the surface of the pipes is subjected to electrical treatment or other types of protection. The most “painful” processes for steel pipes are corrosion processes. From the outside they are provoked by excess moisture, and from the inside by internal roughness and butt seams. Once corrosion appears, it gradually begins to grow, thereby reducing the throughput capacity and filling the internal space of the pipe. The result is breaks and leaks, which leads to unscheduled repairs and replacements of pipelines.
Another area of application for round galvanized pipes is the furniture industry. They are widely used in the manufacture of frames and internal filling of sliding wardrobes or dressing rooms. Also, GOST for round steel pipes allows the material to be used when assembling metal structures or individual metal products.

Differences and features of steel pipes
The main classification of round steel pipes is made according to the method of their manufacture:
- electric welded ones are available in two types - straight-seam and spiral-seam;
- seamless.
They also have differences in rolling methods:
- cold molding;
- hot molding.
An electric-welded round steel pipe is made from steel strips or rolled sheets using the molding method, followed by welding the seam along the axis or in a spiral. The process involves the use of special equipment. Spiral-seam pipes are much less common than straight-seam pipes, and they are obtained by molding the strip in a spiral. In this case, the joint is welded in a simultaneous continuous mode using a special seam. In the manufacture of products, two types of welding are used:
- contact high-frequency – for pipes from 10 to 530 mm;
- electric arc – from 428 to 1420 mm.

Visually, the seam during high-frequency welding is practically invisible. Electric arc welding technology involves the application of three seams, which increases the strength characteristics of the joint. First, the main central seam is laid, and then the connection is welded from the outside and inside products.
Electro welded pipes, the diameter of which allows for internal work, the inside is cleaned (ground), removing irregularities and thickenings formed after welding. If it is impossible to carry out such work, the inner surface is left without treatment.
Seamless steel pipes are manufactured in several ways:
- pressing;
- drawing;
- forging;
- rolling;
- centrifugal casting.
Thermoforming is performed on special equipment. The workpiece is heated to the recrystallization temperature. This method allows us to obtain high-strength products that can withstand severe loads, including internal pressure. Cold formed round metal pipe obtains the specified dimensions by cold deformation on equipment designed for this process.
The difference between seamless and electric-welded pipes is the presence or absence of a weld. Their manufacturing methods have significant differences in technology, and, as a result, they are different specifications.

Manufacturers produce several more types of steel pipes:
- soldering;
- with metal or non-metallic coating;
- with special processing - turned, ground, polished.
The most common today are water-gas pipes (WPG) and longitudinally welded electric welded (ESW) pipes. They are widely used in urban and suburban housing construction when performing utility networks. They are cheaper than seamless analogues, thanks to simpler production technology and the use of ordinary carbon steels, the most accessible in metallurgy.
Depending on the type of molding, when producing BS pipes, they rely on different regulatory documents:
- for hot-formed - GOST 8732-78 and GOST 8731-74;
- for cold-formed - GOST 8734-75 and GOST 8733-74.
Each of the documents indicates in what form a round steel pipe should be produced, product range, tolerances, installation rules, acceptance and storage, and much more.
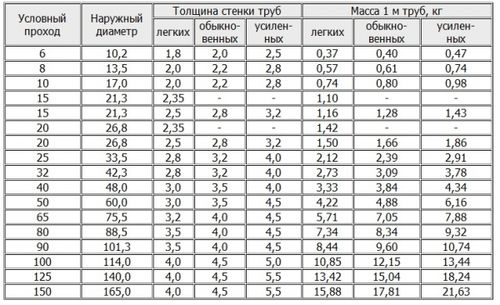
GOST 8732-78 defines the dimensions of the outer diameters of seamless hot-formed pipes ranging from 20 to 550 mm with a wall thickness from 2.5 to 75 mm. Also, the tables indicate the mass of products in kilograms per linear meter. The document states that pipes, in relation to length, can be manufactured:
- measured;
- multiples of measurements;
- unmeasured;
- approximate length based on consumer instructions.
The typical length is 4-12.50 meters. But at the request of the customer, this rule is deviated.
GOST 8731-74 indicates technical requirements to hot-formed seamless pipes. It establishes the acceptable:
- steel grades;
- yield limits;
- temporary tensile strength;
- relative elongations.
Standards require that the surface of the pipes be free of cracks and flaws, but minor dents and traces of stripping are allowed. Products are allowed to be cut using autogens or plasma cutting, but only if the wall thickness reaches 20 mm or more.
For seamless steel pipes up to 20mm thick, it is recommended to cut off the chamfers during the manufacturing process for ease of welding work.

GOST 8734-75 defines what range of cold-formed round steel pipes can be made. Their measured length varies between 4.5-9 meters, and their unmeasured length can be 1.5-11.5 meters. They are divided according to wall thickness and diameter:
- for extra-thin-walled ones - 0.3...0.5 mm with a diameter of 5-40 mm; 0.3...1.0mm with a diameter of 42-170mm; 0.3...4mm with a diameter of 180-250mm;
- for thin-walled ones - 0.6...1.5 mm with a diameter of 5-40 mm; 1.2…3.2 mm with a diameter of 42-170mm; 4.5...24mm with a diameter of 180-250mm;
- for thick-walled ones - 1.6...1.8 mm with a diameter of 5-40 mm; 3.5...7mm with a diameter of 42-170mm
- for extra-thick-walled ones - 2.0...24 mm with a diameter of 5-40 mm; 7.5…24mm with a diameter of 42-170mm
GOST 8733-74 regulates technical requirements for cold- and heat-deformed pipes. In particular, this applies to the material of manufacture.
The standard describes the same characteristics as GOST 8731-74, relating to seamless pipes, as well as acceptance and testing rules.
The range of steel pipes with a spiral seam is specified in GOST 8696-74. The standards apply to general purpose pipes and do not apply to oil pipelines or main gas pipelines. Their outer diameter is in the range of 159-2520mm, and the wall thickness is 3.5...25mm.
Spiral welded pipes are manufactured in lengths of 10 and 12 meters, but standards allow, in extreme cases, the production of short products of at least 6 meters. GOST also defines acceptable indicators:
- deviations;
- edge offsets;
- ovality;
- curvature.
The same document provides technical characteristics of the products.

Electric welded pipes with straight seam
The range of steel pipes of this type is presented in GOST 10704-91. Unmeasured products are produced in lengths of 2...5 meters. Measuring pipes can have dimensions of 5...12 meters. Moreover, their diameter is 10-1420mm with a wall thickness of 1.0...32mm. Deviations and tolerances are discussed in the document separately and in sufficient detail.
Technical characteristics of longitudinally welded steel pipes are presented in two regulatory documents:
- GOST 10705-80;
- GOST 10706-76.

They define:
- mechanical properties of metal;
- the presence of seams and the correctness of their location;
- maximum deviations;
- presence of defects;
- process and types of tests;
- acceptance requirements.
Marking of steel pipes
Each steel pipe is marked taking into account the requirements of GOST 10692-80. It emphasizes that products with a diameter of more than 159 mm are subjected to this procedure. In this case, the wall thickness should not be less than 3.5 mm. Marking is done in several ways:
- rubber stamp;
- electric pencil;
- electrograph;
- branding;
- indelible paint by hand.
Smaller pipe diameters are marked with labels, especially if the products are supplied in bags.
The label must indicate:
- steel grade;
- Name of product;
- pipe size;
- manufacturer's trademark.
In addition, seamless pipes are marked with the wall thickness and batch number.
Packaging and transportation
Products with a diameter of up to 159 mm are bundled into bags or tightly packed into wooden containers or boxes. The tying is done with wire in at least three places. Pipes over 159 mm are bundled exclusively in transport packages.
It should be noted that packing wire must not be used for lashing. For this purpose, special clamps must be provided.
It is allowed to move round steel pipes to the site by any type of long cargo transport. During storage, stacks are separated by spacers.
The exceptionally widespread use of round pipelines is explained by its main feature: with a minimum external surface area, the product has a maximum internal volume. It has not yet been possible to come up with something more perfect for moving liquid and gas products.
Round pipe: varieties
With minimal differences in the composition of the feedstock, steel water pipelines differ noticeably in quality. The reason for this is the manufacturing method. It also determines the application of the product.
Electric welded pipeline
Of all types of rolled metal, it has the lowest strength characteristics. But at the same time, these qualities themselves are so high in steel products that the vast majority of water and gas pipelines are constructed from electric welded options.
The manufacturing method includes cutting a strip - tape, rolling it into a blank and welding along the seam. Depending on the location of the seam, round steel pipes are divided into 2 types.
- A product with a straight longitudinal seam - regulated by GOST 10704-91, used for pressure and non-pressure supply systems of all types. The seam is considered its weak point. Pipelines are produced with diameters from 10 to 1420 mm and wall thicknesses from 1 to 32 mm.

This is the most popular type of rolled metal; its range includes the largest number of standard sizes.
- Products with a spiral seam - in this case, the tape is rolled in a spiral, and, accordingly, welded in a spiral. The strength characteristics of this option are much higher, and the cost is noticeably lower than that of a solid-rolled pipeline. The range of round pipes with a spiral seam includes products of large diameter - from 150 to 2520 mm with wall thicknesses from 3.5 to 25 mm. In the photo you can see samples.
"Hot" rental
This type of product belongs to the category of seamless pipeline and is highly resistant to internal and external pressure.
The blank here is a solid metal rod. It is pulled through a piercing mill, where it turns into a hollow cylinder. Forming is accompanied by heating. The hot billet is fed to the rollers, where it is stretched and compressed to the specified dimensions.
In this case there is no seam. The product is more resistant to corrosion.
GOST for round pipes - 8732-78, regulates the dimensions and chemical composition products. The range includes products with diameters from 29 to 550 mm and wall thicknesses from 2.5 to 75 mm.

Cold-formed pipes
The manufacturing process differs little from hot rolled forming. However, all the described actions are performed without heating. But since cold deformation contributes to the emergence of stress on the surface of products, after molding the finished pipeline undergoes heat treatment. This method gives products unusually high strength and accuracy. For aircraft and instrument making, for example, only cold-rolled products are used.

The products are regulated by GOST 8734-75. The range of round steel pipes includes products with a diameter from 5 to 250 mm and wall thickness from 0.3 to 24 mm.
Additional items
When installing any system, in addition to the main elements, additional ones are required. These details may be absolutely necessary or, conversely, optional, but their use makes installation easier and gives a more aesthetic appearance.

Plugs for round pipes can be divided into decorative and functional.
- The first include metal elements made in the form of balls or even figures. They protect the pipeline from moisture or debris getting inside. Their typical use is as fence caps. Polymer and rubber ones are much less aesthetically pleasing: their role is reduced only to protection.
- Functional ones are designed to ensure the operation of the system. During partial dismantling or repair, a plug is installed in place of the cut off branch. In emergency situations, when the main line breaks, the consequences of the rush are minimized in this way. Several types of plugs are used.
- Threaded - the thread can be internal or external, the plug itself is round faceted or grooved and even quite decorative. With its help, water pipelines no larger than 50 mm in size are suppressed.
- Flange is a flange without holes, secured with bolts with an appropriate gasket to ensure tightness. Used on products with a diameter of more than 50 mm.
- Rubber pneumatic plug – used in emergency situations.

Steel pipes are widely used in a wide variety of industries. They are used in mechanical engineering, the oil and gas industry, public utilities, etc. There are several types of steel. They can differ in the manufacturing method, size and type of material used for production. Steel pipe range different types determined by GOSTs.
Seamless products
Basically, all modern steel pipes are divided into two large groups: hot-rolled and welded. The first type is more expensive. Therefore, such products are used less often than welded ones. The range of steel is determined by GOST 8732-78. The relationship between the size of such pipes and their weight is given in special tables. The parameters may, for example, be as follows.
Size | Weight 1 m |
The range of electric-welded and furnace-welded steel pipes will be discussed below. Their parameters are also precisely determined by GOSTs.

How are seamless pipes made?
Products of this variety are produced from steel grades 35 and 45 on a continuous mill. In this case, so-called black blanks are used. The latter are stitched on a rolling mill and then sent to a circular saw to trim the end of the pipe. Then the finished product is sent to the cross-section mill for straightening and reducing the ovality of the section.
Welded pipes: reasons for popularity
Products of this type, as already mentioned, are more popular than seamless ones. Such pipes have been used in the national economy for quite some time. However, in last years their popularity has increased significantly. This is primarily due to the development of new, more advanced welding methods, which make it possible to obtain the most reliable and durable products. So, for example, in 1941, only 38.8% of welded pipes were produced. The rest was seamless. At the same time, the share of electric welded ones was only 0.8%. By 1965, these figures had increased to 50% and 35%, respectively.
Scope of use of welded pipes
Today such products are used everywhere. Most often they are used for laying various kinds of pipelines intended for pumping oil, gas, water, etc. Also, this type of pipe is usually used in public utilities. In this case, they are used for laying water pipes and sewer systems. Welded pipes are also used for assembling overhead gas pipelines, drainage systems etc.
Mechanical engineering is another area that uses welded pipes. They are also used for the manufacture of various kinds of architectural elements: canopies over entrances, awnings, children's swings, horizontal bars, etc. agriculture Irrigation systems are collected using them.

Main types of welded pipes
Products of this type can differ in:

From the article we will learn how, according to what regulatory documents and why steel pipes are produced.
Pipe classification
How are the pipes different?
- Linear dimensions. The length, diameter and wall thickness of the pipe can be measured with simple instruments; The assortment can be viewed in the corresponding standard.
Corresponding to what? The method by which the pipe was produced. Hence the next point. - Production method. There are welded spiral and straight-seam pipes; seamless hot-deformed and seamless cold-rolled;
- Presence of anti-corrosion coating. This is usually a layer of zinc applied to the inner and outer surfaces of the pipe.
Standards
According to which GOST round steel pipes can be produced?
Electric welded pipes
According to GOST 10704 91, electric-welded steel pipes are produced straight-seam.
What else does the standard say?
- Pipes can be manufactured in unmeasured lengths (from 2 meters for a diameter of up to 30 mm, from 3 meters for a diameter of 30-70 mm, from 4 meters for a diameter of 70-152 mm and from 5 meters for pipes with a diameter of over 152 millimeters);
- It is possible to produce pipes of measured length (5-9 meters in the diameter range up to 70 mm, 6-9 meters in the diameter range from 70 to 219 mm and 10-12 meters in the diameter range from 219 to 426 mm). Pipes with a diameter of over 426 mm are produced exclusively in unmeasured sizes;
- Pipes can also be produced with lengths that are multiples of the measured length. In this case, the multiple size must be at least 250 mm, and the allowance for each cut must be 5 millimeters (unless other parameters are agreed upon with the customer);
- Minor deviations from the specified diameter are acceptable; Tolerances can be seen in the corresponding table in the appendix.
A complete list of sizes that steel pipes GOST 10704 91 can have can also be found in the appendix to the article.

Please note: this GOST does not apply to spiral-welded steel pipes; their range is indicated, for example, in GOST 20295-85 and GOST 8696-74.
Hot-formed seamless pipes
Hot-deformed pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 8732 - 78. The full range can be found in the appendix to the article.
In addition to diameter, specific gravity and wall thickness, GOST for hot-formed steel pipes says the following:
- Pipes can be produced in unmeasured lengths from 4 to 12.5 meters or in measured lengths within the same limits;
- It is possible to produce pipes with a length that is a multiple of the measured length, with an allowance for each cut equal to five millimeters;
- Maximum length deviations should not exceed +10 millimeters for pipes with a length of up to 6 meters and +15 for pipes with a length of 6 meters or more or a diameter of 152 millimeters;
- The maximum deviations of the diameter and wall thickness of the pipe are regulated by tables, which can again be found in the appendix;
- Neither the difference in wall thickness nor the ovality of the pipes should take them beyond the maximum deviations in diameter or wall thickness;
- The curvature of any arbitrary section of the pipe is limited to 1.5 mm/1 meter of length for pipes with a wall thickness of less than 20 millimeters, 2 millimeters for walls with a thickness of 20-30 millimeters and 4 mm for walls with a thickness of 30 mm or more.

Cold-formed seamless pipes
Their production is subject to the GOST 8734-75 standard.
What is useful to know about these pipes?
- They are divided into extra-thin-walled, thin-walled, thick-walled and extra-thick-walled. The criterion is the ratio of the outer diameter of the pipe to the thickness of its walls; For thin-walled and extra-thin-walled pipes, the absolute value of the wall thickness is also important.
Extra-thin-walled pipes have a diameter-to-wall ratio of more than 40 or a wall thinner than 0.5 mm with a diameter of up to 20 mm; thin-walled - from 12.5 to 40 or a wall of 1.5 millimeters with a diameter of up to 20 mm; thick-walled pipes have a diameter-to-wall ratio in the range of 6-12.5; extra-thick-walled - less than six.
- Pipes can be produced in measured lengths in the range of 4.5 - 9 meters with a maximum length deviation of +10 millimeters or in unmeasured lengths from 1.5 meters to 11.5;
- It is also possible to produce pipes with a length that is a multiple of the measured length. Pipes can have a length from 1.5 to 9 meters with an allowance for each cut of 5 millimeters.
- According to GOST, cold-formed steel pipes may have maximum deviations from the specified dimensions specified in the appendix.

Thick-walled pipes are, in any case, seamless pipes
Water and gas pipes
Water and gas pipe steel GOST 3262 75 is separated into a separate standard, although from a production point of view it is electric welded. However, intended for water and gas pipelines (it is given in the appendix).
Besides:
- Pipes (measured and unmeasured lengths) are produced in the range from 4 to 12 meters;
- They can be supplied either without thread or with cut or rolled pipe threads;
- When supplying a pipe with rolled threads, it is allowed to reduce the internal diameter of the pipe by up to 10 percent along the entire length of the thread;
- The curvature of the pipe should not exceed 2 mm/meter of length for a nominal bore of up to 20 millimeters and 1.5 mm for a nominal bore of over 20 mm.
Important: there is no separate standard or range for galvanized pipes.
However, according to this GOST, galvanized steel pipes are manufactured.
In addition, galvanizing is provided for straight-seam electric-welded pipes.
However, nothing prevents you from galvanizing absolutely any pipe, no matter what technology it was produced using.

Production
Welded pipes
The raw material for any welded pipe is a flat steel sheet; however, most often it is delivered from the metallurgical plant rolled into a roll.
- The sheet is cut into narrow longitudinal strips;
- The strips are welded into an endless narrow strip;
- The tape is rolled by rollers into a round piece with an open seam;
- After which the seam is boiled;
- The pipe is calibrated in the next rolls;
- The seam is tested for leaks. Eddy current flaw detection is most often used, but ultrasonic flaw detectors are also available;
- The pipe is cut into pieces of the required length and sent to the warehouse.
Important: pipes welded with TIG - a tungsten electrode in an inert gas environment - are considered the most durable.
However, HF-welded pipes made using induction welding with high frequency currents are noticeably cheaper. The reason is the welding speed is approximately 20 times higher compared to TIG.
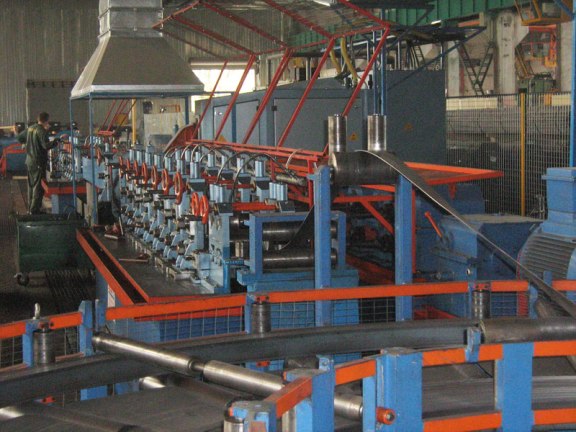

At one end of the line you can see a narrow steel sheet. On the other are finished welded pipes. The presence of a person is only necessary for control
Seamless pipes
Production of hot-deformed pipe in general outline looks like that:
- A monolithic cylindrical blank - a rod - is heated in a furnace to a temperature above the recrystallization point of steel; in this case the metal becomes plastic;
- On a piercing mill, the workpiece is transformed into a hollow cylinder. Externally, it is already a pipe, but rather irregularly shaped and with dimensions far from the target;
- After which the actual rolling of the workpiece in rollers begins- its hot deformation. The future pipe acquires the required diameter and wall thickness, then cools and calibrates;
- The finished pipe is cut into pieces of the required length and stored.

The production of cold-deformed seamless pipe differs in only two aspects:
- After the piercing mill, the workpiece (it is called a sleeve) is cooled with water and all further operations are carried out cold;
- Before final calibration, a mandatory production step is annealing - heating to the recrystallization temperature and cooling. In this case, the internal stresses accumulated during deformation leave the metal; in addition, it becomes more viscous.
Please note: thick-walled steel pipes are produced seamlessly.
The walls of a hot-deformed pipe can reach a thickness of 75 millimeters, and of a cold-deformed pipe - 24 mm.
If necessary, it is possible to produce extra-thick-walled pipes outside the standards. It is carried out by drilling a calibrated workpiece.
Galvanizing
If it is necessary to provide a pipe with an anti-corrosion coating, so-called galvanizing is used.
There are quite a few ways to coat a pipe with a layer of zinc; on an industrial scale, however, only two methods are used in the production of pipes:
- Hot galvanizing. The pipe is immersed in molten zinc. It has a melting point much lower than steel; after it cools, a thin, uniform film forms on the surface of the pipe;
- Galvanic galvanizing. In an acid solution environment, a significant potential difference is created between the zinc electrode and the pipe; the electrode dissolves and zinc settles on the surface of the pipe.
The main disadvantage of the method is the need to dispose of toxic electrolyte containing zinc salts.





