GOST 23009-78
GOST 23858-79
GOST 26433.0-85
GOST 26433.1-89
GOST 26633-91
5. EDITION (April 2004) with Amendment (IUS 3-91)
This standard applies to concrete and reinforced concrete structures made from heavy concrete and intended for the construction of round wells for underground pipelines of sewer, water and gas networks.
The structures are used in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings of a particular pipeline.
1.TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. Structures should be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and technological documentation approved by the manufacturer, according to working drawings of series 3.003.1-1/87 and 3.900.1-14.
(Amendment)
1.2. Main parameters and dimensions
1.2.1. Designs are divided into types:
KFK - working chamber of a well for household (fecal) sewerage;
KDK - the same, intra-block networks;
KLK - the same storm sewer;
KLV - the same, storm sewer, water intake;
KVG - the same, water and gas networks;
KS - wall ring of the working chamber or well neck;
KO - support ring;
PO - base plate;
PD - road slab;
PN - bottom plate;
PP - floor slab.
1.2.2. The shape and main dimensions of the well structures must correspond to those specified in the application.
In cases provided for by the working drawings of a particular pipeline, structures may have embedded products, as well as niche openings and cutouts that differ in location and size from those adopted in the working drawings of the 3.003.1-1/87 and 3.900.1-14 series.
(Amendment)
1.2.3. Consumption rates for concrete and steel on well structures must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings for these structures.
1.2.4. Floor slabs are divided into groups according to bearing capacity depending on the depth of the slabs and the load on the backfill soil surface in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings.
1.2.5. Structures are designated by marks in accordance with the requirements of GOST 23009. The design mark consists of alphanumeric groups separated by hyphens.
In the first group, the standard size of the structure is given. The letters indicate the type of construction, the numbers before the letters indicate the serial number of the standard size (if necessary), the numbers after the letters (rounded to the nearest whole number) indicate (in decimeters):
For working chambers and support rings - their internal diameter;
For bottom and floor slabs - the internal diameter of the wells;
For wall rings - their internal diameter and height;
For base and road slabs - hole diameter.
In the second group, for floor slabs, the group according to load-bearing capacity is indicated.
In the third group for floor slabs or in the second group for other structures indicate:
For structures operated under exposure conditions aggressive environment, - indicator of concrete permeability, denoted by a capital letter: N - normal permeability, P - reduced permeability, O - especially low permeability;
Additional design characteristics (presence of embedded products, holes, niches and cutouts), indicated in the brand by Arabic numbers or letters.
Example symbol(brand) of a working chamber type KFK with an internal diameter of 1250 mm:
KFK13
The same, wall ring with an internal diameter of 2500 mm, height of 1190 mm:
KS25.12
The same, a floor slab covering a well, with an internal diameter of 2000 mm, with a hole with a diameter of 1000 mm (standard size 2PP20), second group in terms of load-bearing capacity:
2PP20-2
Note. It is allowed to accept the designations of construction grades in accordance with the working drawings for these structures until they are revised.
1.3. Characteristics
1.3.1. Designs must meet the requirements of GOST 13015 *:
________________
GOST 13015-2012, hereinafter in the text
- strength, rigidity and crack resistance; in this case, there are no requirements for testing structures by loading;
According to the actual strength of concrete (at design age and tempering age);
Frost resistance and water resistance of concrete;
According to the thickness of the protective layer of concrete to the reinforcement;
To steel grades for reinforcing and embedded products, including for mounting hinges;
For corrosion protection.
1.3.2. Structures should be made of heavy concrete in accordance with GOST 26633 * classes or grades of compressive strength specified in the working drawings of the structures.
________________
* In the territory Russian Federation the document is not valid. GOST 26633-2012 is valid - Note from the database manufacturer.
1.3.3. The normalized tempering strength of concrete is taken equal to 70% of the class or grade of concrete in terms of compressive strength.
The specified standardized tempering strength of concrete can be reduced or increased in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.
1.3.4. The water absorption of concrete structures must correspond to that established in the design documentation for a specific structure or specified when ordering structures.
1.3.5. For the reinforcement of structures, the following types and classes of reinforcing steel are used:
Thermomechanically strengthened rod of classes At-IIIC and At-IVC according to GOST 10884 *;
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 10884-94 is in force. - Database manufacturer's note.
Hot rolled rod classes A-I, A-II and A-III according to GOST 5781;
Reinforcing wire of class BP-I according to GOST 6727.
1.3.6. The shape and dimensions of reinforcement and embedded products and their position in structures must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings.
1.3.7. Welded reinforcement and embedded products must meet the requirements of GOST 10922 *.
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 10922-2012 is valid
1.3.8. In cases provided for by the working drawings of wells, running brackets must be installed inside the wall rings, located along the height of the ring every 300 mm and protruding from the inner surface of the rings by 120 mm.
Running brackets should be made of reinforcing steel of classes A-I and A-II according to GOST 5781.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, wall rings may be manufactured without running brackets, provided they are installed on the construction site.
1.3.9. The running brackets must be protected from corrosion in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings of the wells.
1.3.10. The values of actual deviations of the geometric parameters of structures should not exceed the limits specified in Table 1.
Table 1
In millimeters
Name of deviation of geometric parameter | Name of geometric parameter | Prev. off |
Deviation from linear size | Height (thickness) of the structure: | |
St. 1000 to 1600 | ||
Inner diameter of working chambers, wall and support rings, outer diameter of floor slabs and bottoms, diameter of manholes and holes for pipelines: | ||
St. 1000 to 1600 | ||
Length and width of base and road slabs | ||
Position of holes and cutouts | ||
Deviation from flatness of the bottom surface of floor slabs (when measured from a conventional plane passing through three points) | Outer diameter of floor slabs: | |
St. 1000 to 2500 | ||
1.3.11. Requirements for surface quality and appearance structures - according to GOST 13015. In this case, the quality of structural surfaces (with the exception of joint surfaces) must meet the requirements established for category A6. The surfaces forming a joint between structures that are monolied at the construction site are subject to the requirements established for category A7.
It is allowed, by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, to apply to all surfaces of working chambers, wall and support rings the requirements established for category A7.
1.4. Completeness
1.4.1. Working chambers are supplied to the consumer complete with floor slabs.
1.5. Marking
1.5.1. Marking of structures is in accordance with GOST 13015. Markings are applied to the outer side surface of the structures.
2. ACCEPTANCE
2.1. Acceptance of structures is in accordance with GOST 13015 and this standard. In this case, the designs accept:
Based on the results of periodic tests - in terms of frost resistance, water resistance and water absorption of concrete;
Based on the results of acceptance tests - in terms of concrete strength (class or grade of compressive strength and tempering strength), compliance of reinforcement and embedded products with working drawings, strength of welded joints, thickness of the protective layer of concrete to the reinforcement, accuracy of geometric parameters, quality of the concrete surface.
Acceptance of structures for strength, rigidity and crack resistance is carried out according to a set of standardized and design indicators in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.
2.2. Acceptance of structures in terms of accuracy of geometric parameters, thickness of the protective layer of concrete to reinforcement, and surface quality is carried out based on the results of random inspection.
2.3. The document on the quality of structures in accordance with GOST 13015 must additionally indicate concrete grades for frost resistance and water resistance of concrete (if these indicators are specified in the order for the manufacture of structures).
3. CONTROL METHODS
3.1. The strength of concrete structures is determined according to GOST 10180 * on a series of samples made from a concrete mixture of the working composition and stored under the conditions established by GOST 18105 **.
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 10180-2012 is valid;
** The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 18105-2010 is in force. - Database manufacturer's note.
When testing by non-destructive methods, the actual tempering compressive strength of concrete should be determined ultrasonic method according to GOST 17624 * or with mechanical devices according to GOST 22690, as well as other methods provided for by the standards for concrete testing methods.
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 17624-2012 is valid. - Database manufacturer's note.
3.2. The frost resistance of concrete is determined according to GOST 10060.0 - GOST 10060.2 * on a series of samples made from a concrete mixture of the working composition.
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 10060-2012 is in force. - Database manufacturer's note.
3.3. The water resistance of concrete is determined according to GOST 12730.0 and GOST 12730.5.
3.4. Water absorption of concrete is determined according to GOST 12730.0 and GOST 12730.3.
3.5. Welded reinforcement and embedded products are controlled according to GOST 10922 and GOST 23858.
3.6. The dimensions and position of reinforcement and embedded products, as well as the thickness of the protective layer of concrete before the reinforcement are determined according to GOST 17625 or GOST 22904.
3.7. Dimensions, deviations from the flatness of structures, the width of the opening of surface technological cracks, the dimensions of cavities, sagging and edges of concrete structures are checked by the methods established by GOST 26433.0 and GOST 26433.1.
3.8. The dimensions of the structures are checked as follows:
The outer and inner diameters of the working chambers, wall and support rings, floor slabs and bottoms are measured along two mutually perpendicular diameters;
The thickness of the walls of the working chambers and wall rings is measured in four places along two mutually perpendicular diameters;
The height of the working chambers and wall rings is measured along four generatrices in two diametrically opposite sections;
The thickness of the slabs and support ring is measured in four places in two mutually perpendicular directions.
4. TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
4.1. Transportation and storage of structures - in accordance with GOST 13015 and this standard.
4.2. The structures are transported and stored in working position.
4.3. Structures should be stored:
Working chambers - in one row;
Wall rings - in two rows in height in accordance with the diagram shown in Figure 1;
- support rings and plates - no more than six rows in height on spacers (linings) in accordance with the diagram shown in Figure 2.
Damn.1. Scheme for storing wall rings of wells
Scheme for storing wall rings of wells
Damn.1
Damn.2. Scheme for storing floor slabs and well bottoms
Scheme for storing floor slabs and well bottoms
1 - gaskets (linings); 2 - mounting loops.
Other storage schemes are permitted, provided the safety of structures is ensured and safety requirements are met.
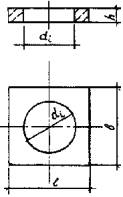
APPENDIX (required). SHAPE AND MAIN DIMENSIONS OF WELL STRUCTURES
APPLICATION
Mandatory
table 2
Name and form | Design size | Dimensions, mm |
|||
Working chamber types KDK and KFK | |||||
Working chamber types KLV and KLK | |||||
Working chamber type KVG | |||||
Wall ring of the working chamber or well neck | |||||
Support ring | |||||
Base plate | |||||
Road slab | |||||
Bottom plate | |||||
Floor slab for water intake wells | |||||
Floor slab for wells of sewer, water and gas networks | |||||
1 - niche (only in slabs of standard sizes 3PP20 and 2PP25) | |||||
Notes: 1. The internal surfaces of working chambers and wall rings can have a technological slope of no more than 1.5%. In this case, the internal diameter and wall thickness in the middle of the height of the structure must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings of the structures.
2. The side faces of slabs produced in one-piece molds may have a technological slope of no more than 10%.
3. It is allowed to increase the height of the wall rings by multiples of 300 mm up to a height of 1790 mm.
4. It is allowed to produce floor slabs of standard sizes 1PP20 and 2PP20 with a thickness of 150 mm on existing equipment until 01/01/93.
Electronic document text
prepared by Kodeks JSC and verified against:
official publication
M.: IPK Standards Publishing House, 2004
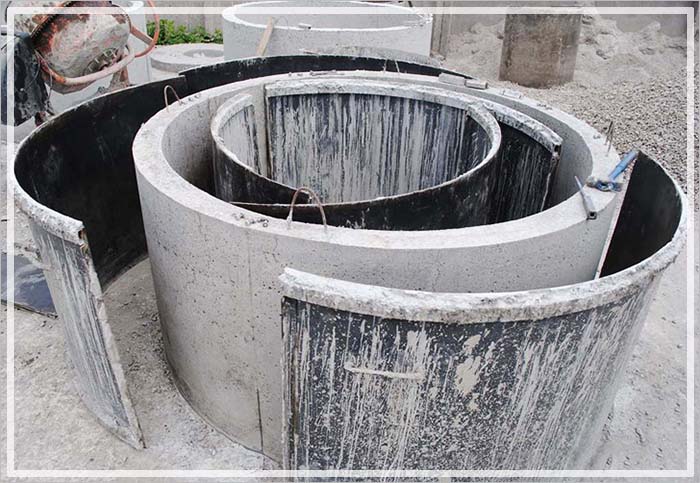
Like any industrial product, reinforced concrete rings for wells must comply with state standards or technical specifications. If it does not comply with them, the product loses the properties declared by the certificate. This ring cannot be installed in a well.
Normative standard
The parameters of reinforced concrete well wall rings, including additional ones (another name is additional ones), and neck rings are regulated by GOST 8020-90 “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures for sewer, water supply and gas pipeline wells. Specifications» edition dated 04.2004 with amendments to IUS 3-91. Date of introduction: 07/01/1990. Valid instead of GOST 8020-80.
Adjustable ring parameters
This standard applies to all concrete and reinforced concrete rings intended for the construction of round reinforced concrete wells, underground pipelines and various networks. It regulates the following indicators:
- Basic parameters and dimensions, markings of rings (additional rings are a subtype of wall rings);
- Characteristics of materials: concrete, reinforcement, embedded parts, ring running brackets;
- Requirements for the appearance of rings and the quality of surfaces;
- The magnitude of deviations of the geometric parameters of the rings;
- Completeness of reinforced concrete products;
- Ring markings;
- Acceptance of reinforced concrete products;
- Control methods:
- strength, frost resistance, water resistance, water absorption of concrete;
- welded embedded parts and reinforcement products;
- ring sizes, sizes of chips and inhomogeneities.
- Measurement of concrete products;
- Transporting rings.
Schemes for storing rings (wall, additional and neck), bottoms and slabs of wells are also given. The mandatory annex establishes the shapes and main dimensions of the structures of wall reinforced concrete rings (including additional ones) and well neck rings:
- internal diameter;
- external diameter;
- height.
Other regulatory documents

| GOST 5781-82 | Hot rolled steel for reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures. |
| GOST 6727-80* | Cold-drawn low-carbon steel wire for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures. |
| GOST 10060.0-95 | Concrete. Methods for determining frost resistance. |
| GOST 10060.1-95 | Concrete. Basic method for determining frost resistance. |
| GOST 10060.2-95 | Concrete. Accelerated methods for determining frost resistance during multivariate freezing and thawing. |
| GOST 10180-90 | Concrete. Methods for determining strength using control samples. |
| GOST 10884-94 | Reinforcing steel thermomechanically strengthened for reinforced concrete structures. |
| GOST 10922-90 | Welded reinforcement and embedded products, welded connections of reinforcement and embedded products of reinforced concrete structures. General technical conditions. |
| GOST 12730.0-78 | Concrete. General requirements to methods for determining density, humidity, water absorption, porosity and water resistance. |
| GOST 12730.3-78 | Concrete. Method for determining water absorption. |
| GOST 12730.5-84 | Concrete. Methods for determining water resistance. |
| GOST 13015-2003 | Reinforced concrete and concrete products for construction. Are common technical requirements. Rules for acceptance, marking, transportation and storage. |
| GOST 17624-87 | Concrete. Ultrasonic method for determining strength. |
| GOST 17625-83 | Reinforced concrete structures and products. Radiation method for determining the thickness of the protective layer of concrete, dimensions and location of fittings. |
| GOST 18105-86 | Concrete. Strength control rules. |
| GOST 22690-88 | Concrete. Determination of strength by mechanical methods of non-destructive testing. |
| GOST 22904-93 | Reinforced concrete structures. Magnetic method for determining the thickness of the protective layer of concrete and the location of reinforcement. |
| GOST 23009-78 | Prefabricated concrete and reinforced concrete structures and products. Symbols (brands). |
| GOST 23858-79 | Concrete and reinforced concrete products. Materials testing methods. |
| GOST 26433.0-85 | |
| GOST 26433.1-89 | System for ensuring the accuracy of geometric parameters in construction. Rules for performing measurements. |
| GOST 26633-91 | Concrete is heavy and fine-grained. Technical conditions. |
What does non-compliance with regulations entail?

The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for administrative liability of manufacturers for non-compliance with the above regulatory documents in the manufacture of reinforced concrete rings. Namely: Article 19.19 “Violation of the requirements of technical regulations...”, paragraphs 1-3.
Violation of technical standards in the production of rings leads to a decrease in their quality. Thus, the use of concrete other than that regulated by GOST 8020-90 will result in a decrease in the strength of the ring, its frost resistance, and water resistance. Failure to comply with the technology can lead to the formation of air voids inside the ring, chips, and exposed reinforcement, which will also affect the properties of the ring. Such products must be rejected by the manufacturer.
The use of reinforced concrete rings that do not meet current standards leads to a decrease in the service life of the well and an early forced replacement of the rings.
STATE STANDARD OF THE USSR UNION
CONCRETE STRUCTURES
AND REINFORCED CONCRETE FOR WELLS
SEWER, WATER
AND GAS PIPELINE NETWORKS
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
GOST 8020-90
STATE CONSTRUCTION COMMITTEE OF THE USSR
Moscow
STATE STANDARD OF THE USSR UNION
Date of introduction 01.07.90
This standard applies to concrete and reinforced concrete structures made from heavy concrete and intended for the construction of round wells for underground pipelines of sewer, water and gas networks.
The structures are used in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings of a particular pipeline.
1. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1 . Structures should be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and technological documentation approved by the manufacturer, according to working drawings of series 3.003.1-1/87 and 3.900.1-14.
(Amendment)
1.2 . Main parameters and dimensions
1.2.1 . Designs are divided into types:
KFK - working chamber of a well for household (fecal) sewerage;
KDK - the same, intra-block networks;
KLK - the same, storm sewer;
KLV - the same, storm sewer, water intake;
KVG - the same, water and gas networks;
KS - wall ring of the working chamber or well neck;
KO - support ring;
PO - base plate;
PD - road slab;
PN - bottom plate;
PP - floor slab.
1.2.2 . The shape and main dimensions of well structures must correspond to those specified in .
In cases provided for by the working drawings of a particular pipeline, structures may have embedded products, as well as niche openings and cutouts that differ in location and size from those adopted in the working drawings of the 3.003.1-1/87 and 3.900.1-14 series.
(Amendment)
1.2.3 . Consumption rates for concrete and steel on well structures must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings for these structures.
1.2.4 . Floor slabs are divided into groups according to their load-bearing capacity, depending on the depth of the slabs and the load on the surface of the backfill soil according to the instructions of the working drawings.
1.2.5 . Structures are marked with marks in accordance with the requirements GOST 23009 . The design mark consists of alphanumeric groups separated by hyphens.
In the first group, the standard size of the structure is given. The letters indicate the type of construction, the numbers before the letters indicate the serial number of the standard size (if necessary), the numbers after the letters (rounded to the nearest whole number) indicate (in decimeters):
for working chambers and support rings - their internal diameter;
»bottom and floor slabs - internal diameter of wells;
»wall rings - their internal diameter and height;
»base and road slabs - hole diameter.
In the second group, for floor slabs, the group according to load-bearing capacity is indicated.
In the third group for floor slabs or in the second group for other structures indicate:
for structures operated under conditions of exposure to an aggressive environment, the concrete permeability indicator, denoted by a capital letter: N - normal permeability, P - reduced permeability, O - especially low permeability;
additional design characteristics (presence of embedded products, holes, niches and cutouts), indicated in the brand by Arabic numbers or letters.
Example of a symbol(brand) of a working chamber type KFK with an internal diameter of 1250 mm:
KFK13
The same, wall ring with an internal diameter of 2500 mm, height of 1190 mm:
KS25.12
The same, a floor slab covering a well, with an internal diameter of 2000 mm, with a hole with a diameter of 1000 mm (standard size 2PP20), second group in terms of load-bearing capacity:
2 PP20-2
Note: It is allowed to accept the designations of construction grades in accordance with the working drawings for these structures until they are revised.
1.3 . Characteristics
1.3.1. Designs must meet the requirements of GOST 13015.0:
in terms of strength, rigidity and crack resistance; in this case, there are no requirements for testing structures by loading;
according to the actual strength of concrete (at design age and tempering age);
on frost resistance and water resistance of concrete;
along the thickness of the protective layer of concrete to the reinforcement;
to steel grades for reinforcing and embedded products, including for mounting hinges;
for corrosion protection.
1.3.2 . Structures should be made of heavy concrete according to GOST 26633 classes or grades of compressive strength specified in the working drawings of the structures.
1.3.3 . The normalized tempering strength of concrete is taken equal to 70% of the class or grade of concrete in terms of compressive strength.
The specified standardized tempering strength of concrete can be reduced or increased in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.0.
1.3.4 . The water absorption of concrete structures must correspond to that established in the design documentation for a specific structure or specified when ordering structures.
1.3.5 . For the reinforcement of structures, the following types and classes of reinforcing steel are used:
thermomechanically strengthened rod class At- III C and At-IV C according to GOST 10884;
hot rolled rod class A- I, A-II and A-III according to GOST 5781;
reinforcing wire class VR- I according to GOST 6727.
1.3.6 . The shape and dimensions of reinforcement and embedded products and their position in structures must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings.
1.3.7 . Welded reinforcement and embedded products must meet the requirements GOST 10922.
1.3.8 . In cases provided for by the working drawings of wells, running brackets must be installed inside the wall rings, located along the height of the ring every 300 mm and protruding from the inner surface of the rings by 120 mm.
Running brackets should be made of reinforcing steel classes A- I and A-II according to GOST 5781.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, wall rings may be manufactured without running brackets, provided they are installed on the construction site.
1.3.9 . The running brackets must be protected from corrosion in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings of the wells.
1.3.10 . The values of actual deviations of the geometric parameters of structures should not exceed the limits specified in table. .
Table 1
mm
|
Name of geometric parameter |
Prev. off |
|
|
Deviation from linear size |
Height (thickness) of the structure: |
|
|
± 5 |
||
|
± 8 |
||
|
± 10 |
||
|
St. 1000 to 1600 |
± 12 |
|
|
± 15 |
||
|
± 20 |
||
|
Inner diameter of working chambers, wall and support rings, outer diameter of floor slabs and bottoms, diameter of manholes and holes for pipelines: |
||
|
± 6 |
||
|
St. 1000 to 1600 |
± 8 |
|
|
± 10 |
||
|
± 12 |
||
|
Length and width of base and road slabs |
± 10 |
|
|
Position of holes and cutouts |
||
|
Deviation from flatness of the bottom surface of floor slabs (when measured from a conventional plane passing through three points) |
Outer diameter of floor slabs: |
|
|
over 1000 to 2500 |
||
1.3.11. Requirements for the quality of surfaces and the appearance of structures are in accordance with GOST 13015.0. In this case, the quality of structural surfaces (with the exception of joint surfaces) must meet the requirements established for category A6. The surfaces forming a joint between structures that are monolied at the construction site are subject to the requirements established for category A7.
It is allowed, by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, to apply to all surfaces of working chambers, wall and support rings the requirements established for category A7.
1.4 . Completeness
1.4.1. Working chambers are supplied to the consumer complete with floor slabs.
1.5 . Marking
1.5.1 . Marking of structures - by GOST 13015.2 . Markings are applied to the outer side surface of the structures.
2. ACCEPTANCE
2.1 . Acceptance of structures - by GOST 13015.1 and this standard. In this case, the designs accept:
based on the results of periodic tests - in terms of frost resistance, water resistance and water absorption of concrete;
based on the results of acceptance tests - in terms of concrete strength (class or grade in terms of compressive strength and tempering strength), compliance of reinforcement and embedded products with working drawings, strength of welded joints, thickness of the protective layer of concrete to the reinforcement, accuracy of geometric parameters, quality of the concrete surface .
Acceptance of structures for strength, rigidity and crack resistance is carried out according to a set of standardized and design indicators in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.1.
2.2 . Acceptance of structures in terms of accuracy of geometric parameters, thickness of the protective layer of concrete to reinforcement, and surface quality is carried out based on the results of random inspection.
2.3 . In the document on the quality of structures according to GOST 13015.3 Additionally, concrete grades for frost resistance and water resistance of concrete should be given (if these indicators are specified in the order for the manufacture of structures).
3. CONTROL METHODS
3.1 . The strength of concrete structures is determined by GOST 10180 on a series of samples made from a concrete mixture of the working composition and stored under the conditions established GOST 18105.
When testing by non-destructive methods, the actual tempering compressive strength of concrete should be determined by the ultrasonic method in accordance with GOST 17624 or mechanical devices in accordance with GOST 22690, as well as other methods provided for in the standards for concrete testing methods.
3.2 . Frost resistance of concrete is determined by GOST 10060 on a series of samples made from a concrete mixture of the working composition.
3.3 . The water resistance of concrete is determined by GOST 12730.0 and GOST 12730.5.
3.4 . The water absorption of concrete is determined by GOST 12730.0 and GOST 12730.3.
3.5 . Welded reinforcement and embedded products are controlled according to GOST 10922 and GOST 23858.
3.6 . The dimensions and position of reinforcement and embedded products, as well as the thickness of the protective layer of concrete before the reinforcement are determined by GOST 17625 or GOST 22904.
3.7 . Dimensions, deviations from the flatness of structures, the opening width of surface technological cracks, the dimensions of cavities, sagging and edges of concrete structures are checked by methods established GOST 26433.0 and GOST 26433.1.
3.8 . The dimensions of the structures are checked as follows:
the outer and inner diameters of the working chambers, wall and support rings, floor slabs and bottoms are measured along two mutually perpendicular diameters;
the thickness of the walls of the working chambers and wall rings is measured in four places along two mutually perpendicular diameters;
the height of the working chambers and wall rings is measured along four generatrices in two diametrically opposite sections;
the thickness of the slabs and support ring is measured in four places in two mutually perpendicular directions.
4. TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
4.1 . Transportation and storage of structures - according to GOST 13015.4 and this standard.
4.2 . The structures are transported and stored in working position.
4.3 . Structures should be stored:
working chambers - in one row;
wall rings - in two rows in height in accordance with the diagram shown in Fig. ;
support rings and plates - no more than six rows in height on spacers (linings) in accordance with the diagram shown in Fig. .
Scheme for storing wall rings of wells
Crap. 1
Scheme for storing floor slabs and well bottoms
1 - gaskets (linings); 2 - mounting loops
Crap. 2
Other storage schemes are permitted, provided the safety of structures is ensured and safety requirements are met.
APPLICATION
Mandatory
SHAPE AND MAIN DIMENSIONS OF WELL STRUCTURES
Table 2
|
Name and shape of the structure |
Design size |
Dimensions, mm |
|||
|
l´ b or A |
|||||
|
Working chamber types KDK and KFK
|
|||||
|
Working chamber types KLV and KLK
|
|||||
|
Working chamber type KVG |
|||||
|
Wall ring of the working chamber or well neck
|
|||||
|
Support ring
|
|||||
|
Base plate
|
1700 ´ 1700 |
||||
|
Road slab
|
2500 ´ 1750 |
||||
|
2800 ´ 2000 |
|||||
|
Bottom plate
|
|||||
|
Floor slab for water intake wells
|
|||||
|
Floor slab for wells of sewer, water and gas networks
1 - niche (only in slabs of standard sizes 3PP20 and 2PP25) |
|||||