The most common American standard for steel flanges is ASME/ANSI B16.5 “Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings” NPS 1/2 to NPS 24.
This standard, like domestic GOSTs, contains descriptions of standard sizes, approximate masses and tolerances for DN ½″…24″ (NPS, in inches) and PN flanges of classes 150…2500 (Class, in psi).
ASME/ANSI steel flanges, their design and surface treatment
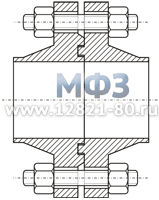
Welding Neck Flange: API, ANSI/ASME flanges
Figure 1. Collar flange.
Weld Neck Flange ASME/ANSI, API
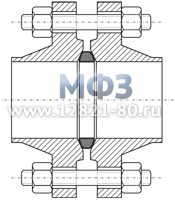
Flat welded steel flanges (Slip-on Flanges)

Figure 2. Flat flanges -
Slip On Flange ANSI/ASME
Slip-on flanges, also standardized in most pressure classes and DN sizes, are popular due to their simplicity and application. This forged flange fits onto the end of the pipe and is typically designed so that the flange extends beyond the end of the pipe to about 0.375" (9.5 mm).
Flat flanges are especially intensively used for low pressure pipelines: Class 150 (PN 20) or Class 300 (PN 50).
Threaded Flanges or Screwed Flanges

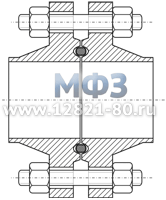
Figure 3. Threaded flange -
Threaded ANSI/ASME Flange
Threaded flanges (ASNE/ANSI, Threaded or Screwed Flanges) are attached to the pipe using threads, just like other fittings with threaded connection. After screwing onto the pipe, such a flange can be welded to it to strengthen the connection.
Although ASME threaded flanges are standardized by American codes for many pressure classes and nominal diameters, threaded flanges are used in exceptional cases of small diameters and low pressure classes.
Free flanges (Lap Joint Flanges, or Lapped Flanges, or Van Stone Flanges)
Loose flanges are used on frequently disassembled sections of pipelines.

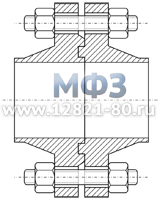
Figure 4. Loose flanges -
Lap Joint Flanges ASME/ANSI
Lap Joint Flanges are designed to tightly press the end weld ring or pipe collar. Lapped Flanges ASME/ANSI flanges can rotate freely around the pipe when not connected.
ASME/ANSI Lap Joint flanges can be used in all pressure classes and are available in a full range of sizes. The pressure is transmitted to the gasket via a flange and sealing surface welded ring.
Advantages of Lap Joint ANSI/ASME flanges during installation and disassembly
Flanges have the following special advantages during installation and dismantling:
- Free rotation around the pipe makes it easier to align mounting holes for mounting bolts or opposing flanges;
- the lack of contact of the flange with the working fluid in the pipe often allows the use of inexpensive carbon steel flanges with stainless pipes;
- loose flanges do not come into contact with the transported medium, therefore, it is possible to reuse ASME/ANSI flanges that have served even on pipelines that are highly susceptible to internal corrosion.
Socket Weld Flanges (ANSI/ASME Socket Weld Flanges)
|
Figure 5. Female flange - | ANSI/ASME Socket Weld Flanges are similar to flat flanges, but have a recess at the back of the flange formed by a small collar. During installation, the end of the pipe is inserted and welded into the flange socket. However, a socket flange connection is not as strong as a butt weld flange connection, so this type of flange is always limited to NPS 4 (DN 100) and smaller sizes and has lower pressure tolerances. The advantage of ANSI/ASME female flanges is ease of preparation and assembly flange connection. |
Blind Flanges ASME/ANSI
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Flanged Faces
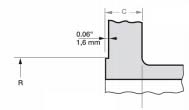
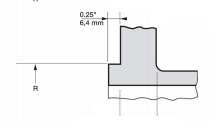
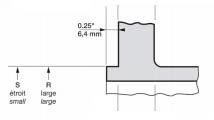
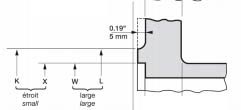
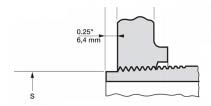
ANSI/ASME Class 150 (PN 20) flanges and Class 300 (PN 50) flanges of all types except loose flanges are typically provided with a 0.06" (1.6 mm) high lip seal (which is included in the thickness of the flange). ANSI flanges greater than High pressure valves are equipped with a 0.25" (6.4 mm) extension in addition to the existing flange thickness.
In this case, these types of flanges can be equipped with a variety of other sealing surfaces, such as tongue and groove, tongue and groove, etc.
Loose flanges are manufactured with a flat surface, since loose flanges do not have a sealing surface.
ASME/ANSI B 16.5 Class 150 (PN20) Forged Steel ASTM-105 Flanges
As an example, we present here the main characteristics of forged flanges ASME/ANSI B 16.5. The table rows with a white background show the characteristics of the flanges in the American measurement system (inches, pounds). Rows with a gray background give alternative values in SI units (millimeters, kilograms).
| NPS | Bolt holes | Collar diameter | Approximate weight (ANSI flange weight) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN | Number of holes | dia. bolt. resp. | dia. bolt. env. | nest depth | base | top | glad. rounded | ||||
| H | J | K | L | M | N | r | WN | SO, Threaded, SW | Blind | L.J. | |
| ½ | 4 | 0.62 | 2.38 | 0.38 | 1.19 | 0.84 | 0.12 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 15 | 4 | 16 | 60.3 | 10 | 30.2 | 21.4 | 3 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| ¾ | 4 | 0.62 | 2.75 | 0.44 | 1.50 | 1.05 | 0.12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 20 | 4 | 16 | 69.8 | 11 | 38.1 | 26.6 | 3 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 1 | 4 | 0.62 | 3.12 | 0.50 | 1.94 | 1.32 | 0.12 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 25 | 4 | 16 | 79.4 | 13 | 49.2 | 33.5 | 3 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 1¼ | 4 | 0.62 | 3.50 | 0.56 | 2.31 | 1.66 | 0.19 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 32 | 4 | 16 | 88.9 | 14 | 58.7 | 42.1 | 5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| 1½ | 4 | 0.62 | 3.88 | 0.62 | 2.56 | 1.90 | 0.25 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| 40 | 4 | 16 | 98.4 | 16 | 65.1 | 48.3 | 61 | 81 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| 2 | 4 | 0.75 | 4.75 | 0.69 | 3.06 | 2.38 | 0.31 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 50 | 4 | 20 | 120.6 | 17 | 77.6 | 60.4 | 8 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| 2½ | 4 | 0.75 | 5.50 | 0.75 | 3.56 | 2.88 | 0.31 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 65 | 4 | 20 | 139.7 | 19 | 90.5 | 73.0 | 8 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 |
| 3 | 4 | 0.75 | 6.00 | 0.81 | 4.25 | 3.50 | 0.38 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 8 |
| 80 | 4 | 20 | 152.4 | 21 | 107.9 | 88.9 | 10 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 3.6 |
| 3½ | 8 | 0.75 | 7.00 | - | 4.81 | 4.00 | 0.38 | 12 | 11 | 13 | 11 |
| 90 | 8 | 20 | 177.8 | - | 122.2 | 101.6 | 10 | 5.4 | 5.0 | 5.9 | 5.0 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.75 | 7.50 | - | 5.31 | 4.50 | 0.44 | 15 | 13 | 17 | 13 |
| 100 | 8 | 20 | 190.5 | - | 134.9 | 114.3 | 11 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 7.7 | 5.9 |
| 5 | 8 | 0.88 | 8.50 | - | 6.44 | 5.56 | 0.44 | 19 | 15 | 20 | 15 |
| 125 | 8 | 23 | 215.9 | - | 163.5 | 141.3 | 11 | 8.6 | 6.8 | 9.1 | 6.8 |
| 6 | 8 | 0.88 | 9.50 | - | 7.56 | 6.63 | 0.50 | 24 | 19 | 26 | 19 |
| 150 | 8 | 23 | 241.3 | - | 192.1 | 168.3 | 13 | 10.9 | 8.6 | 11 | 8.6 |
| 8 | 8 | 0.88 | 11.75 | - | 9.69 | 8.63 | 0.50 | 39 | 30 | 45 | 30 |
| 200 | 8 | 23 | 298.4 | - | 246.1 | 219.1 | 13 | 17.7 | 13.6 | 20.4 | 13.6 |
| 10 | 12 | 1.00 | 14.25 | - | 12.00 | 10.75 | 0.50 | 52 | 43 | 70 | 43 |
| 250 | 12 | 26 | 361.9 | - | 304.8 | 273.0 | 13 | 23.6 | 19.5 | 31.8 | 19.5 |
| 12 | 12 | 1.00 | 17.00 | - | 14.38 | 12.75 | 0.50 | 80 | 64 | 110 | 64 |
| 300 | 12 | 26 | 431.8 | - | 365.1 | 323.8 | 13 | 36.3 | 29.0 | 49.9 | 29.0 |
| 14 | 12 | 1.12 | 18.75 | - | 15.75 | 14.00 | 0.50 | 110 | 90 | 140 | 105 |
| 350 | 12 | 29 | 476.2 | - | 400.0 | 355.6 | 13 | 50.0 | 41.0 | 63.5 | 47.6 |
| 16 | 16 | 1.12 | 21.25 | - | 18.00 | 16.00 | 0.50 | 140 | 98 | 180 | 140 |
| 400 | 16 | 29 | 539.7 | - | 457.2 | 406.4 | 13 | 64.0 | 44 | 5.81 | 81.6 |
| 18 | 16 | 1.25 | 22.75 | - | 19.88 | 18.00 | 0.50 | 150 | 130 | 220 | 160 |
| 450 | 16 | 32 | 577.8 | - | 504.8 | 457.2 | 13 | 68.0 | 59.0 | 99.8 | 72.6 |
| 20 | 20 | 1.25 | 25.00 | - | 22.0 | 20.0 | 0.50 | 180 | 165 | 285 | 195 |
| 500 | 20 | 32 | 635.0 | - | 558.8 | 508.0 | 13 | 81.6 | 75.0 | 129.0 | 88.5 |
| 24 | 20 | 1.38 | 29.50 | - | 26.12 | 24.00 | 0.50 | 260 | 220 | 430 | 275 |
| 600 | 20 | 35 | 749.3 | - | 663.6 | 609.6 | 613 | 118 | 99.8 | 195.0 | 125.0 |
The following abbreviations are used in the table header:
- NPS - flange diameter in inches,
- DN - flange diameter in millimeters,
- H - number of holes for fasteners;
- J—diameter of holes for fasteners;
- K is the diameter of the bolt circle;
- L is the depth of the nest;
- M - base of the collar of the collar and bell flanges, Weld Neck, Socket Weld Flange;
- N - welded end of the collar of the collar flange Flange Weld Neck;
- r is the radius of rounding of the Socket Weld Flange;
- WN - collar ANSI flanges B16.5 Weld Neck;
- SO - flat flanges Slip On;
- Threaded - Screwed threaded flanges;
- SW - socket flanges, Socket Weld Flange;
- LJ - loose flanges, Lap Joint Flanges.
Conclusion
Studying foreign standards for flanges allows you to learn from other people's mistakes and successes. The experience of Engineering Union LLC, quality and stock makes it possible to efficiently fulfill regular customer orders and maintain highly competitive ones.
Bibliography
- Yufin V. A. Pipeline transport of oil and gas.. - M.: Nedra, 1976.
- Flange type duct joint assembly: Pat. US4218079 USA F16L23/00.. - 1980.
By accessing this page, you automatically accept
We produce a wide range steel flanges: corrosion-resistant flanges, stainless steel, flanges made of carbon and alloy steels, cold-resistant and heat-resistant flanges, equal bore flanges and transition flanges, flat flanges and collar flanges, according to Russian and foreign standards.
What is a flange
Flange- this is a metal disk used for mutual butt fastening of pipes, cylinders, seals, and generally hollow (cylindrical and other shaped) objects, in particular cases also for mutual fastening of sheets (in boilers, tanks, etc.), and the flanges are narrower do not have a disk shape. In pipes, the steel flanges are for the most part left as they came from the casting or forge; occasionally, however, they are sharpened to lathe. When connecting two objects with flanges, circles made of various soft materials are placed between the flanges. The flanges are pressed (when the bolts are deployed) into these spacer circles, and thus the tightness of the joint is achieved. Rice. 1, 2 show a flange connection of two steel pipes native flanges.
Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
In other words, the main advantage of using steel flanges is to provide a hermetic, collapsible connection of sections of pipelines, vessels, containers, apparatus, tanks containing or transporting substances in the liquid or gaseous phase. Flanges are not fastening parts, but serve as supports for fasteners.
|
|
|
Standard steel flanges
Flanges according to domestic standards GOST, OST, ATK

Flanges of various diameters
For flanges, as well as for other pipeline parts, the Russian standard GOST 28338-89 establishes a parametric series of 49 values nominal diameter(DN, Dу, DN, nominal internal diameter of the pipeline), measured in mm. Flange diameter- one of its main characteristics, but it is not the exact basic flange size.
Flanges DN 15, 20, 25, 50, 80, 100, 200 Most often they are made from rolled metal using the hot stamping method. Medium bore flanges are manufactured from cast annular steel blanks. Large diameter flanges (500, 600, 800, 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200, 2400, 2800, 3000, 3400, 4000 mm) can be made from forged blanks.
Flanges of various RU
Another main parameter of flanges is conditional pressure(Ру, PN, kgf/cm², MPa), as the highest permissible excess operating pressure at a temperature of 20°C. The GOST 26349-84 standard defines a parametric series of 26 values from 0.1 to 800 kgf/cm².
Flanges DIN, EN (flanges according to European standards)
We produce steel flanges according to European standards: flanges EN 1092-1(Euronorms, European Committee for Standardization), DIN flanges(Deutsches Institute fur Normung, German Institute for Standardization).
The EN 1092-1 standard is largely based on the DIN standards. The following is a table of conformity between EN 1092-1 and DIN. The table shows the types of steel flanges according to EN 1092-1, indicating the equivalent DIN standards for each nominal pressure. Flange types described only in EN 1092-1, but not described in DIN, are marked with a "+". The "-" sign means that there is no standard for that pressure. The underlined standard numbers are taken from DIN.
| Types of steel flanges | Type according to EN | Nominal pressure (PN) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,5 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 25 | 40 | 63 | 100 | 160 | 250 | 320 | 400 | ||
Plate flanges for welding(flat welded steel flange) | 01 | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | ||
|
02 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
|
04 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
|
11 | ||||||||||||
|
12 | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | ||
|
13 | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | |||||
Blind flanges(steel flange plugs) |
05 | + | - | - | - | - | |||||||
Flanges according to American standards ANSI/ASME B 16.5, ANSI/ASME B 16.47, API 6A
Nominal diameter of flanges (DN, Dу, DN) according to American standards, it is measured in inches (1″ = 2.54 cm). Magnitude nominal pressure of flanges (PN, PN) designated by a number of classes (Class, pound-force per square inch, lb/in², psi, pounds per squared inch): 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000 .
| 1 psi = 0.00689476 MPa | 1 MPa = 10.19716213 kgf/cm² | 1 psi = 0.070306955 kgf/cm² |
| Pound-force per square inch (psi, pounds per squared inch, lbf/in², lb.p.sq.in.) | MPa | Technical atmosphere (at, at, kgf/cm², ati) |
|---|---|---|
| 150 | 1,03 | 10,55 |
| 300 | 2,07 | 21,09 |
| 400 | 2,76 | 28,12 |
| 600 | 4,14 | 42,18 |
| 900 | 6,21 | 63,28 |
| 1500 | 10,34 | 105,46 |
| 2000 | 13,79 | 140,61 |
| 3000 | 20,68 | 210,92 |
| 5000 | 34,47 | 351,53 |
| 10000 | 68,95 | 703,07 |
| 15000 | 103,42 | 1054,60 |
| 20000 | 137,90 | 1406,14 |
We manufacture ANSI/ASME B16.5 flanges with nominal bore 1/2″ - 24″; Large diameter flanges (26″ - 60″) are manufactured according to requirements ASME/ANSI B16.47. (ASME - American Society of Mechanical Engineers - American Society of Mechanical Engineers, ANSI - American National Standards Institute - American national institute standards). For high pressure classes (pressure class ≥ 2000 lbs) up to 20,000 in the petrochemical industry they are used API 6 A flanges(API - American Petroleum Institute, American Petroleum Institute). API 6A flanges are similar to ANSI B 16.5 in size, but differ in materials of construction; they cannot be connected to each other without being subjected to full operating pressure. API threaded flanges have a collar height greater than ASME B 16.5 flanges. The following table provides a comparison steel flanges ANSI/ASME B 16.5 And flanges API 6 A.
| Flange type | Pressure class | Conditional pass | Old values conditional API passes |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASME | API | ASME | API | |||
| Welding Neck ( collar flanges) | 600 | 2000 | 2″ – 10″ | 2 1/16 — 11 | 1 1/2 — 10 | |
| 900 | 3000 | 2″ – 10″ | 2 1/16 — 11 | 1 1/2 — 10 | ||
| 1500 | 5000 | 2″ – 10″ | 2 1/16 — 11 | 1 1/2 — 10 | ||
| Threaded and integral flags (threaded flanges, welded flanges) | 900 | 3000 | 2″ – 20″ | 2 1/16 — 20 3/4 | 1 1/2 — 20 | |
| 1500 | 5000 | 2″ – 10″ | 2 1/16 — 11 | 1 1/2 — 10 | ||
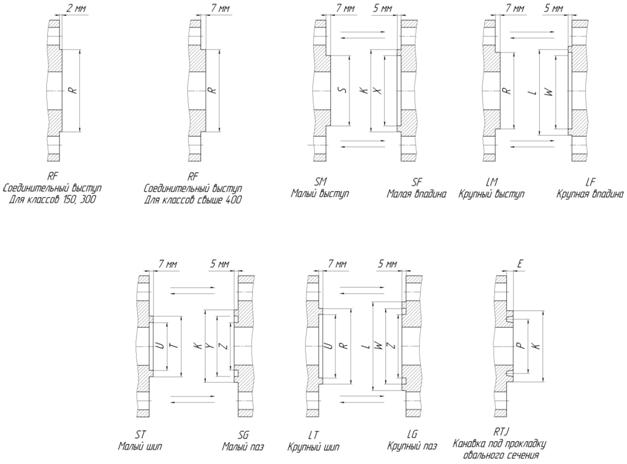
Suggested nomenclature ANSI/ASME flanges, API (Flange designs).

According to customer drawings, we produce steel flanges with an extended welded part (flanges with an extended collar, a long welded flange with a collar) (Long Weld Neck Flanges) and a sealing surface according to American standards. Flanges of this type are used for openings of vessels, tanks, heat exchange equipment, etc.
Designs of the sealing surface of steel flanges
Flange versions according to GOST and ATK
Sealing surface of steel flanges- the contact surface of the two flanges that make up the flange connection. The flanges in the flange connection must have matching sealing surfaces. For the main, so-called straight flange, having a recess for the gasket, the opposite flange with a projection is called counter flange(counter flange, companion flange, mating flange), since the shape of its sealing surface corresponds to the shape of the contact surface of the first flange. In various flange connections, steel flanges with sealing surface designs in accordance with GOST 12815-80 are used. Below are cross-sections of flange connections with different types of sealing surfaces.
|
|
|
|
|
|
To ensure greater tightness, flange connections with steel gaskets and lenses are used. Round steel gaskets with an octagonal cross-section are used for flanges in accordance with GOST 28759.4-90 and OST 26-842-73. These steel seals provide a more effective sealing of the flange connection compared to oval gaskets, however, oval gaskets are more versatile in application: they can also be used for octagonal gasket grooves.
Types of sealing surface of flanges DIN, EN
European standards DIN and EN 1092-1 require the production of steel flanges with sealing surfaces ( flange facing types) presented in the following table. The sealing surfaces of EN 1092-1 flanges for low PN are made with a roughness of Ra=3.2…12.5 µm; for high PN, processing with a roughness of Ra=0.8…3.2 µm is used (such designs are underlined in the table).
| Sealing surface type | Description according to DIN 2526 | Version according to EN 1092-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standards | Execution (Type) | ||
|
DIN 2641/2642 |
||
DIN 2527 |
|||
|
DIN 2630, 2631, 2632, 2633, 2634, 2635 |
Type C |
Type B1 (main application for PN 2.5 - PN 40) |
Type B2(main application for PN 63 - PN 100) |
|||
|
DIN 2512 (PN 10 - PN 160) |
||
|
DIN 2512 (PN 10 - PN 160) |
||
|
DIN 2513 (PN 10 - PN 100) |
||
|
DIN 2513 (PN 10 - PN 100) |
||
|
DIN 2514 (PN 10 - PN 40) |
||
|
DIN 2514 (PN 10 - PN 40) |
||
|
DIN 2696 (PN 63 - PN 400) |
||
|
DIN 2695 (PN 63 - PN 400) |
||
Versions of sealing surface of flanges ANSI, ASME, API
Designs of sealing surfaces of API 6A flanges comply with API 6B standards (for R oval, R octagonal, RX type gaskets) and API 6BX (for BX type steel gaskets).
| Type of sealing surface | Conditions of use | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Drawing | |
| Raised Face Flange(steel flange with raised connection) | 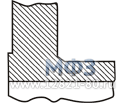 |
Class 150, 300 (PN 20 - 50) |
 |
Class ≥ 400 (PN ≥ 68) |
|
| Male Flange(steel flange with projection, open-ended male) |  |
Class ≥ 300 (PN ≥ 50) |
| Female Flange(steel flange with cavity, open-ended “female”) | 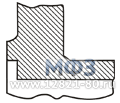 |
Class ≥ 300 (PN ≥ 50) |
| Small Male Flange(steel threaded flange with projection) |  |
Class ≥ 150 (PN ≥ 20) |
| Small Female Flange(steel threaded flange with socket) |  |
Class ≥ 150 (PN ≥ 20) |
| Tongue Flange(steel flange with tenon) | 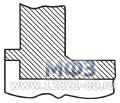 |
Class ≥ 300 (PN ≥ 50) |
| Groove Flange(steel flange with groove) |  |
Class ≥ 300 (PN ≥ 50) |
| Ring Joint Flange (RJ)(flange for round steel gasket) | 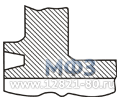 |
ASME B16.5 Flanges Class ≥ 150 (PN ≥ 20) |
API 6B Flanges (Type R ring joint: oval, octagonal) Class 5000 - 10000 (PN 345 - 690) |
||
API 6B Flanges (Type RX ring joint) Class 5000 - 10000 (PN 345 - 690) |
||
API 6BX Flanges (Type BX ring joint) Class 5000 - 20000 (PN 345 - 1380) |
||
Special steel flanges to order
Let's make special flanges (non-standard), such as: high-pressure flanges (flanges with a tongue-and-groove sealing surface for a pressure of 250-300 kg/cm²; counter flanges; flanges to order; flanges for special equipment, flanges for connecting sections of pipelines of various standards, flanges for pipe shut-off valves, adapter flanges, as well as gas flanges; flanges according to drawings (the drawing is agreed upon by the customer).
Our plant is ready to produce flanges with sealing surfaces according to foreign standards ANSI, ASME, API, DIN, EN: flanges for Ring Joint Gaskets types RX, BX, R Octagonal, R Oval, flanges for lens seals, flanges for oval and octagonal gaskets . We will complete the valve flanges with sealing gaskets and fasteners.
Selection of steel for flanges
Flanges for pipelines with low performance requirements are made from the following steels:
- 20FA - 20FA flanges;
- 3, 20 (ASTM A 105 Gr1, A 106 GrA, B, A 659 CS Type 1020, A 794 CS Type 1020, EN 1.1151, AISI 1020, DIN C22E) - carbon steel flanges.
Cold-resistant flanges with easy weldability made of steel 09G2S (ASTM A 516-65, A 561 Gr70, A 516-55, A 516-60) (structural low-alloy for welded structures) - flanges for cryogenic temperatures and severe winter climatic conditions.
Heat-resistant flanges exposed to high temperatures of the external and internal environment are made of steel:
- 10Х11Н23Т3МР - heat-resistant flanges made of high-alloy steel;
- 15Х5М (American analogues: A 193 Grade B5, A 182 Grade F5) - heat-resistant flanges made of low-alloy martensitic steel;
- 13HFA.
We offer flanges made of corrosion-resistant steel. Flanges made from these steel grades can be used at chemical facilities:
- 10Х17Н13М2Т (UNS S31635, AISI 318, 316H, 316Ti, DIN EN X10CrNiMoNb18-12, 1.4583, 1.4571, X10CrNiMoTi18-12, X10CrNiMoTi18-10, X6CrNiMoTi17-12 -2) — heat-resistant stainless steel flanges;
- 08Х18Н10Т (AISI 321, UNS S32100, DIN EN 1.4878, 1.4541, X6CrNiTi18-10, X12CrNiTi18-9, X10CrNiTi18-9) - heat-resistant stainless flanges;
- 10Х17Н13М3Т (UNS S31635, DIN X10CrNiMoTi18-12, 1.4573, GX3CrNiMoCuN24-6-5, AISI 316Ti) - heat-resistant stainless flanges;
- 10Х11Н23Т3МР - heat-resistant stainless steel flanges;
- 12Х18Н10Т (AISI 321) - flanges made of austenitic steel, stainless steel cryogenic flanges for use in dilute solutions of acetic, phosphoric, nitric acids, solutions of salts and alkalis at temperatures from -196 to +600 °C under pressure, flanges with unlimited weldability;
- 06ХН28МДТ (DIN 1.4563, UNS N08028) - heat-resistant stainless steel flanges;
- 14Х17Н2 (AISI 431, DIN X20CrNi72, X22CrNi17) - heat-resistant stainless steel flanges;
- 20Х13 (AISI 420, ASTM A 580 420, A 276 420) - stainless heat-resistant flanges.
Thus, the use of different grades of steel gives us the opportunity to produce flange connections for different operating conditions: flange connections for chemically active environments, for high-pressure pipelines, for high and low operating temperatures.
Production of flanges from various blanks
The technological capabilities of our enterprise allow us to produce flanges and other rotating parts with DN from 200 to 3000 mm (flanges DN, Dn up to 3000) weighing up to 7 tons.
Casting flanges
Our centrifugal electroslag casting plant provides high quality cast metal through electroslag smelting refining. Fur. At the same time, the properties of the blanks are not inferior to forged ones in terms of strength, but are superior to them in terms of impact strength and ductility.
Forged flange
Steel blanks for flanges can be produced using hot stamping technology. An important advantage of this production method is the low price of flanges and the short production time of flanges.
Manufacturing of flanges from forgings
We produce collar flanges, flanges of vessels and apparatus, flanges of large nominal diameters from forgings. Flanges from forgings are manufactured upon prior request.
Flange quality control
We carry out the following points to control the properties of flanges:
- macro- and microstructure;
- geometric control;
- incoming, outgoing control chemical composition;
- mechanical indicators of steel (properties).
We will equip shut-off and control pipeline valves with flanges

Connection valve flanges must be attached to mating welded pipe flanges. The company "Hardware and Flange Plant" completes flanged gate valves, valves, dampers, taps, valves and other pipeline equipment standard and special flanges.
We will complete with flanges valves, pipe shut-off and control fittings various types and shut-off and control butterfly valves. We complete the valves with flanges:
- control valves;
- control valves, throttle and shut-off valves;
- combination non-return and shut-off valves.
We will also equip with flanges rotary return valves of types RZI and RZN with Dn from 500 to 3000 mm, pressures Pn 2.5, 6, 10, 16, 25, 40, pressure classes ANSI 150, 300, operated in the temperature range from -50 C to + 200 °C.
We will produce flanges for critical components and pipelines. We will produce components and assemble the flange assembly according to the assembly drawings.
Please check prices for ASME/ANSI B16.5 and B16.47 flanges with managers by phone or via the feedback form.
ASME/ANSI B16.5 and B16.47 are adopted by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
According to ASME/ANSI standards, product parameters are established: nominal pressure, operating temperatures, materials used, dimensions, tolerances, markings, tests, type of fasteners.
Threaded flanges are divided into different kinds by size, method of fastening and shape of the sealing surface.
The ASME/ANSI B16.5 standard regulates the manufacture of flanges in sizes from NPS 1/2 to NPS 24 with nominal pressure classes 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500 and 2500 psi (in MPa, respectively: 1.03; 2.07; 2.76; 4.14; 6.21;
ASME/ANSI B16.47 covers the same categories of equipment with sizes from NPS 26 to NPS 60 and pressure rating classes 75, 150, 300, 400, 600 and 900 psi.
The standard covers cast and forged flanges, as well as steel flange plugs and flange fittings (cast, forged and sheet steel). In addition, ASME/ANSI B16.5 codes and guidelines cover flange, gasket, and connection fastening.
The nominal diameter of flanges (DN, Dу, DN) according to American standards is measured in inches (1″ = 2.54 cm). The value of the nominal flange pressure (PN, PN) is indicated by a number of classes (Class, pound-force per square inch, lb/in², psi, pounds per squared inch): 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000.
Exact translation of Ru flanges from the American system
| Pound-force at square inch | MPa | Technical atmosphere (at, at, kgf/cm², ati) |
|---|---|---|
| 150 | 1,03 | 10,55 |
| 300 | 2,07 | 21,09 |
| 400 | 2,76 | 28,12 |
| 600 | 4,14 | 42,18 |
| 900 | 6,21 | 63,28 |
| 1500 | 10,34 | 105,46 |
| 2000 | 13,79 | 140,61 |
| 3000 | 20,68 | 210,92 |
| 5000 | 34,47 | 351,53 |
| 10000 | 68,95 | 703,07 |
| 15000 | 103,42 | 1054,6 |
| 20000 | 137,9 | 1406,14 |
1 psi = 0.00689476 MPa; 1 MPa = 10.19716213 kgf/cm²; 1 psi = 0.070306955 kgf/cm²
ASME/ANSI Flange Types
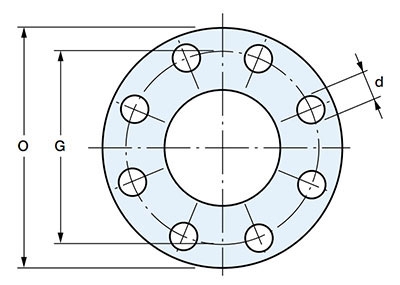
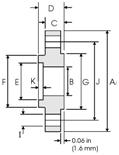
- O—outer flange diameter;
- G is the distance between axes of the flange mounting holes;
- d—diameter of flange mounting holes
1. Flanges ANSI/ASME Slip On (Flange SO) - steel flat welded flanges.
During installation, flat steel flanges are put on the pipe and welded to it. DN: 1/2″-60″. Class: 150-1500, for 1500 lbs only 1/2″-2 1/2″ (ANSI B 16.5); 75-350 (ANSI B 16.47).
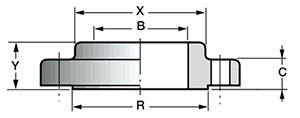
- Y—flange height;
- C—body thickness;
- B - internal flange diameter
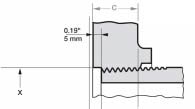
2. ANSI/ASME Threaded (Screwed, ST) Flanges - threaded steel flanges.
Threaded flanges are used with great restrictions in special cases. Their main advantage is the ability to assemble without welding at high pressure in pipeline sections where the use of welding is limited by safety standards. Threaded steel flanges cannot be used in conditions of strong temperature fluctuations and mechanical deformations, since there is a high probability of depressurization of the connection.
DN: 1/2″-3″.
Class: 150-1500, for 1500 lbs only 1/2″-2 1/2″ (ANSI B 16.5).
- Y—flange height;
- C—body thickness;
- R is the diameter of the pressing surface;
- X is the diameter of the weld joint;
- T - thread length
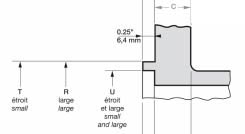
3. ANSI/ASME Welding Neck Flanges (WN, Weld Neck) - collar (steel butt welded) flanges.
Collar (skirt) flanges are butt welded to the end of the pipe. This connection provides resistance to deformation, low and high temperatures, and reduces turbulence in the area of the flange connection. Butt welded steel flanges are most often used for pipelines with high loads.
DN: 1/2″-60″.
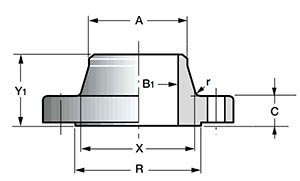
- Y 1 - flange height;
- C—body thickness;
- R is the diameter of the pressing surface;
- X is the diameter of the welding collar;
- B 1 - diameter of the internal flange;
- r—radius
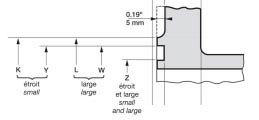
4. Flanges ANSI/ASME Lap Joint (LJ, Lapped Flange) - lap welded flanges (flanges with an overlap joint, free flanges).
Slip-on flanges are similar in shape to flat Slip-On flanges, but have a rounded inner edge near the sealing surface for a tight seal against the end weld ring. Flanges of this type are not welded to the pipe, but can rotate freely around it. Lap weld flanges are used on frequently disassembled sections of pipelines. These connections are easy to install because the mounting holes are easily aligned with the opposite flange. Loose flanges do not come into contact with the environment, so they do not have to be made of corrosion-resistant steel.
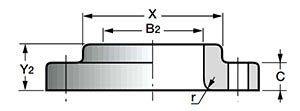
- DN: 1/2″-24″.
- Class: 150-1500, for 1500 lbs only 1/2″-2 1/2″ (ANSI B 16.5).Y 2 - flange height;
- C—body thickness;
- X is the diameter of the weld joint;
- B 2 - diameter of the internal flange;
- r—radius
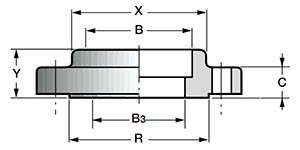
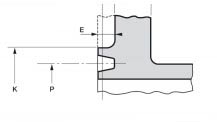
5. ANSI/ASME Socket Weld Flanges (SW) - flanges with a socket for welding (socket flanges).
Socket flanges (steel flanges with a cavity for welding) are placed on the end of the pipe and welded to it. A socket weld flange is similar to a flat flange, but the radius of the hole in the weld surface of the socket weld flange is greater than the internal radius of the pipe by approximately the thickness of its wall.
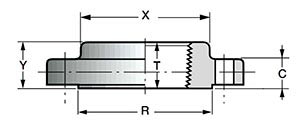
- DN: 1/2″-24″.
- Class: 150-1500, for 1500 lbs only 1/2″-2 1/2″ (ANSI B 16.5).Y - flange height;
- C—body thickness;
- R is the diameter of the pressing surface;
- X is the diameter of the weld joint;
- B—groove diameter;
- B 3 - internal flange diameter
6. Flange ANSI/ASME Blind (Blank) - steel flange plugs.
Steel flange plugs (steel welded flanges without a hole in the middle) are used to close the end section of a pipeline or to access its intermediate section.
DN: 1/2″-60″.
Class: 150-2500 (ANSI B 16.5); 75-900, for 900 lbs only 26″-48″ (ANSI B 16.47).
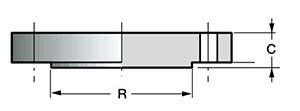
- C—body thickness;
- R - diameter of the pressing surface
The ASME/ANSI standard specifies the following flange options.
| Scheme | Name |
|---|---|
 |
Raised face - Connecting lip for class 150 and 300 |
 |
Raised face - Raised face for class 400 and above |
 |
Large or small male face - Wide or narrow male face for class 300 and above |
 |
Large or small female face - Wide or narrow female face for class 300 and above |
 |
Small male face on end of pipe - Narrow lip (end of pipe) for class 150 and above |
 |
Small female face on end of pipe - Narrow cavity (end of pipe) for class 150 and above |
 |
Large or small tongue face - Wide or narrow tongue face for class 300 and above |
 |
Large or small groove face - Wide or narrow groove for class 300 and above |
 |
Ring joint face - Octagonal or oval gasket for class 150 and above |
FLANGES TO ASME B 16.5
The Steel Pipe Flanges and Flange Fittings standard was published on June 16, 1977 as ANSI B16.5-1977 (American National Standards Institute).
In 1982, the American National Standards Committee B16 was reorganized into the ASME (The American Society of Mechanical Engineers) Committee, operating under ANSI-accredited procedures.
After approval by the Standard Committee and ASME, ANSI approved on April 7, 1988 new edition as the American National Standard designated ASME/ANSI B16.5-1988 and on October 3, 1996, this publication was approved by ANSI as ASME B16.5-1988.
1. Welding Neck (WN) flanges
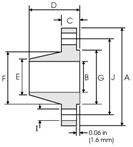
They are butt welded to the end of the pipe and are typically used where severe operating conditions require high quality production. Since the internal diameter of the flange must correspond to the internal diameter of the pipe, when placing an order it is necessary to indicate the diameter of the flange hole.
2. Slip-On (SO) through flanges
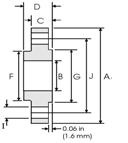
This type of flange fits over the end of the pipe and is typically installed so that the face of the flange is 0.375 inches (9.5 mm) beyond the end of the pipe. This allows for double-sided welding of the flange - one weld is welded for strength to attach the flange spigot to the pipe, and a seal weld is welded inside the flange at the end of the pipe. If operating conditions allow, then a sealing weld is not made. Through flanges are most often used when larger low pressures- class 150 (PN 20) or class 300 (PN 50) design pressure limits used.
Many pipe designers choose not to use through flanges for higher pressures due to the following:
a) The connection between the flange and the pipe is not as strong as when using flanges with a weld neck;
b) Such a connection between the flange and the pipe is more susceptible to corrosion.
3.Threaded flanges (TF)
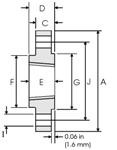
They are connected to the pipe like all other threaded fittings and can be welded to seal the flange to pipe connection. Manufactured to suit most nominal diameters and pressure ratings.
4. Lap Joint (LJ) welded flanges 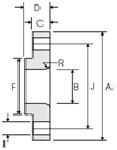
Used in pipe systems that use overlapped connections between the cut ends of pipes. They can be used at any pressure and are produced for all nominal diameters. Flanges of this type are put on the pipe, but are not welded or attached to it in any other way; The connection pressure is transferred to the seal through the pressure of the flange to the rear of the lap joint.
Free-rotating flanges have a number of special advantages:
1. Free rotation around the pipe makes it easier to align the bolt holes of the opposite flange;
2. the lack of contact with liquid in the pipe often allows the use of inexpensive carbon steel flanges complete with corrosion-resistant pipes;
3. In systems that quickly wear out or corrode, flanges can be refurbished for reuse.
5. Welded flanges with a socket for welding Socket-welding (SW)
Features a recess at the back of the flange for connection to the end of the pipe, which is attached by welding around the flange sleeve. Because weld joints are less strong than butt weld joints, the use of this type of flange is almost entirely limited to NPS (Nominal Pipe Size), small nominal diameters, and low pressure ratings.
The main advantage of this type is the ease of preparation and installation.
6. Blind flanges (B)

Manufactured for all nominal pressures and nominal diameters, they are solid stampings used to cover the ends of a pipe system and provide easy access to the interior of the pipeline.
Based on the shape of the contact surfaces, ASME flanges are divided into the following versions: