If you want your area near your house to be constantly dry and clean, so that the foundation of the house is not exposed to moisture, does not rot or collapse, so that puddles do not form and there is no discomfort, then you definitely need drainage. Arrangement of surface water drainage is one of the main tasks during the construction of a site using landscape work.
Aquiferous. An underground porous, water-bearing geological formation. Backwater. An increase in the elevation of the water surface caused by some obstruction, such as a narrow opening in a bridge, building, or fill material that restricts the area through which water flows.
Height above sea level. Water surface area corresponding to a flow that has a one percent probability of being equal to or exceeded in given year. Basic flow. A discharge stream derived from groundwater sources as distinguished from surface runoff.
- Foundation drainage
-
- Installation of drainage pipes
- Drainage wells
- Drainage systems
- Types of surface drainage
- Linear water drainage and drainage
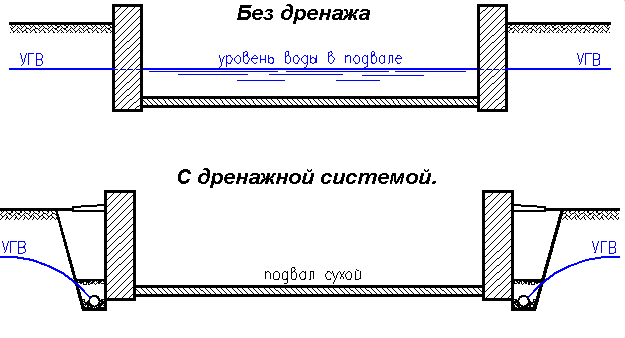
Drainage solves the problems of organized output groundwater and rainwater runoff into the drainage system. Organized drainage of rainwater prevents water from entering through adjacent groundwater in the basement of the house. There are two main options for draining water - linear drainage and point drainage.
A prominent point of a known elevation from which other elevations can be established. A narrow shelf or flat area that disrupts the slope. Best management practices. Methods of design, construction and Maintenance and criteria for objects storm sewer, which minimize the impact of stormwater runoff levels and volumes, prevent erosion and control pollutants.
Storm drainage power. The maximum flow that can be transported or stored in a storm drainage facility without affecting public or private property. Drainage basin. A chamber, usually constructed at the curb line of a street to receive surface water into a sump storm drain, having at its base a sediment trap designed to store sand and detritus below the overflow point.
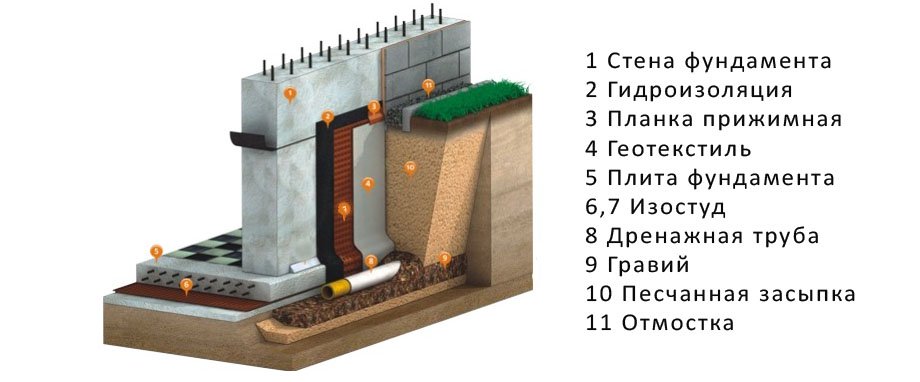
Foundation drainage
 In case of high humidity, in order to prevent damage to the house, we recommend that you install drainage for the foundation of your personal plot. This is an engineering design that protects the house from moisture by removing excess water.
In case of high humidity, in order to prevent damage to the house, we recommend that you install drainage for the foundation of your personal plot. This is an engineering design that protects the house from moisture by removing excess water.
Chicken wire. Woven wire fabric with an opening size of approximately 1½ inches. Boat Chute. A high-velocity open channel to convey water down a steep slope without erosion. A sewer system that carries both sanitary wastewater and stormwater runoff.
Drainage system maintenance
Circuit. An imaginary line on the surface of the earth connects points of the same elevation. Contour line. A line on a map that represents an outline or points of equal height. District Inspector. A constitutional officer of a district, elected to a four-year term from the district as a whole. The surveyor's primary responsibilities include maintaining annexation descriptions, a legal survey book, and a section corner guide. The surveyor is also an honorary member of the County Drainage Board and is the technical authority for the construction, renovation and maintenance of all regulated drains or proposed regulated drains in the county.
By installing drainage on the site, you will protect your home from damage such as:
- mold;
- frost;
- increased humidity in basements (flooding);
- icing and so on.
An effective drainage system and proper installation of drainage pipes imply the use of material that does not retain moisture, for example, crushed stone. It is possible to lay drainage and storm sewer simultaneously. But the top of the edge of the pipes must be lower than the base of the house. Crushed stone is poured into the trench in a layer of about 15 centimeters, then it is leveled according to the specified parameters and compacted. The slope for pipes must be calculated accurately. Turns, bends, etc., are installed using flexible parts of the structure.
Other major responsibilities of the Superintendent include administration of filter filtration programs, membership on the County Plan Commission, and certification to the Commission on alcoholic drink Indiana State. Cross section. A graph or graph of ground elevation through a stream valley or portion thereof, usually along a line perpendicular to the stream or direction of flow.
Calvert. An enclosed pipeline used to transport surface drainage water under a road, railroad, canal, or other obstruction. Cut and fill. The process of earth grading by excavating a portion of a higher area and using the excavated fill material to raise the surface of an adjacent lower area.
Seals are not installed in the coupling elements. For the drainage system to work properly, the pipe must be laid so that there is water-permeable material near it.
The trench of the drainage pipes is filled with earth, from which all stones must be removed. From the foundation to the surface there must be a layer of crushed stone or other material without water penetration. If the house has basements or basement rooms, then you need to waterproof the outside of the foundation, for example, using film. You can also change the structure of the soil and regulate moisture absorption. The soil and material should be backfilled at an angle of 1:50 relative to the house.
Life design. The period of time during which an object must perform its intended function. Storm design. A selected storm event, described in terms of its probability of occurring once within a specified number of years, for which drainage control improvements or flooding are designed and constructed.
Detention. Stormwater management through temporary storage and controlled release. An embankment to restrict or control water. Often built along the banks of a river to prevent overflow of low-lying areas: dams. Discharge. Typically the speed of water flow. The volume of fluid passing through a point per unit time is usually expressed as cubic feet per second, cubic meters per second, gallons per minute or millions of gallons per day.
Why does increased soil moisture occur?
Waterlogging of the soil can occur for a number of reasons:
- the garden area is surrounded by houses with deep foundations;
- the homestead territory is located on a slope from which water flows (stream, groundwater, melted snow, etc.);
- The garden area is located in a lowland.
What does high soil moisture cause?
In addition, high humidity can damage the vegetation in the garden area, and it can also affect buildings located in this area. In winter, the wet ground freezes and begins to expand. As a result, layers of soil begin to press on the foundation of the house. This leads to the fact that the basement becomes unusable, cracks form on the walls, window and door openings become warped.
An artificial, open drainage path into or into which excess surface water or groundwater drained from land, stormwater runoff, or streams of water that flow either continuously or intermittently. A submerged slot or perforated pipe or other conduit or ditch for holding excess ground water or surface water. Drainage. The removal of excess surface water or groundwater from the land using ditches or underground drains. The area merges into a stream at a given point. He can be different sizes for surface flow, subsurface flow and base flow, but usually the surface flow area is considered as the drainage area.
To prevent this from happening, an effective drainage system is necessary. Excess moisture from the surface passes into pipes (drains) connected to each other, and is then discharged outside the garden area. But this is a rather rough explanation of how the drainage system works; in reality, everything is much more complicated. There are several types of drainage systems that are installed taking into account the characteristics of the soil and the location of the garden area. For example, clay soil does not allow moisture to pass through very well, and this leads to stagnation of water in the area.
Drainage board. A board consisting of three to five people, including the district manager or members appointed by the executive body. Improved drainage. An activity within or adjacent to a natural stream or man-made bluff designed primarily to improve the capacity, drainage, erosion and sedimentation control, or stability of the drainage path.
Drainage shed. Drainage area. Drainage strip. A natural or artificial stream, closed pipeline or depression that carries surface water. The term is generally applied to all types of drains and watercourses, whether artificial or natural.
Horizontal drainage systems
Most popular now horizontal systems drainage are considered deep and linear drainage. To remove water from the roof of the house and drain it outside the territory, linear drainage is installed.
Deep drainage is considered the most complex system. The condition of the entire garden area will depend on how the deep drainage system is installed. To set up this system you need to be very careful. Moreover, there is no need to overuse the shallow installation of drains, as this can lead to uneven drainage of the garden area. Deep drainage can be laid in individual areas, or throughout the entire territory according to the principle of parallel straight lines or a Christmas tree. In many ways, the option of installing a deep drainage system implies the presence of all kinds of obstacles and obstacles on the territory (buildings, fences, trees, etc.). Drains must run perpendicular to the collector, which ensures the removal of water.
Dredging. A method of enlarging streams, lakes, or reservoirs by cleaning and removing solids from the bottom. Erosion. Wear and tear of the earth's surface by water, wind, ice, gravity, or other geological agents. Excess precipitation. The amount of precipitation that passes directly from the area.
Farm or field tiles. A small diameter clay pipe installed in an agricultural area to provide drainage or agricultural land. Filter strip. Typically a long, relatively narrow zone of undisturbed or planted vegetation used to slow or collect sediment for the protection of watercourses, reservoirs, or adjacent properties.
What you need to know when designing a drainage system
Options for the location of drains and the composition of the soil are the main conditions, without taking into account any drainage system will simply be useless pipes. For soil that does not permeate moisture well, systems with frequent drains are installed. For example, for clay soil systems are installed where drains are located every 11 meters, and for sandy soils every 52 meters.
Gate flap. A device that allows fluids to flow in only one direction in a pipe. Backflow preventers are used on outlet pipes to prevent backflow during flooding situations. The ground is immediately adjacent to the flow, which floods when the discharge exceeds the transport of the normal channel. The canal's own and current or future canal-adjacent areas may be subject to standard or 100-year flood conditions. Any normally dry area that is susceptible to flooding from any natural source.
The effectiveness of soil drainage depends significantly on how deep the drains are located. Here you need to find a middle ground. So that groundwater does not flood the area and feeds the plants at the same time. Here it is necessary to take into account not only the composition of the soil, but also the plants growing here. For example, for a traditional English lawn you need to install drains to a depth of 25 centimeters. The slope with which drains are laid in the ground depends on the thickness of the drains themselves. The thinner the drainage pipes, the greater the slope required.
The floodplain includes both the strait and flood areas. The channel of a river or stream and those portions of the flood plains adjacent to the channel which are reasonably necessary to effectively carry and discharge the peak flow of the normal flow of any river or stream. The constructed channel is lined with erosion-resistant materials used to convey water to steep grades without erosion. Stock drain. A pipe or series of pipes that collects groundwater from the foundation or base of a structure to improve stability.
Gabions. Wire mesh, usually rectangular, filled with rock and used to protect channels and other sloping areas creates erosion. Gradation. The slope of a road, canal or natural ground. Finished surface of a canal, roadbed, top of an embankment or bottom of an excavation; Any surface prepared to the design height to support a structure, such as paving or pipe installation.
Installation of drainage pipes

Installation of ground drainage pipes is done in specially made trenches at a given depth. Moreover, the width of the trenches must be at least 3 pipe diameters. Geotextiles are placed on top of the drains, which are then covered with a layer of crushed stone. The thickness of the crushed stone must be equal to the diameter of the drain. Then everything is covered with sand and covered with fertile soil. Sometimes, if it is not possible to discharge water into tanks or reservoirs, drainage systems are equipped with a pump and a well.
Finish the surface of a canal, roadbed, top of an embankment or bottom of an excavation or other area of land to a smooth, level condition. Gradient. Change in height, speed, pressure or other characteristics per unit length. Source of the stream.
Water upstream of a structure or point on a stream. Hydrograph. A graph showing, for a given point in a stream, the flow, stage, velocity, or other property of water over time. Impenetrable. Avoid penetration. Penetration. The passage or movement of water into the soil.
Intermittent flow. A stream that stops flowing during very dry periods. Inversion. The inner bottom of a culvert or other pipeline. Surveyor. A person licensed under the laws of the State of Indiana to practice land surveying.
Before starting to develop a ground drainage system, it is necessary to determine the groundwater level (GWL). It is almost impossible for an ordinary person without specialized equipment to do this with his own hands; to do this, you need to invite specialists who will make a topographic survey of the territory and detailed diagrams plot. A specialist can calculate the groundwater level for any time of the year.
Land use management. The means by which the land may be placed into regulation, including such matters as zoning, subdivision regulation, and floodplain regulation. Non-point source pollution. Pollution that enters a body of water from a diffuse source within a watershed and is not the result of distinguishable, limited, or discrete means of transport.
Open drain. A natural watercourse or constructed open channel that carries drainage water. From-autumn. The point, location, or structure where wastewater or drainage discharges from a pipe or open drain into a receiving body of water. Point of removal of water from a stream, river, lake, tap water or artificial sewerage. Output channel. A waterway constructed or altered primarily to transport water from man-made structures such as small canals, tile lines, and seeps.
Closed and open ground drainage system
Drainage systems can be closed or open. The latter are quite cheap and easy to work with. To install an open drainage system, you just need to make drainage ditches throughout the entire garden area and make sure that the ditches do not become clogged. Moreover, they are required to pass at a slope from the building outside the territory of the house.
Peak discharge. The maximum instantaneous flow from a given storm condition at a specific location. Percolations. Movement of water through the soil. Percolation speed. The rate, usually expressed in inches per hour or inches per day, at which water moves through the soil.
Characteristics of large diameter drainage pipes for ditch
A stream that maintains water in its channel throughout the year. A numerical measure of the activity of hydrogen ions, the neutral point - all pH values below 0 are acidic, and all above 0 are alkaline. Any conspicuous, limited and discrete conveyance, including, but not limited to, any pipe, ditch, channel, tunnel, conduit, well, discrete crack, container, rolling stock, concentrated animal feeding operation, or ship or other floating vessel, of which contaminants are Or can be released.
The closed view has several varieties. The closed system is designed quite simply: the main element of its installation is the inclusion of soft drains. To do this, you need to make ditches, pour a layer of sand or crushed stone, and a layer of earth on top.
Another type of closed systems is a linear water drainage system and the arrangement of drainage trays. This drainage system requires a specific determination of the load on the garden area:
- class “A” - laying paths in the garden area;
- class “B” - arrangement of garages and parking lots for cars weighing up to 5 tons;
- class “B” - arrangement of garages and parking lots for cars weighing up to 20 tons.
The choice of trays, safety gaskets, and gratings used will depend on the load class. The number of drain lines will depend on the size of the area and the type of soil. The most popular device option drainage systems today is laying drainage pipes. Most often, polymer pipes are used, which are considered quite durable and reliable.
Drainage wells
No drainage system can do without a well. The drainage well can be rotating, absorbing or receiving water. Rotary wells are installed in areas where wastewater turns; it is these wells that provide the direction of movement for wastewater.
A water intake well is needed to remove wastewater outside the territory. This well can also be installed for watering the area.
An absorption well is installed to release wastewater into the ground.
Drainage systems

These are protective devices used to protect your backyard area from the aggressive action of groundwater. The financial investment in these mechanisms is quite high, but the payback time for capital investments is quite fast. Restoring damaged soil will cost much more than the cost of drainage itself.
Drainage systems are a system of branched pipes connected to each other and have many holes on the walls located along the area protected from water. This is where water flows through the ground and moves to a water collection well located at the lowest part of the property. The installation depth of the drainage itself depends on the boundary of the accumulation of water in the well.
The groundwater accumulated through the drainage system can be used to irrigate the garden area or discharge into a drainage ditch. The absorption of water from the lower layers of the soil is inversely proportional to the depth of the well. The level of vegetation on the site determines the need for a drainage system. This system is really useful if the vegetation cannot adapt to the conditions as a result of waterlogging of the soil. The carrying capacity of the soil, taking into account surface and groundwater, varies significantly, which is reflected in the soil.
This is a whole complex of interconnected subsystems and elements, which include linear drainage, point drainage, underground drainage system, collector well and sewer pipelines.
- Point drainage has two main characteristics: the first is the local collection of melt and rainwater, the other is protection from dirt. In the first installation method, storm water inlets are installed under roof gutters, under irrigation taps and in other places where local water collection is needed. In another embodiment, shoe cleaning systems or dirt-protecting complexes are used, which are installed in pits near the door.
- In places where an organized and quick removal of melt, rain and other excess (for example, car washes) moisture is needed, a surface linear drainage system is installed. This complex consists of sections of various lengths of sequentially fixed and buried sand traps and channels. They are covered with removable grilles, which have decorative and protective functions.
- Sewage pipelines in complex drainage systems play the role of moving water collected in the household territory to the final container (collector). Sewer pipelines are a system that consists of pipes for external sewerage, as well as many transition, rotary, connecting, and all kinds of shut-off and inspection fittings for them.
- An underground drainage system is a network of drainage pipes installed underground according to a specific system. At the same time, underground drainage systems have observation wells that serve to monitor the operation of the system and flush out in case of flooding. There are two main areas for using an underground drainage system: drainage of a personal area and drainage of the foundation of a building. Drainage of the territory of a personal plot can be shallow - to collect melt and rainwater, or deep - to reduce the overall level of groundwater in the territory. Drainage for the foundation of a house can also be of two types: ring and wall. Wall-mounted is used if the house has a ground floor or basement, ring-type - if they are absent.
- The drainage system ends with a collector well. These wells can be: water absorption or water intake. The collected water from the water intake well is collected for subsequent irrigation or discharged outside the territory. The absorption well is installed without a bottom, and removes the water collected by the drainage system into the lower soil layers.
Also plays a very important role in collecting and removing excess water from the territory. drainage system on the roof. It greatly complements the complex drainage system and makes it completely complete.
Types of surface drainage
 Now, in addition to deep drainage, which is used to reduce groundwater, another type of drainage system is being installed - surface water drainage and drainage systems. Surface drainage for removing and collecting water on roads, sidewalks, lawns of personal and country areas, cottages. This drainage, taking into account the use of water drainage elements, is divided into linear and point drainage.
Now, in addition to deep drainage, which is used to reduce groundwater, another type of drainage system is being installed - surface water drainage and drainage systems. Surface drainage for removing and collecting water on roads, sidewalks, lawns of personal and country areas, cottages. This drainage, taking into account the use of water drainage elements, is divided into linear and point drainage.
Linear water drainage and drainage
Water drainage and linear drainage systems are installed to collect water over a large area. Their main advantage is that they do not require complex soil preparation. For linear drainage, you only need to organize slopes on both sides of the drain. This linear drainage of water allows you to cover a large area of the site and reduce the length of storm sewers, which are much easier to install and maintain than surface outlet water.
So, let’s summarize how profitable it is to install a ground drainage system. For most owners country house a drainage system seems like an unnecessary expense. In fact, a huge amount of excavation work, the purchase of polyethylene plastic pipes and protective membranes, installation concrete wells for drainage - all these are significant and additional financial costs. But without this, the house will not last long; it will require significant repairs, and constant moisture will cause serious problems.
Drainage pipes protect various areas from excess moisture. This design prevents flooding of basements and basements, the spread of mold, rotting of the roots of gardening plants, etc. by absorbing water from the soil through special holes. New generation PVC drainage pipes are completely ready for installation and do not require additional effort in drilling holes. The geotextile shell acts as a filter that limits the entry of soil into the pipes. The corrugated surface allows you to bend the pipe at an angle of up to 900 without the risk of damaging the integrity of the material.
Drainagecorrugated perforated pipes in a filter for drainage.
The drainage system allows you to solve a number of operational problems in a summer cottage or garden plot that are caused by high groundwater levels. Laying drainage pipes allows you to timely collect and drain excess water, ground or flood, into drainage wells.
Laying drainage pipes is necessary in the following cases.
- Increased groundwater levels in the garden plot, preventing good soil productivity.
- If there is a need to drain wetlands where agricultural activities cannot be carried out due to high humidity.
- If it is necessary to drain the site for construction work.
- For draining groundwater from the foundation of any finished buildings. Near country houses, drainage is simply a necessary attribute from the very beginning of the construction of a building.
- In summer cottages. All types of drainage systems are usually used here: ditches that remove excess moisture from the roots of trees and fruit plants, and laying a system of pipes in the soil to remove moisture from outbuildings.
Stable operation of the drainage system depends on correct installation pipes and the entire system, so this process should be approached especially carefully, correctly calculating the depth and quantity. As for the materials used for the manufacture of pipes, ongoing tests prove that PVC drainage pipes are significantly superior in their characteristics to other types of materials (rubber, cement, etc.). PVC drainage pipes are durable and flexible structures, often corrugated and perforated, of various circumferences, in which filter fabric (geotextile or coconut fiber) can also be used. Such pipes with a corrugated structure have enough high level ring rigidity, which makes them the best option for domestic internal drainage systems. They are easily installed in the soil using special parts and fittings and serve for a long time and reliably.
Advantages of PVC pipes
- Increased flexibility. If desired, such a product can even be rolled into a ring.
- High strength of the product. It is advisable to bury a drainage pipe made of solid materials in trenches no more than 2 meters deep, and high-strength polyethylene is immersed to a depth of up to 15 meters.
- Corrosion resistance. Plastic pipes do not rust.
- Very long service life. Corrugated and flexible PVC drainage pipes will lie in the ground and will serve flawlessly for at least 50 years.
- Possibility of filtering wastewater using a geotextile filter built into the pipe body.
- Low cost compared to ceramics. Low cost and availability of related materials.
It is important not only to choose the right pipes, but also to carry out proper installation, the main condition of which is the completion of drainage (trenches where the pipes will be laid). The installation process of drainage pipes consists of several stages.
- First, they dig a trench of the required depth in those areas where it is necessary to remove drainage water.
- Next, pipes for drainage are placed on top of the embankment, filling them with gravel. Then the structure is covered with the geotextile remaining outside and covered with earth.
 |
 |
 |
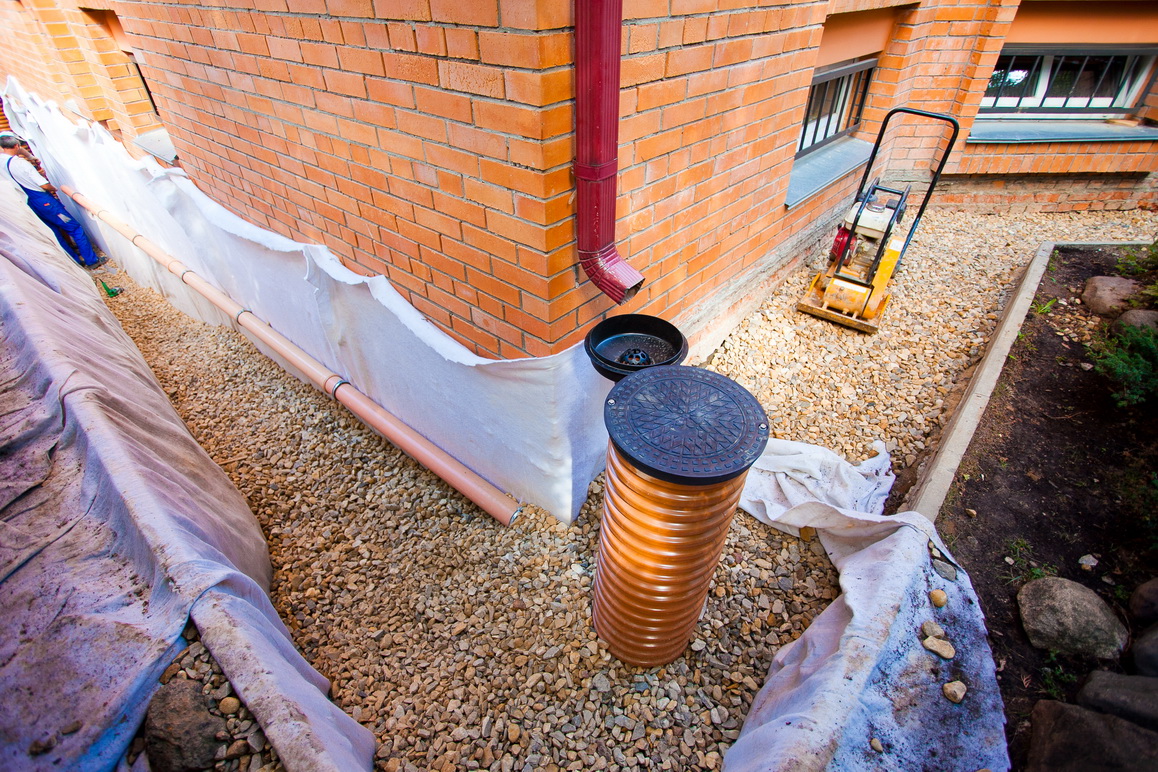
Laying foundation drainage pipes
First, they dig a trench of the required depth around the perimeter of the house to drain sufficient volumes of water from the foundation.
Filter materials, such as geotextiles, are placed at the bottom of the dug trench, leaving long edges of the material outside the trench.
Crushed stone or sand is poured on top.
Our company offers owners of land plots and country houses high-quality PVC drainage pipes for the installation of drainage systems. Ask all your questions to our specialists. We will help you make a choice and ensure delivery of the purchased goods.




