Properly designed ventilation in a boiler room is a prerequisite for its operation. Neglecting this aspect can lead to a concentration of carbon monoxide in the room, which poses a direct threat to the health of those living in the house. Depending on the type of heating equipment used various ways air circulation in the boiler room.
Tasks
In addition to professional and pipelines in a private house, it is necessary to prepare the premises in advance for use as a boiler room. Along with compliance with fire safety rules, it is necessary to ensure air exchange in the room.
The rules for organizing ventilation are described in detail in SNiP II-35-76 (you can download them on our website). According to them, for boiler houses that do not have permanent maintenance personnel, the following ventilation standards have been adopted:
- For gas equipment it is necessary to ensure 3-fold air exchange within 1 hour of boiler operation. This does not take into account the volume of air required to maintain the combustion process.
- The optimal height of the boiler room should be 6 m. But since this is practically impossible to achieve in a private home, the air exchange rate should be increased at the rate of 25% for each meter of decrease in height.
- If it is impossible to ensure the required air flow through the ventilation ducts, a forced air exchange system is installed naturally.
These conditions are common for gas and solid fuel boiler houses. There are slight differences in where ventilation is installed. But before you buy necessary equipment and to make air channels, it is necessary to calculate their geometric parameters.
Ventilation calculation
A correctly drawn up calculation is the basis for designing a boiler room in a private house. A professional scheme includes many parameters - floor plan, equipment installation location, its characteristics, etc. But for domestic boiler houses, the calculation can be significantly simplified (all). To do this, the following room parameters are required:
- Volume.
- Air flow speed. This value should not be less than 1 m/s.
- The coefficient of increase in air exchange rate depending on the height of the ceilings.
These characteristics are necessary to calculate the optimal diameter of the air channel. As an example, consider a room with the following input data:
- The dimensions of the boiler room are 3*4*2.7 m (width, length, height). Volume – 32.4 m³.
- The air exchange rate taking into account the coefficient is equal to – (6-2.7)*0.25+3= 3.8
Those. in one hour with natural ventilation 3.8 * 32.4 = 123 m³ of air should come out.
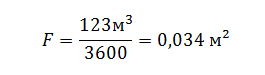
Since in practice round pipes are installed as ventilation elements, it is correct to recalculate the resulting area value in diameter - 204 mm. The best option would be to install a pipe with the nearest standard diameter of 200 mm.
In this case, a channel was designed to remove air from the room. The supply air vent should have the same parameters.
If an air shaft is already installed in the boiler room, and its diameter is less than the calculated one, then forced ventilation can be installed. Most often, a standard fan is used for this, the power of which should compensate for the missing performance of natural ventilation.
Installation Rules
 The choice of forced or natural method of air exchange in the boiler room depends on its parameters. After the calculations have been completed, you can begin installing the system.
The choice of forced or natural method of air exchange in the boiler room depends on its parameters. After the calculations have been completed, you can begin installing the system.
Air channels can be positioned both vertically and horizontally. However, for effective operation the following conditions exist:
- Horizontal structures can only be installed for forced ventilation. They should not have turning sections, and the maximum length is determined by the power of the equipment.
- Vertical areas are necessary for natural air exchange. Their height should not be less than 3 m. This is necessary to create the proper thrust.
The best option would be to use a combined system. If the forced one fails, the natural method will be able to partially compensate for its functions.
Regardless of the chosen system, the volume of outgoing air must be equal to the incoming air. Therefore, one should not forget about installing equipment of appropriate power in the supply channel.
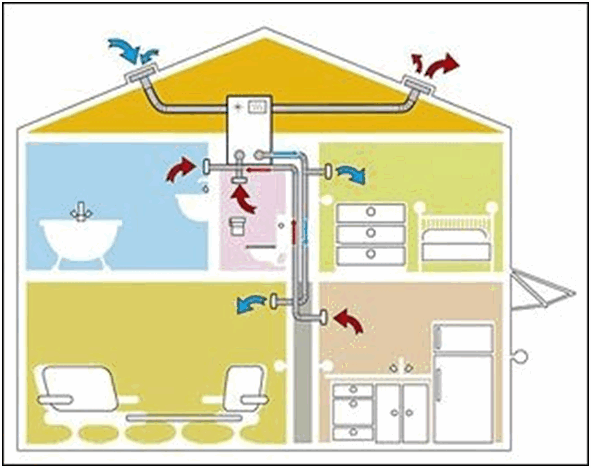
The location of the system elements must be tied to the heating equipment. The supply duct is located in the working area of the boiler, and the exhaust duct is located in the upper part of the room. Moreover, the distance between them should be as wide as possible. For solid fuel equipment It is necessary to install additional forced ventilation in the area where soot appears.
Calculating the ventilation of a boiler room in a private house is an important step in ensuring conditions for normal operation of equipment and safety. If the project is complex circuit of several heating boilers, it is best to use the services of professionals. In some cases, it is necessary to install an air purification system from harmful gases with appropriate filters.
24/11/2008 17:04:54
Every schoolchild knows that combustion is a special case of the oxidation process involving oxygen. In order for there to be fire and flame, air and the oxygen contained in it are necessary. The operation of an atmospheric boiler in this sense is no exception. When burning gas, any boiler, like a vacuum cleaner, absorbs air, which is then thrown into the chimney in the form of various oxides. For each boiler, the documentation indicates the volume of air consumed. The more powerful the boiler, the more air it consumes.
Often in private construction this fact is not given any importance. But in vain. A running boiler sucks air out of the house, creating a vacuum. This in itself is not scary if the walls of the house or window openings contain a sufficient number of cracks through which air from the street enters. However, in Lately With the use of airtight plasters and modern window systems, houses become impenetrable to the flow of air from outside. But the laws of physics cannot be canceled. IN heating season A vacuum will be created in the house and the air from outside will tend to inward. In sealed houses, there is only one way for outside air to enter - ventilation ducts (hoods), which are usually located in bathrooms and kitchens. If the vacuum created by the boiler is greater than the resistance ventilation duct, the so-called reverse thrust. All odors that seem to be escaping through the ventilation ducts will not only remain in the room, but will also actively spread throughout the house along with the air entering from the street.
There is only one solution to this problem - forced ventilation. It can be common for the whole house or directly in the boiler room. From the point of view of ventilation science, it is extremely undesirable to make an influx only into the boiler room, since in the event of an accident there is a possibility of gas spreading to the entire house. In theory, the boiler room should only have hoods. However, gas services do not prohibit installing supply valves in boiler rooms. General system ventilation is usually an expensive and complex system, so the cheapest and effective way ensure the flow of air - a supply valve directly into the boiler room or in the immediate vicinity of it. There are special valves with a special design, but they often make, simply put, a hole in the wall with a diameter of 100-150 mm. This is more than enough for the normal functioning of a medium-power boiler (20-30 kW). A sewer or ventilation pipe can be inserted into the hole made. Cover the outside of the pipe with a net to prevent leaves and insects, and place a simple one inside check valve. The cost of such a solution is minimal, and the efficiency is very high. Practice has shown that in winter the supply valve does not freeze. Despite the low temperature outside, the air temperature in the boiler room is slightly lower than in the general house.
Sometimes the diameter or location of the supply valve does not allow enough air to pass through to compensate for the air flow of the boiler. In this case, it is advisable to use the simplest fans, selecting the required air flow rate 15% -30% more than the boiler flow rate. Part of the fan power will be used to overcome the resistance of the valve, mesh, filter, air duct (if any). Partial air must escape through a natural ventilation duct, which is mandatory in boiler rooms. Significant air pressure through the supply valve in the boiler room cannot be done! It also makes sense to turn on the fan automatically when the boiler is operating for the same purpose - so as not to create excess pressure in the boiler room.
2014-01-08 14:09:50 | Yuri
Now they sell special pipes for gas boilers, a pipe in a pipe. One brings in cold air, the other removes smoke.
2013-11-24 09:59:57 | Andrey_B
Vladimir, if the draft is overturned, it means there is insufficient air flow in the house, that is, in this way (by reverse draft) the system balances the balance between exhaust and supply.
1. If there are sources of powerful air outflow, for example, a boiler, ensure a sufficient amount of air inflow. Typically, the boiler's air consumption standards are indicated in its documentation.
2. Calculate debit for ventilation ducts. And if it is very large, but there is no inflow, then either cover/close the ventilation ducts, or provide additional inflow.
3. After eliminating the imbalance, where reverse draft has formed, it may be necessary to warm up the ventilation duct so that it starts working for exhaust again.
2013-11-23 10:42:36 | Vladimir
I had a pull over in the bathroom. It’s impossible to wash - it’s cold in the bathroom. what to do?
2011-11-27 11:16:56 | Andrey_B
Alexander, do you mean forced ventilation?
The easiest way is a hole in the wall. For natural inflow, the hole must have a diameter larger than the diameter of the chimney. When installing a fan, the diameter of the hole can be made smaller. I also recommend installing a filter.
2011-11-26 22:46:49 | Alexander
boiler with a turbo hood, how can it be easier to make ventilation if there is a vent. no channels?
2011-08-16 08:51:41 | Andrey_B
Tim, the simplest supply valve is located only in the boiler room.
At the moment centralized system the ventilation of the house is not running. If you supply air to living spaces, of course it will be necessary to provide heating.
2011-08-15 21:35:49 | Tim
“The stronger the frost, the higher the temperature of the coolant, the hotter it is in the boiler room.”
Andrey, did I understand correctly - you have one inlet for both the boiler room and the residential premises? Therefore, cold air is supplied to living spaces? Is there any discomfort in severe frosts?
2011-08-11 23:38:46 | Andrey_B
Tim, at the moment there is no provision for heating the supply air. In winter, the boiler room does not drop below +26 +28. The stronger the frost, the higher the temperature of the coolant, the hotter it is in the boiler room. The supply air is heated automatically. What you really need is a filter. The boiler room is dusty. The most surprising thing is that even in winter there is a lot of dust, or rather suspended matter such as fine sand. This is unlikely to be a problem for the boiler, but it lies in a thick layer on all pipes and fittings.
2011-08-11 17:14:45 | Tim
Question about ventilation of residential premises. Andrey, do you turn on the outside air heating during severe frosts? Or are you simply significantly reducing air exchange?
According to current regulatory documents, ventilation in the boiler room must ensure the safe operation of all equipment used. In this case, the use of various schemes is allowed, which must guarantee the supply of the required amount of air not only for the operation of the boilers, but also to prevent the possibility of accumulation of dangerous combustion products or gaseous fuel.
Main functions and requirements for boiler room ventilation
If errors in the design of ventilation networks for residential premises can only lead to a decrease in living comfort, then violations in the ventilation system of boiler rooms can lead to very real tragic consequences. The ventilation device in the boiler room must first of all ensure:
- Supplying the required amount of air for the operation of boiler equipment. Depending on the type of fuel used, this indicator may vary. But all regulatory documents indicate the need to supply into the room at least three times the volume of air required for stable operation of the boiler. If this indicator decreases, a significant part of the ventilation will work only on the boiler, and the risk of accumulation of combustion products or fuel in the room will increase.
- Carbon monoxide, which is considered one of the main components of combustion products, is one of the most dangerous chemical compounds. It prevents the blood from absorbing oxygen and at certain (even small concentrations in the atmosphere) can lead to death even after one breath. That is why the main requirements for boiler room ventilation are aimed at preventing the formation of such accumulations.

It is precisely three times the volume of air entering the room that can provide safe operation boiler room But it is worth remembering that this standard applies to rooms whose height is at least 6 meters. Considering that rooms with smaller dimensions are mainly used as boiler rooms in private houses, it became necessary to significantly adjust this figure.
According to existing requirements, with a room height of up to 6 meters, it is necessary to increase the volume of incoming air at the rate of 25% of the standard for each meter of height.
That is, for a boiler room with a ceiling of 4 meters, the air flow (and, accordingly, the performance of the ventilation system) should be increased by half the standard value.
In addition, you should also pay attention to such a parameter as the speed of air movement through the supply and exhaust air ducts. It should not be less than 1 m/s.
Ventilation schemes used for boiler rooms
The choice of ventilation scheme depends on the characteristics of the equipment used and the room itself. Basically, ventilation in the boiler room of a private house can work according to various existing schemes, the main thing is to ensure the flow of the required amount of air.
- To provide some boiler rooms, standard natural ventilation systems are sufficient. When deciding whether forced ventilation is needed in a boiler room, be sure to consider the possibility of using cheaper natural methods.
The flow of fresh air can be carried out through the doors, for which a special louvered grille is installed in it. But in most cases, a special supply pipe is used.
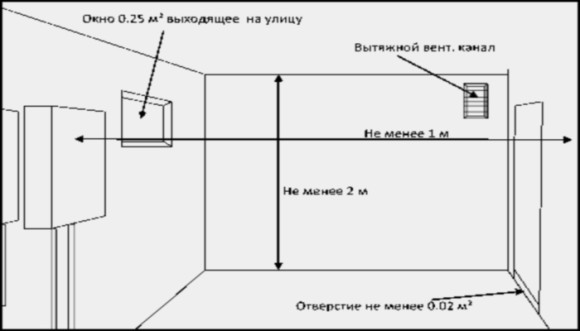
When choosing an option, keep in mind that to provide 1 kW of boiler power, a supply channel with a cross-section of at least 8 square centimeters is required (when supplying air from outside), and if Fresh air served from another room, then at least 30 cm 2.
The length of the supply pipe should be minimal, this will provide greater stability to the ventilation flow. The rules for the location of supply and exhaust air ducts are standard; they should be spaced at the maximum possible distance (on opposite walls diagonally).
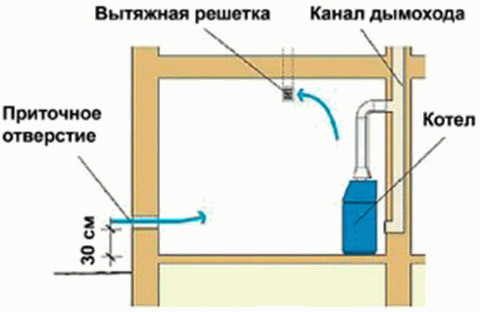
The exhaust air duct must provide a separate removal of air masses outside the building; their movement through adjacent rooms is not allowed, this can lead to the possibility of their contamination.
- If the calculation of ventilation in the boiler room shows the impossibility of using natural schemes, then it is necessary to provide for the possibility of installing an exhaust duct in the corresponding air duct. In this case, it is possible to use fully mechanized ventilation systems, as well as combined ones, in which the fan is intended only to increase the network performance. Using a combined circuit makes it possible to install an automatic system that starts the fan only when the boiler is running, this will allow you to save some money on electricity.
When choosing a fan for a boiler room (especially for a gas one), preference should be given to special models that meet explosion and fire safety requirements.
Such devices have a sealed housing and are protected from the penetration of explosive concentrations of gaseous fuel. In addition, it would be useful to install a supply valve for ventilation of the boiler room, which will provide the ability to regulate the amount of air supplied to the room.
The selection of the cross-section of air ducts and the parameters of other devices for ventilation of the boiler room should be based on preliminary calculations.
Data for calculating ventilation performance in a boiler room
So, ventilation in a gas boiler room is calculated based on the following data:
- Technical characteristics of the boiler equipment used. First of all, the thermal power of the boiler is taken into account, which implies the need to supply a certain amount of air for normal combustion of fuel.
- The area of the room, based on which the required volume of air is determined to prevent possible gas pollution.
- The height of the room, on the basis of which correction factors are determined.

All this information will allow you to determine the optimal performance of the ventilation system in the boiler room. Taking this figure into account, it is necessary to calculate the parameters of the air ducts, while taking into account the minimum permissible air speed (1 m/s). Supply ventilation in the boiler room can be performed using several separate pipes, and their total cross-section must correspond to the design one.
Some features of installing air ducts in a boiler room
When installing air ducts, consider the following requirements:
- Installation of horizontal air ducts is allowed only with a forced ventilation system. In this case, the length of the horizontal sections should not exceed the capabilities of the ventilation equipment. The power of the fans used must ensure the passage of air masses through the air duct, taking into account its aerodynamic resistance.
- Exhaust ventilation in the boiler room can only be installed using vertically located pipes. In this case, the minimum height of the hood should be at least 3 meters, this will ensure the stability of the ventilation stream.
- Do not connect the ventilation network of the boiler room with the common house one.
Modern monoblock forced ventilation systems are considered the most effective. They are characterized by good performance, sufficient to ensure safe operating conditions for the boiler room. In addition to the fact that such systems are compact in size, they are provided with good sound insulation and include filters that make the air in the room cleaner (especially important for solid fuel boiler houses).
The ventilation system is a very important engineering design that plays a key role in creating a good microclimate. It should be in every room, including non-residential ones, and heating rooms are no exception.
Why do you need a ventilation system?
Ventilation in the boiler room of a private house prevents an increase in the concentration of carbon monoxide in the air and combats such a common phenomenon as. The spread of carbon monoxide is deadly, because an increase in its concentration in the air by just 0.2% leads to loss of consciousness followed by respiratory arrest.
A heating boiler burns oxygen to maintain combustion, and the more powerful the boiler, the more it “eats” it. How to replenish its concentration in the air of the boiler room, except through ventilation?
And there must be ventilation, no matter what. There are clear rules that are described in sufficient detail in SNiP 2-35-76.
- In heating rooms equipped gas boilers, it is recommended to provide three air exchanges.
- The height of the building must be at least 6 m; if this is not possible, then the air ratio must be increased at the rate of 25% for each meter of decrease.
- If the required air flow cannot be provided naturally, then installation of equipment for additional air exchange is required.
Ventilation system calculation
 In a heating room, it is not enough to simply organize ventilation; it must be calculated correctly. The correctness of boiler room ventilation calculations is influenced by several factors:
In a heating room, it is not enough to simply organize ventilation; it must be calculated correctly. The correctness of boiler room ventilation calculations is influenced by several factors:
- Volume of the boiler room.
- The speed of air movement through ventilation ducts. For boiler rooms in a private house, this figure cannot be lower than 1 m/sec.
- Increasing the multiplicity depending on the lowering of the ceiling level.
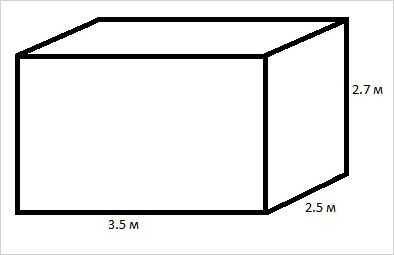
Let's look at an example of a correct calculation natural system ventilation in a private house in which the heating room is located, with dimensions of 2.5 m by 3.5 m and a ceiling height of 2.7 m.
- We calculate the volume of this room: 2.5x3.5x2.7 = 23.62 cubic meters
- Air exchange, taking into account all factors, will be: (6-2.7) x 0.25+3=3.8
- In an hour, air circulation in the boiler room should occur with a volume of 23.62 cubic meters x 3.8 = 89.76 cubic meters.
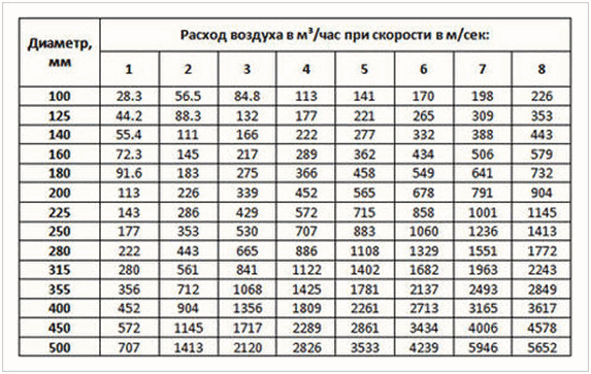
- Based on these data and the table provided, it is easy to calculate the required diameter of the ventilation air ducts, which will ensure the required air exchange (89.76 cubic meters).
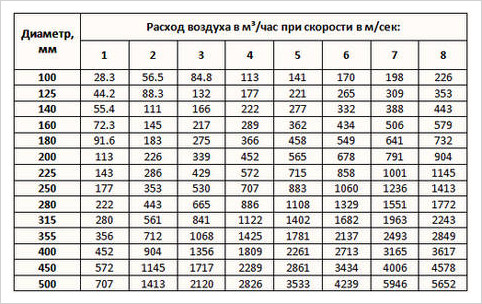 Based on the data in the table, the diameter of the ventilation duct we need must be at least 180 mm. And we only calculated the exhaust duct. The supply pipe should have exactly the same parameters.
Based on the data in the table, the diameter of the ventilation duct we need must be at least 180 mm. And we only calculated the exhaust duct. The supply pipe should have exactly the same parameters.
Ventilation rules
Ventilation of a room with a gas boiler can be. The main thing is that it meets all air exchange and safety requirements. There are several general rules, the observance of which will increase the efficiency of the ventilation system you choose:
- When ventilating a boiler room naturally, horizontal sections of air ducts should not be used. If this cannot be achieved structurally, then an additional fan is installed in the duct. If the ventilation system is forced, then horizontal air ducts do not affect the efficiency of exhaust air removal.
- For natural ventilation to work effectively, draft is needed. To do this, the ventilation pipe must be positioned strictly vertically, and its height must be at least 3 m.
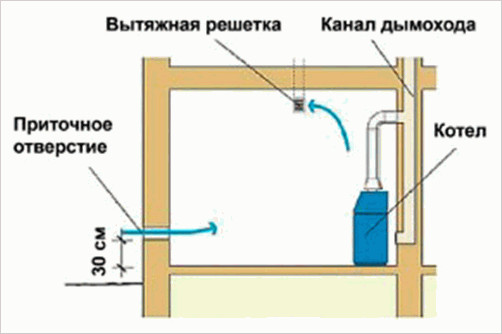 The location of the channels is also very important for the operation of ventilation. The supply air supply should be located in the working area of the heating boiler, in the lower part of the boiler room, and the exhaust air supply should be located at the maximum possible distance from the first - at the top.
The location of the channels is also very important for the operation of ventilation. The supply air supply should be located in the working area of the heating boiler, in the lower part of the boiler room, and the exhaust air supply should be located at the maximum possible distance from the first - at the top.
Equipping a boiler room with general house ventilation
Many people ask the difficult question of how to make ventilation in the house so that it also covers the boiler room. In fact standard scheme natural ventilation, when hoods are in the kitchen and bathroom of the house, will not work here. Either you will have to make separate ventilation, specifically for the boiler room, or connect it to the general house forced air supply and exhaust system.
- You can equip the boiler room with an air intake duct connected to the general exchange system of the house, and install a duct fan of the required performance as equipment. In this case, be sure to use a fire damper.
- There are options for the location of a room with heating equipment installed in it, when organizing natural air exhaust is impossible due to the wrong location. In this case, experts recommend using a draft machine connected to a private home.
- And do not forget about sufficient air flow in the boiler room, since according to fire safety rules it must have a fireproof door, which must close quite tightly, so there will be no air flow there from other rooms, which means natural air exhaust will also not work.
If you have just started a project country house, then we recommend reading the article about for a private home.
Advice:
Calculation and installation of ventilation air ducts is a very important matter, which ensures the normal operation of the equipment installed in the boiler room. If you understand that you cannot cope with such work on your own, it is better to invite professionals. If you have a complex heating system installed with several heating units, it is still better to invite professionals.

Expert approved
Gas heating equipment, the task of which is to heat residential premises and organize hot water supply, must be equipped with ventilation. Heating of the coolant in the gas boiler of an autonomous heating system occurs due to the combustion of natural gas. The combustion process of any fuel, not just a gaseous mixture, requires a constant supply of air containing oxygen. Effective ventilation of a home boiler room with an autonomous gas boiler is one of key aspects successful work heating system. The efficiency of a gas boiler depends on the volume of oxygen entering the combustion chamber.
More air means the fuel burns more completely, the heat output of the boiler increases, and less gas is consumed. Less air means fuel combustion worsens and, as a result, the heat transfer of the gas heating device decreases and gas consumption increases. Let's take a closer look at the purpose of ventilation in a house with autonomous gas heating, its types, and how the basic calculations are made in this case.
In the project of an autonomous heating system, one of the sections is always devoted to ventilation. The significance of this factor for the functioning of the heating system can hardly be overestimated. The main task assigned to ventilation is to ensure the efficient operation of heating devices and to create a regime of complete air exchange in heated rooms.
The second, even more important aspect that you should pay attention to when installing gas heating equipment is ensuring the safety of the heated object during operation of the installed devices. Natural gas is a flammable, explosive substance, therefore, when operating gas heating appliances, all necessary precautions must be taken.
Failure to comply with the requirements for ventilation of gas equipment, violation of the basic technological parameters of air exchange in the boiler room can cause the entry of carbon monoxide and other combustion products into the residential building, dangerous to the life and health of the inhabitants of the house.

Ventilation in a boiler room with a heating gas boiler, if arranged correctly, prevents the accumulation of gas as a result of fuel leakage, reducing its concentration and preventing the formation of an explosive mixture.
Ventilation requirements and main methods of ventilating boiler rooms
Currently, various methods of equipping gas boilers with ventilation are used in industry and in everyday life. The type of ventilation system depends on the type of boiler equipment, its power and the design features of the building.
Important! The main rule when installing boiler room ventilation is that the air flow should be threefold!
In other words, for efficient and safe operation of a gas boiler, the air in the boiler room must change three times in one hour. Otherwise, combustion products will accumulate in the room, since ventilation will only ensure the operation of the boiler.
The requirements for ventilation systems are set out in SNiPs; we list them in a more accessible form:
- the boiler room can be equipped in an extension to the main building, in a separate building or in a room specially allocated in the house for this purpose;
- the boiler room ventilation system must be either separate or connected to the general forced-air system of the building, and it must have a backup option in case of failure of the main one;
- air supply to the boiler room can be carried out both from the outside and from the air mass present inside the residential building, but in both cases the amount of incoming air must match the volume of outgoing air so that there is no pressure difference in the room;
- the diameter of the vent (supply opening) to ensure draft must be maintained in accordance with the standard - 8 cm 2 cross-sectional area of the vent per 1 kW of boiler equipment power in the presence of forced exhaust;
- if the ventilation is natural, then the standard size of the cross-sectional area of the vent is already 30 cm 2 cross-sectional area per 1 kW.
All necessary parameters for ventilation equipment, as a rule, are indicated in the technical data sheet of the gas heating device.
Installing a gas boiler requires precision. Installation gas heating in a private house must be carried out in strict accordance with the data specified in the project and under the supervision of the inspection for the operation of gas equipment. Otherwise, the operation of the boiler will be considered dangerous and its operation will be prohibited.
For reference: during startup tests autonomous heating functionality ventilation systems are checked by a heating engineer. Defects and technical non-compliance with the project may cause refusal to put the heating system into operation.
Types of ventilation of gas heating equipment
Ventilation of gas heating equipment is divided into 2 types according to the method of ventilation:
- natural;
- forced.
Let's take a closer look at these types.
Natural ventilation
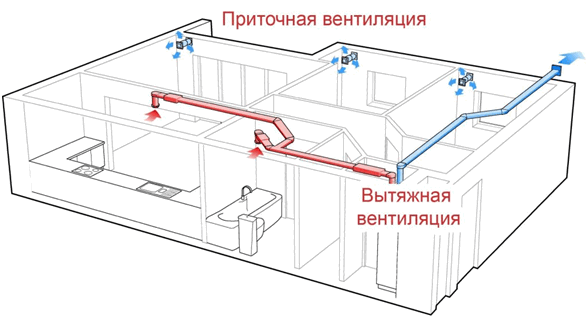
The easiest way to ensure air supply is natural ventilation. This option is independent of external energy sources, but its efficiency may not be high enough due to the design features of the gas boiler and the architectural parameters of the heated room.
The effectiveness of natural ventilation is influenced by ambient air temperature, wind strength and direction, and atmospheric pressure parameters. The intensity of the heating system and the gas pressure in the system can also affect the volume of incoming naturally air and the normal operation of the hood, therefore there is a significant lack of natural ventilation - the dependence of its intensity on a number of factors.
Important! When connecting a gas boiler to a natural ventilation system, it is necessary to use exhaust fans as additional measures to avoid the accumulation of carbon monoxide inside the boiler room and to prevent the formation of an explosive air-gas mixture.
This ventilation method is suitable for small residential buildings equipped with low-power wall-mounted gas boilers. Such boilers do not require a special room and do not require a separate air duct system. It is enough to make a hole with a diameter of 100-150 mm in the outer wall and insert a coaxial chimney pipe into it.
As a more effective and safe alternative to natural ventilation, forced or mechanical ventilation is common today.
Forced ventilation
The forced method of ventilating a boiler room has been used for a long time, and its effectiveness has been proven in practice.
The advantages of forced, or mechanical, ventilation are as follows:
- is equipped at those facilities where natural ventilation is not effective;
- the ability to adjust the intensity of air exchange depending on the operating mode of the boiler;
- the presence of automation in the control to regulate the operation of injection equipment.
Mechanical ventilation is intended for installation in large residential areas. The use of gas heating boilers of significant power and the high intensity of operation of such heating systems put forward increased requirements for ventilation. Therefore it is coercive system, mounted on the basis of calculated data, allows you to ensure effective work powerful gas boilers and the safety of home occupants.
Making calculations
If you want to provide your home with high-quality heating, the issue of equipping gas heating appliances with ventilation should be approached responsibly.
An important point is the diameter of the supply and exhaust air duct pipes - one of the key parameters ensuring efficient operation heating unit. To calculate the characteristics of air ducts, the following are used:
- volume of heated room;
- dependence of the air exchange gain coefficient on the height of the ceilings in the room;
- air supply speed.
Let's look at an example of a calculation. In each situation, the initial data will be individual, but the calculation algorithm will remain the same. Similar calculations can be seen in every project for installing autonomous gas heating equipment.
Room dimensions:
- height H=2.8 m;
- width B=3 m;
- length L=4 m.
We multiply all the parameters:
(2.8 x 4 x 3) = 33.6 m 3.
The resulting figure means the volume of the room - V.
Then the coefficient of increase in air exchange in the room is calculated, depending on the height of the room. The given standard height of 6 meters is taken, and the actual height of the room is subtracted from it: 6m - 2.8m = 3.2 m.
Then the resulting excess value must be multiplied by 0.25 and 3 added to the result.
The resulting result of 3.8 is the calculated value of the air exchange gain factor.
By multiplying the value of this coefficient by the volume of the room, we obtain the volume of air that should enter the boiler room from the ventilation system per hour:
V = 3.8 x 33.6 = 128 m 3
The final figure is the starting point for the subsequent tabular determination of the optimal cross-sectional area of the air duct.
Important! The parameters of the supply ventilation must be the same as the diameter of the hood. Commonly used exhaust pipes and a chimney of round cross-section, ensuring ease of joining and the least resistance when passing air flows.
For clarity, the table shows calculated data on the dependence of the required air volume on the parameters of the air duct.
Conclusion
Having familiarized yourself with the requirements for boiler room ventilation, it is easier to control the progress of work on its installation if the installation is carried out by a third-party contractor. It is strictly forbidden to ignore established norms, standards and rules either at the project stage or during the installation process. Any discrepancy with the design data is a violation and, as a consequence, grounds for prohibiting the commissioning of the system and boiler, since the severity of the consequences of such violations is unpredictable.
Poor ventilation of the boiler room often causes emergency situations in the operation of the heating system, the consequences of which can be very serious. Not to mention that an incorrectly adjusted and installed system becomes the main cause of excessive fuel consumption, which will significantly affect your budget.




