Providing a private home with a ventilation system is one of the primary conditions for its comfortable and safe operation. The presence of a hood allows you to create thermal comfort and microclimate in the premises as a whole, which is important from the point of view of the health and safety of residents. Exist different ways ventilation system device, but in most cases it is a ventilation duct, for which it is important to calculate the dimensions, location, air volumes and other characteristics.
Natural ventilation channels
These are the simplest systems that provide natural air exchange in accordance with the difference in temperature in the house and outside. It is this difference that forms the draft, the force of which forces the air from the room to go outside through the ventilation exhaust lines. To implement such a system, vertical channels are used, lined with hollow blocks or bricks. Despite the external ease of constructing such structures, natural exhaust also requires the presence of inlet openings, which are indicated in the design. The standard dimensions of ventilation ducts of this type are 140x140 mm. The part of the shaft that is located on the roof must be insulated so that the cooled air does not condense water vapor, otherwise water will flow into the room.
Forced ventilation
In this case, mechanical hood is used. Installation involves installing fans in places where ventilation ducts are provided. As a rule, such mines are served by systems with a heat recuperator. In general, the complex should include channels with gratings and anemostats.

For the implementation of mines, tin air ducts are usually used, which are rigid, but there are also plastic ventilation ducts that are practical and resistant to corrosion processes. The second option is more expedient to use if it is planned to equip premises with a complex configuration. One way or another, it is not worth saving on materials for shafts and fans, since deformations in structural elements can cause serious problems during repairs. This is especially true for synthetic materials, the surfaces of which are not easy to maintain, unlike smooth metal shafts.
Large cross section - plus or minus?
Typically, ventilation ducts with a large cross-section are selected. The massive design allows you to service a large volume of air, which has a positive effect on performance. But a large channel also has disadvantages. This is primarily due to installation problems. Among the main requirements of many customers of such systems, it can be noted that the ventilation duct in the house should be hidden from view as much as possible. Only carefully thought out competent wiring will help to fulfill this condition. Otherwise, decorative work may be required with beams or columns under the shafts. The best option for placing large air ducts is in the basement or attic. In residential premises, it is recommended to leave only branches with minimal cross-sections.
Circular channels
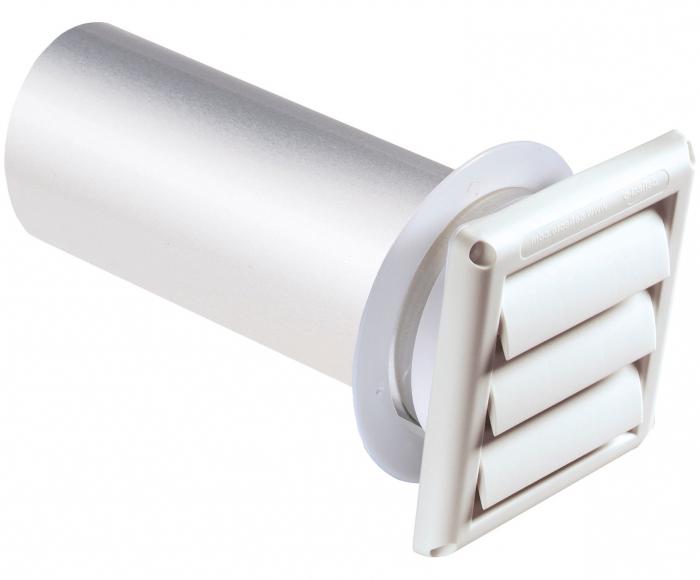

Such air ducts are installed faster, are durable and do not imply depressurization after a certain period of operation. Compared to rectangular channels, such shafts offer less resistance to air movement, which also has a beneficial effect on durability. Therefore, it is advisable to install round ventilation ducts in a private house as a priority, if possible.
The installation is made from spirally twisted metal strips, which experts call “spiro”. Sections of indirect connections with different diameters are mounted using elbows, tees, adapters and other fitting accessories. Installation usually does not cause any difficulties - one component is easily inserted into another. Then the formed joint is sealed with an adhesive film and an exhaust ventilation with reliable sealing is obtained. The diameter of a round spiro-type air duct can vary from 10 to 25 cm, which makes it possible to equip private houses of almost any type with such ducts.

Rectangular channels
It is immediately worth noting one advantage of such channels, for which all shortcomings are forgiven. They are more compact to install and require little space compared to their round counterparts. However, the procedure itself for installing rectangular ventilation ducts is more complex and labor-intensive. In addition, the output is a structure of medium tightness. Air ducts with this cross-sectional shape are connected using flanges, which, in fact, complicates the installation process. Even when purchasing such an air duct, you should add at least 40 mm to its external dimensions to ensure installation and connection.
But there are exceptions, thanks to which this format outperforms round air ducts in terms of residual free space. These are plastic ventilation shafts, the connection of which is made by introducing one fragment into another. Such air ducts are produced in a flat form with a height of 55 mm. But even in this case, the ventilation efficiency will be average, since plastic ventilation ducts with a rectangular cross-section are noticeably inferior in aerodynamics to round air ducts. Accordingly, they can be used only in extreme cases when other options are not suitable.
Flexible ducts

It is not recommended to use elastic materials in the ducts of ventilation systems, but again there are cases when you cannot do without them. The connection of exhaust and supply grilles with rigid shafts requires the use of flexible fragments. This function is performed by the so-called “flexes”. They cannot be classified as full-fledged air ducts - rather, they are transitional parts, the use of which is justified from a constructive point of view. Thanks to the ability to make bends, the ventilation duct is easier to install and make branches in it. In addition, “flexes” reduce vibrations in rigid air ducts, which makes the operation of exhaust shafts quieter.
Where should I place the I/O locations?
In accordance with hygiene standards, exhaust grilles in small single-family houses should be installed directly in the rooms from which the air is to be exhausted. For example, in the bathroom, kitchen, wardrobe or laundry room. This solution will reduce the number of hoods and the length of shafts. But to function effectively, such a ventilation duct must be able to transmit air through individual rooms. Accordingly, doorways must be provided with the possibility of ventilation. To do this, either holes are created in the wall, or a 2-3 centimeter gap should remain in the gap from the floor to the bottom edge of the doors. In addition, in a private house it is necessary to exclude the possibility of air rarefaction and excessive high pressure. To fulfill this condition, the amount of exhaust air must correspond to the volume of injected air.

Valves for ventilation duct
Ventilation valves can perform different functions, being part of a single exhaust system at home. Knowledge of the characteristics of these elements will allow you to determine which of them the ventilation duct will work more efficiently in a particular case. So, air valve In terms of purpose, it is classified into the following types:
- Reverse - In unstable atmospheric conditions, this type of valve prevents changes in the direction of air flow.
- Valve in the mixing chamber - used to regulate the balance of exhaust and clean air.
- Supply air - used to regulate the volume of air served by ventilation.
- Smoke exhaust system valve - required element in the smoke hood.
- Fire damper - special type, which prevents the spread of flame to adjacent rooms through the ventilation system.
Conclusion

Whatever the requirements for the ventilation system in the house, you should approach its design and implementation responsibly. Despite its external harmlessness, exhaust ventilation is responsible for an important characteristic of residential premises - the presence fresh air. In addition, dirty air is discharged through the exhaust ducts, which is not recommended to be breathed according to sanitary and hygienic standards. A clear definition of the needs of each room in the house in terms of ventilation and compliance with installation requirements will allow you to create a productive and durable ventilation system.
The ventilation system in a private home is extremely important. The quality of life in the constructed house will depend on the correctness of its installation and installation. It is advisable to plan the ventilation system at the design stage of the house. If the building has already been built and ventilation is not planned there, then its installation will be more difficult and more expensive.
This system is necessary to create the most comfortable living conditions for people, as well as optimal preservation of the furniture in the house. In the absence of such a system in a private house, windows will fog up, mold will form on the walls, smells of the toilet and fried herbs will be in the air.
Such a microclimate will become dangerous for human life. It will become impossible to live comfortably in such a home.
Features of ventilation in a private house
Ventilation for a private home can be arranged in three different ways.
She may be:
- Natural.
- Exhaust or forced.
- Mixed.
Different rooms in the house have their own characteristics for installing this system:
- Features of installation in the bathroom. Bathrooms in private houses, as a rule, do not have windows, as a result of which it is, in principle, impossible to provide ventilation in these rooms using drafts. During operation, very high humidity and unpleasant odors are formed in such rooms. That is why it is necessary to install forced ventilation in these rooms.
- Features of ventilation in the kitchen. The kitchen is a special room where specific odors and high humidity are constantly present as a result of food preparation activities. In such a situation, natural exhaust will not be enough in any case.
Therefore, in the kitchens they arrange special systems, which can be:
- Dome. Very expensive and powerful ventilation systems, recommended for installation in large kitchens.
- Hanging. The most simple devices, which can only be used in small rooms, since they have very little power.
- Built-in. Distinctive feature Such structures have greater power compared to suspended ones. They can also be built into furniture.
Optimal ventilation for a private home
Choosing the right ventilation system is very important. The best solution There will be a mixed ventilation technology. It includes both natural and forced.
Moreover, two options for such installation are possible:
- The inflow is natural, and the removal of air is forced. In this case, the air flow is produced using special valves, window ventilation, and also through various cracks in the enclosing structures. Removal using mechanical devices.
- The influx is forced, but the removal is natural. In this case it's the other way around. Inflow is carried out using special fans, and removal through valves and cracks in windows and doors.
Natural ventilation
The easiest way to ventilate a room. Air enters the building through cracks in the enclosing structures or specially designed valves; no mechanisms are used. This method has its advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages include the following:
- Lowest cost compared to other systems.
- Simplicity of design.
- Lack of maintenance.
- There is no dependence on power sources.
- No special construction skills are required during installation. You can install it yourself.
With all the advantages of this option, it also has certain disadvantages:
- Limited service area.
- Great dependence on weather conditions.
- Low efficiency. If this system worked very efficiently, then others would not be needed at all.
Where is exhaust ventilation needed?
For this method of air extraction, special equipment is installed during the construction of a private house.
This design compares favorably with the previous one in that, depending on the power, it can serve rooms of any size.
In such structures, it is possible to install equipment to impart a certain humidity, temperature, and ionization to the air. These exhaust systems can be controlled remotely using a special remote control.
For all its advantages, this design also has disadvantages:
- More expensive equipment and components for it.
- There is a need for periodic maintenance and replacement of consumables.
- Direct dependence on energy sources
- Difficult to install. Qualified specialists are required to install this system.
In a private house coercive system necessary only in rooms with high humidity and temperature, such as a kitchen or toilet. Also, if there are gas or any other boiler rooms in the house, a forced ventilation system is needed in these rooms.

Ventilation ducts must be built into the structure of the house at the design stage. They should be present not only in the kitchen and bathroom, but in general in every room of a private house. When constructing a permanent building, ventilation ducts are usually made of brick.
Can be used in frame house construction plastic pipes, or a box made of thin galvanized metal. The main channel is being installed. As a rule, in the central wall, and branches diverge from it into different rooms.
The central pipe leads to the roof of the building. It should be remembered that you should not make many horizontal branches. They greatly reduce cravings. The vertical channel of the central pipe should be twice as long as the horizontal sections.
Installation Standards
- When constructing a central ventilation duct made of brick, the thickness of its walls should not be less than 500 millimeters. With a smaller thickness, in winter, the air in it will quickly cool and fall down, which will lead to malfunctions of this system. If the channel is made of galvanized boxes, then it must be covered with heat-insulating materials.
- The ventilation pipe should be higher than the ridge of the house, this is necessary in order to avoid air turbulence and improve draft.
Basic Rules
- The ventilation system in the kitchen and bathroom must have a combined scheme, natural and forced. A kitchen hood can be used as a forced one, and a ventilation duct must be installed for a natural one. It is most advisable to install the ventilation duct on the opposite wall from the kitchen hood. The width of the suspended hood must be at least the width of the gas stove.
- All rooms in the house must be equipped with ventilation ducts.
- In the bathroom, forced ventilation should turn on automatically when the lights are turned on.
- It is necessary to provide for the installation of replaceable filters in exhaust devices.
Cleaning ventilation ducts
Over time, the ventilation system must be cleaned of dirt and dust. If the ventilation ducts are not long, then this work can be done independently using a vacuum cleaner. If the canal is long, it is better to use the services of specialized organizations.
There are certain advantages to this:
- Cleaning will be carried out by competent, trained specialists.
- The quality of such cleaning will be much higher.
- Firms that engage in this activity have special equipment.
- In addition to cleaning, you can carry out disinfection and disinfection of ventilation.
The installation of this design in a private home is not a luxury, but a necessity. The presence of this design should be laid down at the design stage of the house. Using natural system, you can install it yourself.
If you are planning more complex forced or combined options using special equipment for heating the air, you should contact specialists.
Such complex systems are first calculated in special programs, after which a separate project is drawn up for them. Installation of these structures will require installers with special technical knowledge.
How to make natural ventilation in a private house
Exhaust ducts for natural ventilation must be made from the following areas of the house:
Sanitary facilities - bathroom, toilet, laundry room.
Kitchens.
Dressing room, storage room - if the doors of the premises open into the living room. If the doors open onto a corridor (hall, kitchen), then it is enough to install a supply valve in the room in a wall or window.
The boiler room must have both a ventilation duct and a supply valve.
From rooms separated from rooms with a ventilation duct by more than two doors.
On the floor above the first, if there are entrance doors from the stairs to the floor, ventilation ducts are made from the rooms indicated above, and/or from the corridor, hall.
On the floor above the first, in the absence of entrance doors from the stairs to the floor, ventilation channels and supply valves are installed in each room of the floor.
In other rooms of the house that do not have natural ventilation exhaust ducts, a supply valve must be installed in a window or in a wall.
In addition, natural ventilation channels are arranged for ventilation:
Spaces under the wooden floor of the first floor on joists.
Basement space to protect against radioactive radon gas.
Ventilation duct sizes
The minimum side size of the natural ventilation channel is 10 cm, and the minimum cross-sectional area is 0.016 m2, which approximately corresponds to the diameter of a standard ventilation channel pipe - 150 mm.
Channel minimum size will provide air exhaust in a volume of 30 m3/hour with a vertical pipe length of more than 3 m. To increase the performance of the exhaust, increase the cross-sectional area of the channel or the length of the channel. Channels less than 2m long. do not provide the necessary intensity of natural ventilation.
In practice, the length of the ventilation duct on a floor is usually determined by design considerations - the number and height of the upper floors located above, the height of the attic, the length of the pipe above the roof. On the floor, the length of all channels must be the same. This is done so that the traction force in each channel on the floor is approximately the same.
The cross-sectional dimensions of the channels on the floor are often made the same, but for design reasons - it’s more convenient. The performance of the ventilation channel in a particular room on the floor is adjusted by choosing the size of the ventilation grille.
Ventilation ducts from the premises of the house on different floors are placed side by side, combining them into a block of ventilation ducts.
In a private house, the number of channels is small, so combining air flows from several channels (rooms or floors) into one, as is often done in apartment buildings, not necessary. Each natural ventilation channel in a private house should begin in the room and end at the head on the roof. Any combination of two or more channels impairs ventilation performance.
For design reasons, they try to lay several ventilation ducts from rooms on the same floor side by side, in one place - to create a block of ventilation ducts.
Exhaust ventilation duct block
Examples of rational combination of exhaust ventilation ducts on the floor into one block (riser).
Ventilation channel block
Concrete blocks for laying ventilation ducts.
The cross section of the channel is 12x17cm (204cm2).
Height - 33 cm. Wall thickness 4 cm.
The outside thickness of the block is 25 cm.
The block can have 1-4 holes.
A block of ventilation ducts in stone houses is usually placed inside the load-bearing internal wall of the house or attached to the wall.
The block is laid out from masonry materials, for example, brick. In brickwork it is convenient to make channels measuring 140x140 mm. or 140x270 mm.
They produce hollow concrete blocks specially designed for laying ventilation ducts.
A block of ventilation ducts made of masonry materials must be supported on a foundation or on a reinforced concrete floor.
In other cases, for example, in wooden or frame houses, the block of ventilation channels is assembled from plastic or galvanized steel pipes. The block of pipes is covered with a box.
The performance of a single exhaust ventilation duct with a cross-section of 12x17 cm (204 cm2) made of concrete blocks, depending on the height of the duct and the room temperature:
Natural ventilation performance
To determine performance for intermediate channel heights, plot the channel height versus performance graph.
Similar tables can be found for ventilation ducts that are made of other materials.
However, for ventilation ducts of the same cross-section (204 cm2), but made of other materials, the performance will differ slightly from that indicated in the table. For a channel of a different cross-section, the performance value from the table can be proportionally increased or decreased.
To increase the performance of a ventilation channel of the same height, it is necessary to proportionally increase the cross-sectional area of the channel. For this, for example, choose a concrete block with a hole bigger size, or use a concrete block of several channels of the above size to ventilate one room.
Calculation of natural ventilation of a private house
Calculation of natural ventilation is carried out in order to determine the size of ventilation channels based on the volume of air removed.
When determining the volume of air removed through natural ventilation ducts, it is taken into account that air enters rooms with supply valves from the street, then this air flows into rooms with exhaust ducts, and is removed through the ducts again to the street.
The calculation is carried out for each floor of the house in the following sequence:
Guided by the standards, they determine the amount of the minimum volume of air that must come from the street to ventilate all rooms with supply valves - Qp, m3/hour.
According to the standards, they determine the amount of the minimum volume of air that must go outside to ventilate all rooms equipped with an exhaust ventilation duct - Qv, m3/hour.
Compare the calculated minimum values of air inflow from the street (Qp, m3/hour) and outgoing air (Qb, m3/hour). Usually one of the quantities turns out to be greater than the other. The larger of the two values is taken as the minimum design capacity of all exhaust ventilation channels on the floor - Qр, m3/hour.
Based on the vertical dimensions of the house, the height of the natural ventilation channel on the floor is determined.
Knowing the height of the ventilation channel and the total estimated minimum productivity of all channels on the floor (Qр, m3/hour), the total number of standard channels made of concrete blocks is selected from the table (see above). The total productivity of the selected number of standard channels must be no less than the value of Qр, m3/hour.
The selected number of standard ducts are distributed between the rooms of the house, which must be equipped with exhaust ventilation ducts. When distributing, take into account the need to ensure standard air exchange in each individual room with a ventilation duct.
An example of calculating the natural ventilation of a private house.
For example, let's calculate natural ventilation in a one-story house with with total area floor 120m2. The house has five living rooms with a total area of 90 m2, a kitchen, a bathroom and toilet, as well as a dressing room (storage room) with an area of 4.5 m2. The height of the premises is 3 m. The house has ground floors on wooden joists with natural ventilation of the underground space through a ventilation duct. The height of the ventilated space under the floor is 0.3 m. To install ventilation channels we use concrete blocks - see above.
1. In a private house, the air exchange standard for living rooms where air comes from the street is determined based on at least a single exchange of air volume per hour (air exchange rate = 1 1/hour).
Then, the flow of air from the street to ventilate the rooms:
Qp = 90 m2 x 3 m x 1 1/hour = 270 m3/hour;
2. Air exchange standards for ventilation of rooms and spaces with exhaust ducts: kitchen 60 m3/hour, bathroom and toilet 25 m3/hour in each room; The air exchange rate in the dressing room and the space under the floor on the joists is 0.2 1/hour.
Then, to ventilate these rooms, it is necessary to remove to the street:
Qв1 = 60m3/hour + 25m3/hour + 25 m3/hour = 110 m3/hour - from the kitchen, bathroom and toilet;
Qв2 = 4.5 m2 x 3 m x 0.2 1/hour = 2.7 m3/hour - from the dressing room;
Qв3 = 120m2 x 0.3m x 0.2 1/hour = 7.2 m3/hour - from the space under the floor on the joists;
Total: Qв = 110 m3/hour + 2.7 m3/hour + 7.2 m3/hour = 119.9 m3/hour
3. Compare: Qп > Qв. We accept the minimum calculated total capacity of all exhaust ducts on the floor:
Qр = Qп = 270 m3/hour
4. For a one-story house, the height of the exhaust ventilation duct, taking into account the height of the attic, is assumed to be 4 m.
5. According to the table, for a room air temperature of 20 °C and a channel height of 4 m, we find: the productivity of one standard ventilation channel with an area of 204 cm2 is 45.96 m3/hour. (or 204: 45.96 = 4.44 cm2 - channel cross-section required to pass 1 m3/hour of air.)
Then, the general minimal amount standard ventilation ducts made of concrete blocks in a house are equal to: 270m3/hour: 45.96m3/hour = 5.87. A minimum of 6 exhaust ducts is required to ensure minimum natural ventilation performance in the house.
6. The house has four rooms that need to be equipped with exhaust ventilation ducts - a kitchen, a bathroom, a toilet and a dressing room, as well as a space under the floor, for ventilation of which, for design reasons, two ducts are required - a total of 6 ducts. A minimum of 6 exhaust ducts are required to be installed on a floor in the house, based on the number of rooms and spaces where the installation of a ventilation duct is necessary.
7. In addition, it is necessary to fulfill one more condition - to ensure air exchange according to the standard in certain rooms - in the kitchen at least 60 m3/hour, in the bathroom and toilet 25 m3/hour, in the dressing room 2.7 m3/hour, in the space under the floor 7.2 m3/hour.
To fulfill this condition in the kitchen, one channel of the cross-section we have chosen is not enough. In order to use standard elements for laying ducts, we decide to place a block of two standard ventilation ducts (2x204 cm2) in the kitchen.
In the bathroom, toilet and dressing room we make one standard natural exhaust ventilation channel with a cross-section of 204 cm2 each. To ventilate the space under the floor, we install two channels of 204 cm2 each.
Thus, in total, to ensure minimum ventilation performance in each room with an exhaust ventilation duct, the house needs 7 natural ventilation channels.
As a result, we finally accept 7 channels for construction and check that the ventilation performance meets the design standards:
- in the kitchen there is a block of two ventilation channels (2x204 cm2) with a total capacity of 45.96 m3/hour x 2 = 92 m3/hour. which is more than the standard for a kitchen of 60m3/hour;
- in the bathroom and toilet we install a block of two ventilation channels (2x204 cm2) with a capacity of one channel of 45.96 m3/hour, which is more than the standard of 25 m3/hour;
- in the dressing room we install a single-channel ventilation unit (1x204 cm2) with a capacity of 45.96 m3/hour, which is more than the standard calculation of 2.7 m3/hour.
- to ventilate the space under the floor, we make two channels with a total capacity of 45.96 m3/hour x 2 = 92 m3/hour, which is more than the calculated standard of 7.2 m3/hour.
- the total productivity of all seven ventilation channels on the floor is 92m3/hour + 45.96m3/hour + 45.96m3/hour + 45.96m3/hour + 92m3/hour = 322m3/hour, which exceeds the calculated standard ventilation capacity on the floor of 270 m3/ hour.
From the calculation results it is clear that the minimum required ventilation capacity of rooms with supply valves is provided with a small margin (322 m3/hour > 270 m3/hour). At the same time, the ventilation performance in some rooms with an exhaust duct exceeds the standard tens of times.
Exhaust ducts in the kitchen, bathroom, toilet and dressing room, as well as spaces under the floor, participate in the ventilation of other rooms in the house. Therefore, the performance of exhaust ducts in these rooms is adjusted taking this circumstance into account. Do not reduce ventilation performance in these rooms, for example, by installing small ventilation grilles at the entrance to the duct.
It should be noted that the operation of the fan in the hood above the kitchen stove or in the bathroom should not be taken into account when calculating the air exchange of natural ventilation in these rooms.
The above method for calculating ventilation channels is simplified and not professional. It is better to entrust the design of natural ventilation in the house to specialists.
Ventilation duct above the roof
When there is wind, in air flows flowing around the roof and other obstacles, vacuum zones and zones are formed, like near an airplane wing. high blood pressure. The location of such zones constantly changes depending on the strength and direction of the wind.
If the head of the ventilation duct falls into an area of vacuum, then the draft in the duct increases; if it enters a pressure zone, then the draft in the duct decreases or even overturns, the air begins to move in the opposite direction from the street into the house. It can be especially unpleasant when, in winter, cold air suddenly begins to blow from the ventilation grill into the room.
To reduce the influence of wind on the operation of natural ventilation, the head of the ventilation duct above the roof must be placed at a certain distance.
Location of the ventilation head on the roof of the house
Minimum distances of the head of the natural ventilation channel from the house structures.
a - on flat roof with a slope of less than 12 degrees; b - on pitched roof when the head is located closer than 1 m from the ridge; c - the same, but with the head located further than 1 m from the roof ridge; d - location of the head near vertical surfaces (wind barriers).
Insulation of natural ventilation channels
Cooling the air in the natural ventilation channel leads to a decrease in draft and condensation from the removed air. To protect the ducts from cooling, it is not recommended to place them inside the outer walls of the house.
Ventilation ducts located in external walls, as well as areas passing through an unheated room (attic), must be insulated. It is recommended to insulate areas of ventilation ducts located outside on the roof.
Reduced aerodynamic resistance of ventilation channels
The traction force in the natural ventilation channel also depends on the resistance to air movement along the channel - aerodynamic drag. In order for the resistance to air movement through the channel to be minimal, it is necessary:
Increase the channel cross-section;
There should be no local narrowings or expansions in the channel;
The direction of the channel must be vertical and straight. It is allowed, if necessary, to shift the channel to the side up to 1 m at an angle of no more than 30 degrees. to the vertical. The natural ventilation channel should not have horizontal sections.
Ensure that the walls of the ventilation duct are smooth. In a natural ventilation system it is not allowed to use corrugated pipes. The walls of the channel made of masonry building materials are carefully leveled, the seams are rubbed.



When creating a residential project, the development of various utility networks: water supply, electricity, sewerage. To create a favorable climate for living, it is necessary to properly design ventilation ducts in a private house.
In order for ventilation to work properly and for a long time, it must be carried out based on the norms and rules listed below.
The role of the exhaust pipe in natural ventilation
There are three ventilation options: supply, natural, and supply and exhaust. Typically, in houses the ventilation system is designed in parallel with other networks. But if this was not taken into account in advance, then everything can be corrected by skillfully using natural ventilation. An exhaust pipe will help get rid of many negative consequences if everything is organized correctly.
In order not to disturb the traction force when air moves through the channel, to reduce its resistance, it is not necessary to allow contractions and expansions. The channel must be vertical and straight. Only a displacement is allowed, at an angle of 30 degrees, up to one or two meters.

A necessary condition for effective air exchange is a sufficient flow of air from outside, but dense plastic windows. Even in the summer, when the air temperature inside and outside the house is the same, air movement stops.
Therefore, the best option for a home would be a supply or supply and exhaust ventilation system. The first is suitable for buildings with an area not exceeding 300 square meters. m., and if the area is higher, then it is advisable to use the second one.
What material should the pipes be made of?
If you have come to the right decision - to make ventilation in your house, the next question arises: what material should the ventilation pipes in a private house be made of? Today, there are only two types of channels: round and flat. It is recommended to choose a flat option because such pipes behave much easier during installation, are easier to join and do not sag. To form a channel for air, ventilation pipes made of plastic or metal are used

Today there is a wide range of auxiliary parts: connectors; gratings; all kinds of valves and meshes that are used to create an air duct system.
How to install air ducts
In a finished house, in order not to spoil the interior, it is advisable to construct a system of air ducts in the attic and lead them into the rooms. Everything on the ceiling is masked with decorative grilles. Air supply ducts should only enter living rooms. The supply flow pushes and drives air from these rooms towards auxiliary rooms (kitchen, bathroom), where the main exhaust duct is installed. It is recommended to have two ventilation ducts in the house to make ventilation more efficient. The amount of material is calculated from the area of the room.
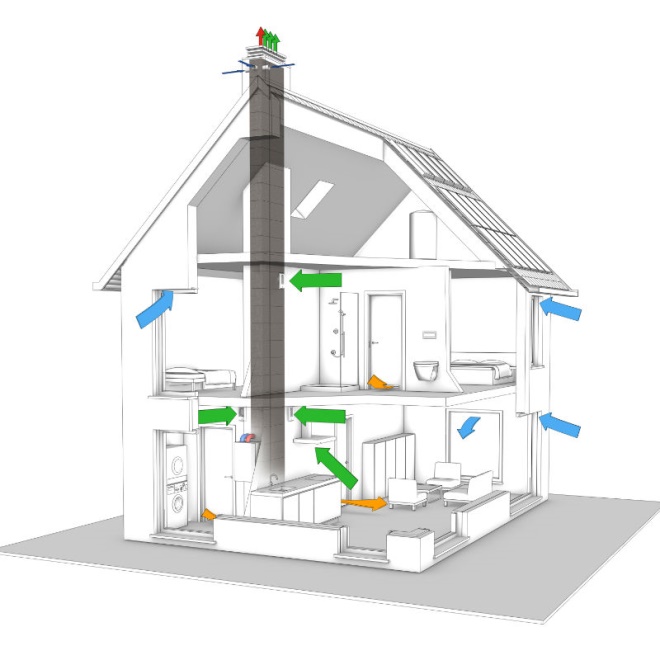
An example of organizing an exhaust duct in a house
Many questions arise. How to make a hole in the roof for exhaust without damaging the roof in several places? When installing air ducts, you must follow the rules:
- Initially, you should draw up a detailed plan (diagram) according to which the wiring locations of all air ducts will be oriented and the exit points through the roof will be marked.
- To simplify the installation of the central duct, it is recommended to drill holes in the roof in advance, which will greatly simplify the work of assembling the ventilation.
- Calculate the length and height of the network and the number of components required.
- To build the system, you need to use specialized materials and parts.
- The areas where the pipe meets the roof should be carefully sealed to prevent rainwater from getting into the gaps. For this purpose, special frames, sealant, and cement are used.

An example of a ventilation duct passing through a roof
The correct selection and installation of ventilation ducts in a private house is the key to efficient and uninterrupted operation of the entire system.
How to ventilate
In houses built from aerated concrete, ventilation can be made of plastic, galvanized steel or asbestos-cement pipes. They can also be used to install aircraft in a house made of gas silicate. In a large house, as a rule, the air duct is extended into each room. To make it easier to install the hood, you can connect the outlet from the bathroom and kitchen into one branch. The work is carried out at the attic level, where all pipes are insulated with insulating material.
For natural ventilation, pipes with a cross-section of 15 cm are suitable; for forced ventilation, it is better to take slightly smaller pipes. A hole of the required size is cut out in the blocks. A 12.5 cm pipe is inserted there and secured with a solution. It is necessary to install an outlet in the first block, to which the ventilation duct is subsequently attached.
If the wall is thin, the channel is made of slate, pre-cut into narrow strips. These sections are mounted in a pre-prepared opening and then plastered over it. You can make ventilation pipes yourself from available material, for example, from corrugated slate. To do this, you need to saw off two half-waves and connect them together with thin wire. The homemade pipe is also mounted on a brick base and plastered inside.
It is forbidden to lay channels in load-bearing walls!
A separate shaft is always equipped for this; this is a fairly convenient way of ventilation in a finished house.
Moments of exhaust structures
The hood plays an important role in a finished house. It also serves as a chimney. Exhaust ventilation ducts should be installed in the kitchen. This arrangement of the channel is completely no coincidence because the air in the kitchen is the most polluted. The exhaust system channel should be shorter, unlike the supply system. This way you can significantly reduce the likelihood of condensation in unheated areas.
For the least resistance to air movement through the exhaust duct, in other words, to increase draft, the following conditions must be met: one duct size, without narrowing; the direction of the pipes is rectilinear without horizontal sections.

Exhaust duct with minimum length
You can achieve greater air extraction efficiency by installing a fan in the central air duct, which will subsequently extract air from the rooms.
For hood over gas stove, as well as heating boiler pipes, use inserts into the main channel, but only above the fan, otherwise it will quickly fail.
About air ducts in the boiler room
Particular attention should be paid to ventilation for a gas boiler in a private house. Usually a special room is allocated for the boiler room. Modern boilers require high-quality chimneys. To clean the room from combustion products, separate ventilation is installed from the hood and gas pipe.
To make it effective, a ventilation duct is installed in the boiler room in the form of two exhaust pipes that go outside and can be installed inside a brick duct. The first serves as a chimney and removes combustion products. The second channel is intended for cleaning and ventilation of the room. It is advisable to equip it with a fan that can rotate in both directions to enhance air exchange into the room. A special steel hood is used, coated with heat-resistant enamel and withstanding high temperatures.

Two pipes for boiler room ventilation
For a gas boiler in a private house, a coaxial chimney is also used, consisting of two pipes located one inside the other. Exhaust gas is discharged through the internal one.
In addition, sections of pipes passing through the attic and other cold rooms must be insulated to prevent condensation from forming on the pipe. You can use special pipes insulated with insulation, or use fire-resistant mineral wool insulation.
Rules for ventilation systems
Let's consider the requirements that will help you correctly install a ventilation system in your home:
- Every hour in living rooms there should be a complete air exchange.
- There should be approximately thirty cubic meters of fresh air per resident
- In an hour, the boiler room should undergo three air exchanges.
- A pipe cross-section of less than ten centimeters cannot be used for the ventilation duct.
- Installation methods must be followed: joints, transitions, turns, inserts.
- The exhaust duct must be vertical and at least three meters long.
- All branches of the supply system must have the same length - thus ensuring the same traction force.
Conclusion
It is possible to ensure good air exchange in the house, namely, to install an effective ventilation system, having knowledge and taking into account all the nuances of installation. If you have doubts about your capabilities, it is better to turn to specialists. Proper organization of air exchange in the house is the key to comfort and health for many years.
As practice shows, customers for the construction of private houses do not always pay due attention to such an important system as ventilation. Unscrupulous construction workers take advantage of this. After all, laying out ventilation and smoke ducts requires some knowledge and skills. And even more so, not many can boast of experience and knowledge of the nuances of how to make ventilation ducts in a house made of aerated concrete.
Ventilation ducts: what are they and why?
In a house made of aerated concrete, ventilation should ideally be built along with the construction of walls
Ventilation ducts are exhaust ducts for the natural ventilation system. Natural ventilation can also be called - round the clock, without mechanical prompting. The installation of ventilation ducts in houses made of aerated concrete blocks is very important. Such buildings especially need good ventilation, since aerated concrete, due to its porous structure, is an excellent moisture absorber. He tends to absorb it not only from the outside, from environment, but also in damp areas inside the house. Because of this, when the temperature drops, the moisture in the pores freezes and expands, which leads to the appearance of cracks. That is why it is necessary to timely remove moisture from those rooms in which it can linger.
Ventilation ducts in a house made of aerated concrete should be provided for the following premises:
- bathroom;
- bathroom;
- kitchens;
- swimming pool;
- boiler room;
- garage;
- cellar
This list also includes the room located directly above the boiler room, regardless of its purpose. Such safety measures are taken to avoid possible ingress of exhaust gases.
The ventilation duct is a durable structure that extends a continuous duct to an elevation above the roof and ensures constant air movement. Basically, the dimensions of the ventilation duct are 120x120 mm, for brickwork - 120x250 mm, wall thickness - 100 mm. Due to the fact that a brick channel for a two-story house weighs approximately 5.5 tons, it is installed on the foundation.
Ventilation ducts in walls made of aerated concrete blocks: engineering standards

In houses built from aerated concrete, special attention is paid to the construction of a ventilation duct. The ability of this building material to absorb moisture, gases, its fragility and inability to withstand high temperatures must be taken into account. Therefore, ventilation ducts are performed in other ways:
- laying out the channel itself and the adjacent brick wall;
- lining with plastic, steel or asbestos-cement pipes;
- installation of a galvanized box, which is lined with aerated concrete blocks.
Ventilation ducts are installed on the roof to a certain height. Violation of the location of the pipe is fraught with poor traction or even its “tipping over”. Thus, a channel installed at a distance of 1.5 m from the ridge should exceed it by 500 mm. If it is located 3 meters from the ridge - level with it in height, more than 3 meters - no lower than an angle of 10° between the ridge and the upper edge of the pipe.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to make a “work of art” out of a ventilation duct and decorate it with devices that are not related to the ventilation system. The end of the pipe can be an umbrella or a deflector, which will improve the operation of natural hood.
Do-it-yourself ventilation ducts in a house made of aerated concrete: brickwork
It is best to trust the construction of ventilation systems for a private home to specialists. If you follow building codes and follow the rules of laying and installation, it is possible to install a hood yourself. First of all, it is determined which of the known methods will install the exhaust duct.
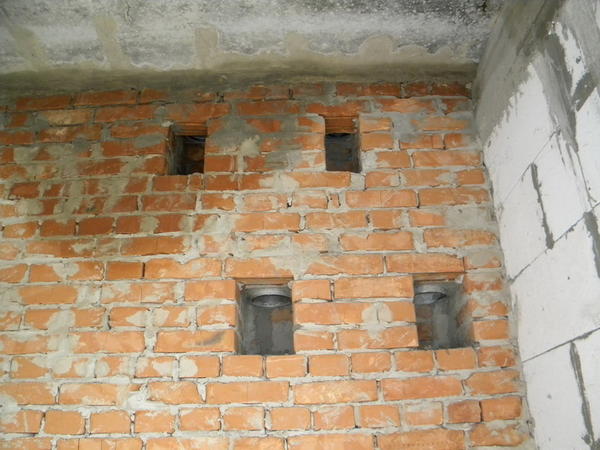

When laying channels with bricks, you need to consider:
- Location - in one of the walls of the room where moisture especially accumulates.
- The fewer channels the better. This issue is resolved geographically - the kitchen and sanitary rooms are located in close proximity to each other (“neighboring”). By the way, this requirement applies not only to ventilation, but also to sewerage and water supply systems.
- The brick structure should not come into contact with the wooden building elements of the house - the temperature of the channel will gradually destroy the wood.
- Only solid brick is used. Laying from hollow facing is also allowed, but with careful filling of the voids with mortar. Silicate, which has the ability to crumble, is not suitable for such work; it does not tolerate temperature regime, formed inside the ventilation duct.
- The channels are tied together, the separators make up ½ brick.
- The brick is laid using a single-row ligation system. When applying the solution for the next row, you must ensure that the mixture does not get inside the channel.
Important! Ventilation in load-bearing wall from aerated concrete, as in other things and in houses made of other materials, it is not laid! This is not a mandatory requirement, but experts recommend it due to the fact that, basically, load-bearing walls are located outside the building - condensation will form on them.
- The inner surface of the ducts, ventilation and smoke, should be as smooth as possible. Therefore, when laying bricks, excess mortar is removed from the joints, and the surface is smoothed with a trowel. Also, there should be no protrusions or depressions on the inner surface - they interfere with normal air circulation.
Particular attention is paid to the seams, which must be filled with mortar and rubbed to prevent combustion products and exhaust air from entering adjacent ducts or rooms of the house. Grouting is done after laying 2-3 rows of bricks. The process is carried out manually, with reciprocating and circular movements along the inner surface of the structure.
Important! The peculiarity of brick ventilation ducts is that they are not equipped with mechanical devices.
Methods for creating effective traction
In addition to laying a channel with bricks, there are two more ways to build it. To use one of them, calculate the minimum volume of air that the channel must output. The cross section will depend on this parameter exhaust pipe, the need for forced ventilation, the number of ventilation ducts and their height.

The method of constructing an air duct from a moisture-resistant material (metal, plastic, asbestos cement) involves laying it from the kitchen, bathroom, toilet, technical rooms, under the ceiling and combining it in the attic into one shaft with access to the roof. This is not a very convenient and not very effective solution to the issue of natural exhaust.
Lining is perhaps a better way to install ventilation ducts in houses made of aerated concrete. It consists of fixing the outlet in the initial block and wiring the system from it. For joining, the air ducts are installed in holes cut into the blocks. Plastic, asbestos-cement or galvanized ventilation ducts must be insulated in places where they pass through the attic and on the roof.
Calculations of productivity and optimal dimensions
Only a specialist can handle calculations that take into account temperature, the number of people living, glass area and other parameters. However, every building owner is able to make a simple approximate calculation of the ventilation of his home using just a few parameters.
So, before building a ventilation duct in a load-bearing wall made of aerated concrete, it is necessary to calculate its performance. For example, let’s take: a one-story house, the area of five living rooms is 80 square meters. m, ceiling height – 2.7 m, kitchen with electric stove, combined bath and toilet, boiler room – 10 sq.m and data from SP 54.13330.2011 “Residential multi-apartment buildings”.
- Inflow – 80x2.7x1=216 cubic meters/hour.
- Required exhaust air removal: kitchen – 60 cubic meters/h; bathroom – 50 cubic meters/hour. boiler room – 100 cubic meters/hour – 60+50+100=210 cubic meters/hour.
- The calculated rate is 216 cubic meters/hour.
The height of the ventilation duct of a one-story house is 4 m. At a temperature of 25°C, the hood capacity is 58.59 cubic meters per hour, therefore, 216/58.59 = 3.69. Based on the calculated data, it is necessary to install 4 air ducts that will ensure effective ventilation of the house.




